Table of Contents
Asian Development Bank
This article deals with the ‘Asian Development Bank .’ This is part of our series on ‘Economics’ which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Introduction
| Established | 1966 |
| Motto | “Fighting poverty in Asia & Pacific” |
| Headquarter | Manila , Philippines |
| Type | Regional organisation, multilateral development & finance institution |
| Members | 67 (48 from Asia and pacific + 19 from outside) |
| India’s membership | India was the founding member of ADB |
| President | Masatsugu Asakawa , Japan (2020- present) |
| Vice – President | Ashok Lavasa (2020 – present ) (He was Election Commissioner and would have become Chief Election Commissioner) |
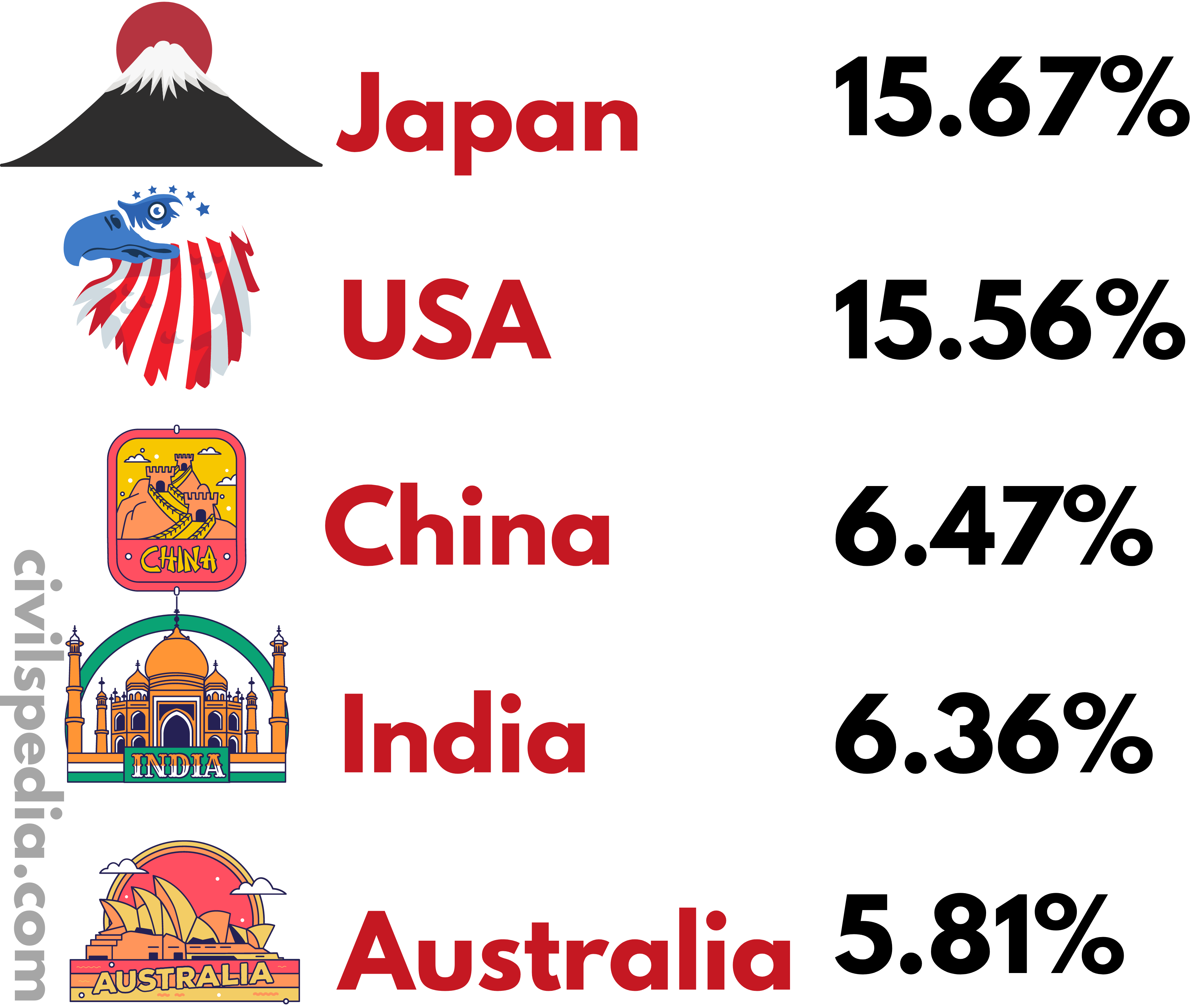
Biggest Shareholders of Asian Development Bank
Principles of ADB
- To make loans & equity investments for its developing members’ economic & social development.
