Last Updated: May 2023 (IRNSS / NAVIC)
Table of Contents
IRNSS / NAVIC
This article deals with ‘IRNSS / NAVIC‘. This is part of our series on ‘Science and Technology which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
How Global Positioning System (GPS) works?
- GPS is the network of 24 Satellites that orbits the Earth transmitting signals back to Earth. GPS triangulates the position by comparing the time when the signal was transmitted by the satellite with the time it was received. With the help of 3 satellites locked by the receiver, the 2D position (latitude & longitude) can be determined, and with 4 satellites, the 3D position can be determined (latitude, longitude & altitude).
- GPS receiver is only a receiver, without any transmitting capability. The satellites contain highly precise atomic clocks, generating some code that keeps transmitting to the Earth.
IRNSS / NAVIC
- At present, only a few countries have fully functional global navigation systems. These include
| USA | NAVSTAR |
| Russia | GLONASS |
| China | Beidou Compass |
| Japan | Quasi-Zenith |
| Europe | Galileo |
- American GPS has 24 satellites covering all parts of the world. Indian GPS (named NAVIC) has just 7 satellites covering India and 1,500 km beyond its borders.
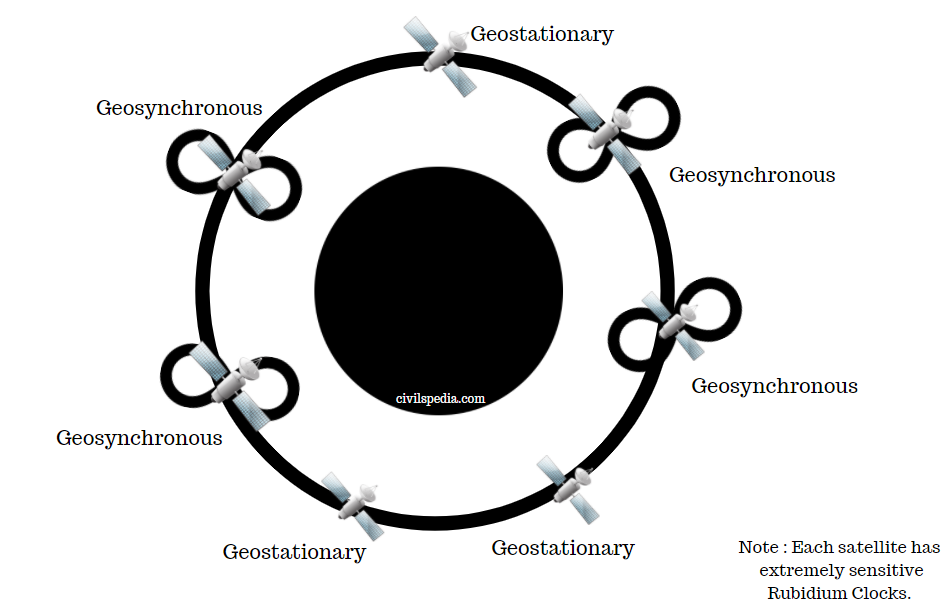
- 7 satellites of NAVIC or IRNCC has the following composition
- 3 Geostationary Satellites
- 4 Geosynchronous Satellites with an inclination of 29 degrees
- Area of Service of IRNSS includes
- Primary Service Area: up to 1,500 km from India’s boundary.
- Extended Service Area: rectangle imagined by 30° S and 50° N and 30° E and 130° E.
- NAVIC has an accuracy of 20 m (compared to 15 m of American GPS).
Timeline
| 1979 | The first satellite of GPS (USA) was launched. |
| 1982 | The first satellite of GLONASS was launched. |
| 2006 | The Indian government approved this project. |
| 2016 April | All 7 satellites were placed in orbit & Modi named this system NAVIC, i.e. Navigation with Indian Constellation. |
Applications of IRNSS
- Terrestrial, aerial and marine navigation.
- Disaster management
- vehicle tracking and fleet management.
- Integration with mobile.
