Last Updated: June 2023 (Regionalism)
Regionalism
This article deals with ‘Regionalism’ . This is part of our series on ‘Society’ which is an important pillar of the GS-1 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
What is Regionalism?
The phenomenon in which people’s political -loyalties become more focussed on a particular region in preference to the nation or other parts of the state of which that region is sub-part is called Regionalism.
In the Indian context, regionalism is rooted in India’s diversity vis a vis caste, religion, language, ethnicity etc. When all these factors get geographically concentrated along with the feeling of relative deprivation, it results in Regionalism.
Is Regionalism a threat to National Integration?
The politics of regionalism has two connotations.
Positive Connotation
This type of Regionalism is not a threat to National Integration. It is manifested in the form of
- The desire for preserving identity based on language, culture and ethnicity
- To protect socio-economic interest
- For administrative convenience
Negative Connotation
Any demand of regionalism that acts as a threat to nation-building efforts is referred to as a negative form of regionalism. For example, Son of Soil policy & demand for secession.
The second form can be seen as a threat, while the first form is not a threat per se.
Characteristics of Regionalism
- Regionalism is conditioned by economic, social, political and cultural disparities.
- Regionalism, at times, is a psychic phenomenon.
- Regionalism is built around as an expression of group identity and loyalty to the region.
- Regionalism supposes the concept of the development of one’s own region without considering the interest of other areas.
- Regionalism prohibits people from other regions to be benefited by a particular region.
Types of Regionalism
- Demand for Separation: It includes the demand to secede from the Indian union and become a sovereign state. E.g., Khalistan, Azad Kashmir, Naga etc.
- Supra-state regionalism: Group of states are involved which share common issues & build common identities. E.g., North-eastern states for economic development and rivalry between North and South Indian States on language.
- Inter-state regionalism: It is between states on specific issues. E.g., disputes between Karnataka and Tamil Nadu over Kaveri and disputes between Punjab and Haryana over Chandigarh and Satluj-Yamuna Link Canal.
- Intra-state regionalism is between the regions within the same state due to a lack of equitable sharing of benefits within the state. E.g., Coastal area vs western region in Odisha and Jaipur (Amer) vs Jodhpur (Marwar) in Rajasthan.
Causes of Regionalism in India
Regionalism is a pre-independence phenomenon. But it became predominant in the post-independence period. The establishment and role of the Justice Party in Chennai, and to a lesser extent, of Akali Dal in Punjab in the pre-independence period are examples of emerging regionalism in India.
1. Linguistic Reorganisation of States
- After Independence, Indian states were divided into linguistic lines. It generated sub-national identity and thus regionalism.
2. Historical and Cultural Factors
- History has divided India into “Aryans” and “Dravidians”.
- Different regions have their own local heroes & people tend to mobilize around them—E.g. Shivaji in Maharashtra, Periyar in Tamil Nadu, or Maharaja Ranjit Singh in Punjab.
3. Colonial Legacy
- Britishers prioritized easy governance, leading to administrative unification and not cultural or linguistic unification. This caused a mismatch between people’s personal identities and the territories they inhabited.
4. Economic Underdevelopment
- Sometimes, the development of a particular community raises the regional aspirations of the community. E.g. After Green Revolution, Sikh Jatts of Punjab became economically prosperous, and they started to demand separate Punjab from other Hindi speaking regions.
5. Politico-administrative Factors
- Some region-based parties use these. E.g., Shiv Sena claims to protect Maratha interests and Akali Dal to protect Punjabi (& Sikh) interests.
- Undue interference in state affairs by the central government gives birth to regionalism.
6. Economic Development
- Sometimes the development of a particular community raises regional aspirations of the community. E.g. after Green Revolution, Sikh Jatts of Punjab became economically prosperous, and they started to demand separate Punjab from other Hindi speaking regions.
7. Religion
- Religion plays a significant role in regionalism when combined with dominance and linguistic homogeneity, as seen in Punjab or fed on a sense of religious orthodoxy and economic deprivation as seen in Jammu and Kashmir.
8. Disintegration of Congress Party
- After Nehru, central leaders started to impose their mandate on regional leaders. As a result, local leaders moved away to form parties like NCP in Maharashtra, Trinamool Congress in West Bengal etc. They encouraged regionalism.
Son of the Soil Movement / Nativist Movement
- “Son of the soil” doctrine argues that the state belongs explicitly to the main linguistic group inhabiting it, the sons of the soil or local residents.