- Provide technical assistance for the preparation & execution of development projects & programs & provide advisory services.
Indian Position in ADB
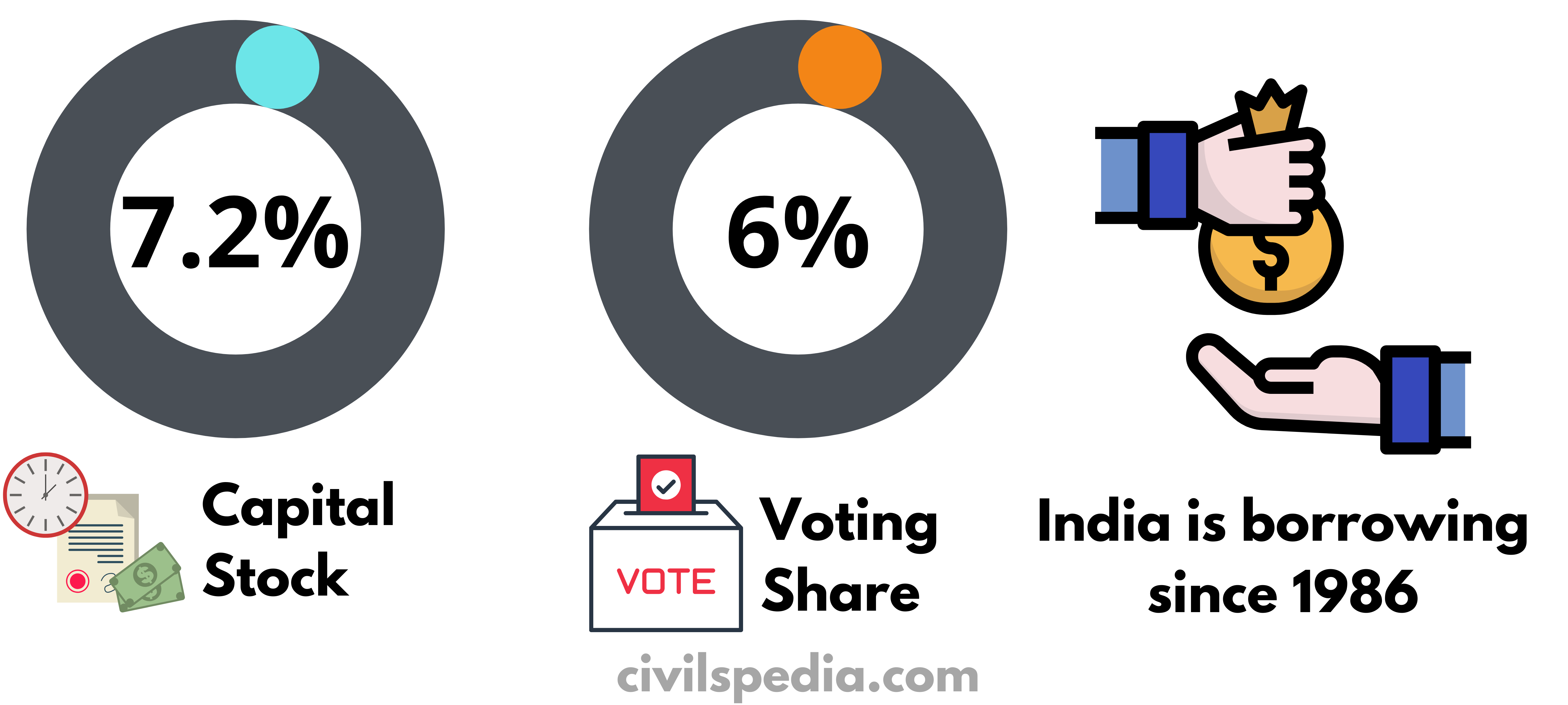
- India’s subscription to Bank’s capital stock is 7.2% & a voting share of 6%.
- India started borrowing from ADB’s ordinary capital resources in 1986. The Banks lending has been mainly in Energy, Transport & Communications, Finance, Industry & Social Infrastructure sectors.
- India holds the position of executive director on the Board of Directors of the Banks => its constituency comprises India, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Lao & Tajikistan.
- India is represented by
| Finance Minister | Governor |
| Secretary | Alternate Governor |