- Precise timing
- Terrestrial navigation aid for hikers and travellers.
- Geotagging of all the assets created under schemes like MNREGA, RKVY etc.
Why should the Indian Government waste money on IRNSS/NAVIC? Why not simply use American GPS at a fraction of that cost?
- Access to a foreign GPS is not guaranteed during a hostile situation. During Indo-Pakistan War (Kargil War) in 1999, the rumour circulated that the US was denying India access to the most precise level of its GPS. Although this rumour was never substantiated, this scenario presented the advantage of having such a system fully under Indian Control.
- Americans sent wrong GPS signals to Iraqi planes during the Iraq war, and the same can happen with India as well.
- It also bolsters the ability of India to serve as a net security provider in the neighbourhood and Indian Ocean Region.
- It will increase the technical prowess of India and help it in becoming a knowledge-based economy.
- It can play a role in relief efforts post disasters such as the tsunami in the Indian Ocean region in 2004.
Use in Diplomacy
- As a goodwill gesture, Modi said that our SAARC neighbours could use it who depend on foreign GPS services.
New developments wrt NAVIC
- December 2020: International Maritime Organisation (IMO) has recognized NavIC as a World-Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS) component. It will enable NAVIC’s utilization in maritime navigation, surveying and others.
- Jan 2020: Qualcomm Technologies has unveiled mobile chipsets supporting the IRNSS/ NAVIC. Now Mobile manufacturers can release NAVIC enabled phones in India.
GAGAN
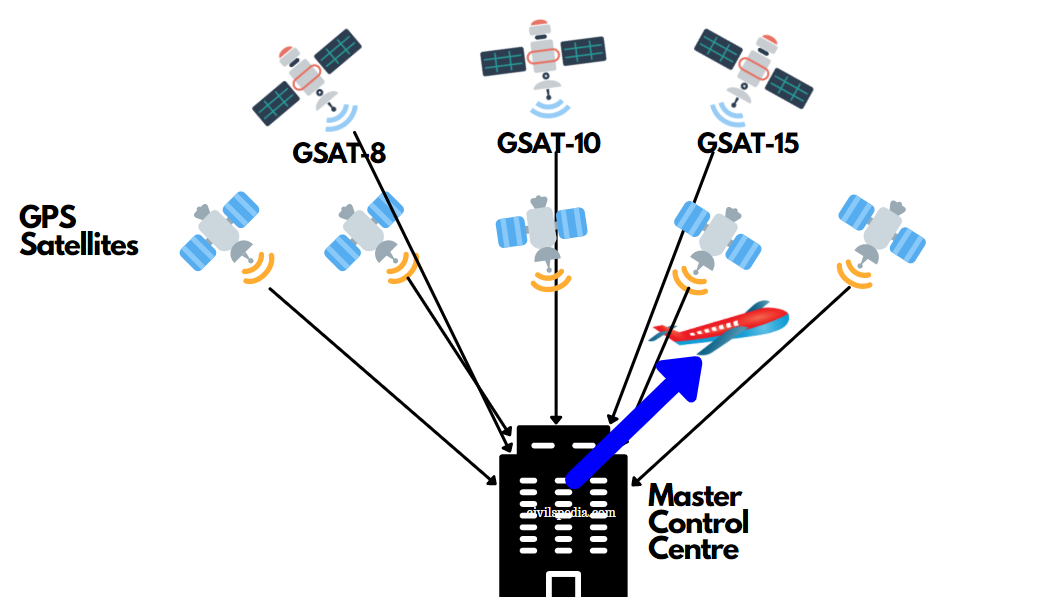
- GAGAN = GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation System
- GAGAN is intended to meet civil aviation requirements, and ISRO has worked with the Airports Authority of India to establish GAGAN.
- It is a satellite-based augmentation system for Civil Aviation purposes.
- It depends on GPS (American navigation system) and Indian satellites like GSAT 8, 10 & 15.
- GAGAN provides position to aeroplanes in the Indian airspace with an accuracy of 3 m.