- The ‘sons of the soil’ or nativist movements emerged in the sixties and seventies in some parts of India.
- Shiv Sena of the sixties and seventies and the Assam movement, which culminated in 1985, belong to this genre.
Why the Son of the Soil?
- Cultural prejudice is the main reason behind the rise of nativist movements. The more dissimilar the immigrant population is ethnically or culturally, the stronger is likely to be the opposition.
- Indian economic model has not been able to create enough employment opportunities. There remains a competition for jobs.
- Rising aspirations of the local middle class.
- Politicians with vested interests try to consolidate their voting base using this—E.g. Shiv Sena in Maharashtra.
Note: In some areas like Punjab, Haryana, Delhi etc., the Son of the Soil theory is not there, but in Maharashtra, Karnataka etc., it is present.
Not Present in Punjab, West Bengal, Delhi etc. because
- Son of Soil theory is for middle-class jobs and not for menial jobs.
- It is not an issue of political parties. E.g., Akali Dal is Jatt dominated party, and Communist Party refused to use anti-migrant sentiments in Calcutta because of its ideological commitment.
- Symbiotic Relationship: Punjabis want cheap agricultural labour. Hence, they don’t raise voices against the immigration of cheap labour from Bihar and Eastern UP.
- In Delhi, culture is purely cosmopolitan.
It is present in Maharashtra because
- Political parties like Shiv Sena, MNS etc. use this as political tool.
- Competition between migrants and nativists is for middle class jobs.
- If national party is weak, the native political parties become more assertive.
Various Regional Aspirations
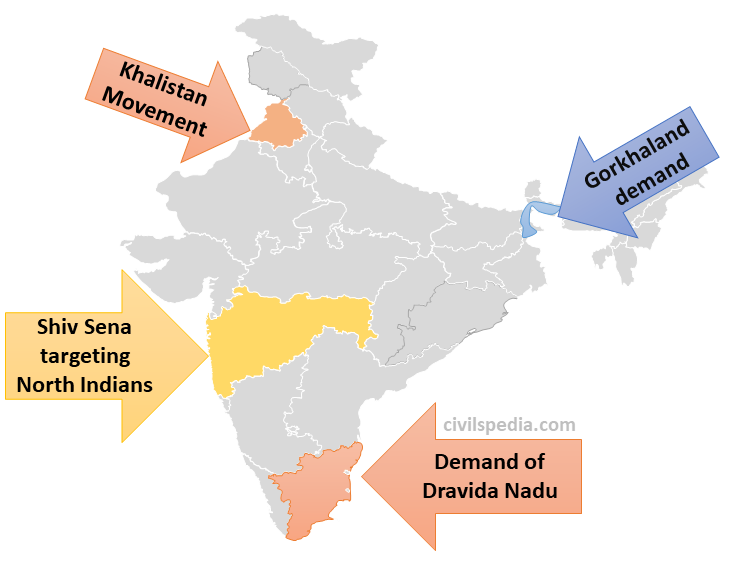
1. Demand of Dravida Nadu (Supranational Regionalism)
- Its genesis lies in the Self-Respect Movement of Tamil Nadu started in 1925.
- Later it stood against the imposition of Hindi on non-Hindi areas.
- The demand of Dravida Nadu in the 1960s made it a secessionist movement.
2. Gorkhaland
- Gorkhas are demanding a separate state of Gorkhaland by seceding from West Bengal.
- Reason
- Gurkhas speak Nepali, while the West Bengal Government of Mamata Banerjee tried to impose Bengali on them by making it compulsory in schools.
- The region is under-developed compared to other parts of West Bengal.
3. Khalistan Movement
- During the 1980s, the Khalistan movement to create a Sikh homeland, often called Khalistan, cropped up in Punjab. This demand also has the colours of communalism, as their demand is only for Sikhs.
4. Shiv Sena and MNS Targeting North Indians
- Shiv Sena & MNS in Mumbai frequently attack North Indians.
Border disputes between States
1. Maharashtra vs. Karnataka
- The border dispute between Maharashtra and Karnataka is over the Belagavi region.
- Belgaum is a Marathi-speaking region in Karnataka. At the time of independence, it was part of the Bombay presidency. But it was integrated with Mysore (now Karnataka) by the State Reorganization Commission. Maharashtra wants it to be unified with Maharashtra.
- Countermovement is run by Kannada groups who argue that Belagavi is now a Kannada-speaking district.
2. Assam vs. Mizoram
- Issues started when Mizoram was the district of Assam and was known as Lushai Hills District. In 1933, the British government demarcated the boundary between Lushai Hills, Cachar district of Assam and neighbouring Manipur state. However, Mizos rejected this demarcation, arguing that Mizos were not consulted while demarcating this boundary.
- Things became more complicated when Mizoram became a full-fledged state of the Indian Union. Subsequently, an agreement was signed between two states that a status quo would be maintained at the no man’s land at the boundary.
3. Andhra and Odisha
- A territorial dispute exists between Andhra and Odisha. Andhra Pradesh demands the inclusion of certain Telugu villages in Odisha. In 2021, the issue became important as the Andhra Pradesh government announced Panchayat polls in a group of villages in Odisha.
Impact of Regionalism in India
Positive Impact
- It can lead to inter-group solidarity in a particular region. People belonging to a region may feel the need to come together to protect their vested interests, setting aside their differences. E.g., Tripura Tribal Autonomous District Council, which was formed in 1985, has served to protect an otherwise endangered tribal identity in the state.
- Due to regionalism, the most important basis for forming identity was language. Hence, it has kept communalism and political identity formation based on religion in check.
- Given the increasing uncertainty in the contemporary globalized world, regionalism has become a source of identity among people.
- Regionalism has helped in promoting democracy in India. Regional parties like Shiv Sena, DMK, Akali Dal etc., fight to capture power via democracy.
- It may induce competition among people of a region and propel them to do better to improve the status of their region. E.g. Competitive Federalism in India.
Negative Impact
- Regionalism at times transforms into secessionism.
- Son of Soil Policy impacts the Fundamental Rights of citizens like right to life or right to carry out any profession.
- It can cause significant damage to private and public property.
- Regionalism creates sub-national feelings in the people. E.g., Naga Nationalism or Punjabi Nationalism vs Indian nationalism.
- Development plans can be implemented unevenly to curb regionalist and secessionist demands.
- Regionalism also becomes a hurdle in international diplomacy. E.g., Tamil Parties impact diplomacy with Srilanka & Trinamool Congress with Bangladesh (like in settlement of Teesta Water dispute).
Ways to Combat Regionalism
- Making India truly federal in word and spirit.
- Doing away with regional imbalances.
- Not imposing single culture on the whole nation. E.g., imposing Hindi in the entire nation will face backlashes from Non-Hindi speaking states.
- As suggested by Sarkaria Commission, three language formulas should be strictly implemented.
- Encouraging ‘People to People’ contact and making people aware of other cultures using TV & Radio.
- Taking steps to end the prejudices of Cow Belt against North Easterners & South Indians.
Federalism to Combat Regionalism
- Other countries with ethnic and linguistic diversities face many problems like secessionist movements as they weren’t able to accommodate regional aspirations.
- Nepal was recently facing Madhesi Agitation.
- Pakistan is facing Baluchi & Sindhi movements.
- Sri Lanka has experienced a Tamil civil war.
- Eritrea seceded from Ethiopia.
- Yugoslavia broke due to various sub nationalisms at play.
- But India, despite such a massive diversity of cultures, is still united. The reason for this is federalism and devolution of power which gives a sense of meeting regional aspirations by various groups.
- Indian federalism provides democratic ways to meet local aspirations of people
- Indian federalism provides democratic ways to meet the local aspirations of people.
- Sovereignty is constitutionally shared. States enjoy significant power. People feel that they are governed by their own people. Cooperative.
- 73rd and 74th Amendments led to the formation of Panchayati Raj and Urban Local Bodies.
- Regions under the 5th and 6th Schedule enjoy certain autonomy.
- Article 371 has special provisions helpful in addressing the concerns of some states.
Other factors why India hasn’t faced Regionalism
- Linguistic reorganization of states: Unlike our neighbours, India recognized early that language is the reason behind regionalism & opted for the linguistic reorganization of the states in 1956. And by 1966, all prominent language speakers have states of their own. It led to the regionalism problem getting subdued in India.
- Unlike other countries, India has a peculiar situation where economically most backward regions are politically most powerful. E.g., UP is one of the most backward states in India, but they decide who will make the Government at Union. Hence, they can’t complain of political apathy & discrimination.
- Economic interdependence between different regions has necessitated migration to different cities and states, thereby reducing loyalties towards a particular region.
- The wave of globalization: India is becoming homogenous under the wave of globalization. Globalisation has subsumed regionalism.
