Table of Contents
Dowry issue in India
This article deals with the ‘ Dowry issue in India .’ This is part of our series on ‘Society’, which is an important pillar of the GS-1 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Introduction
- Dowry is the payment given to the bridegroom’s family at the wedding, either in cash or in kind.
- Dowry Death = When young women are murdered or pushed to commit suicide as a result of constant torture and abuse from spouses and in-laws in an effort to extract a larger dowry.
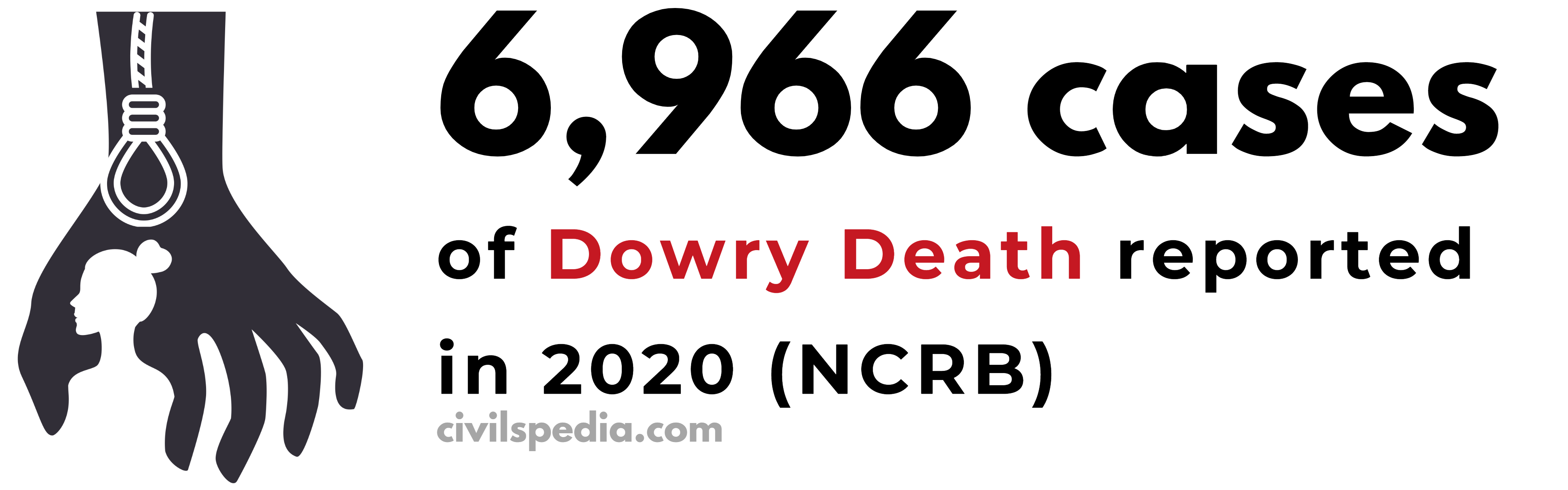
Reasons
- Dowry as part of Indian culture: The exclusion of women from the workforce, especially those belonging to the higher caste, has resulted in the practice of dowry.
- Increasing consumerism: People see dowry as an avenue to fulfil their impossible dreams.
- For some people, paying a dowry at their daughter’s marriage is an investment for fetching a high dowry through their son’s marriage.
New Trend: Earlier, only upper castes indulged in dowry, but now lower castes are imitating higher castes. It is the process of Sanskritization at play.
Effects of Dowry System
- Domestic Violence: Women are at the receiving end and are harassed & tortured.
- Imbalance in sex ratio: Due to the huge burden of dowry, daughters are seen as a financial burden leading to female infanticide & foeticide.
- It is against the Constitutional spirit of Equality and Justice as it violates the Fundamental Rights of women and their parents.
- It negatively impacts the child’s personality.
- It is detrimental to the Indian image at the global level and also goes against Convention on Elimination of all forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW) ratified by India.
Provisions to prohibit dowry
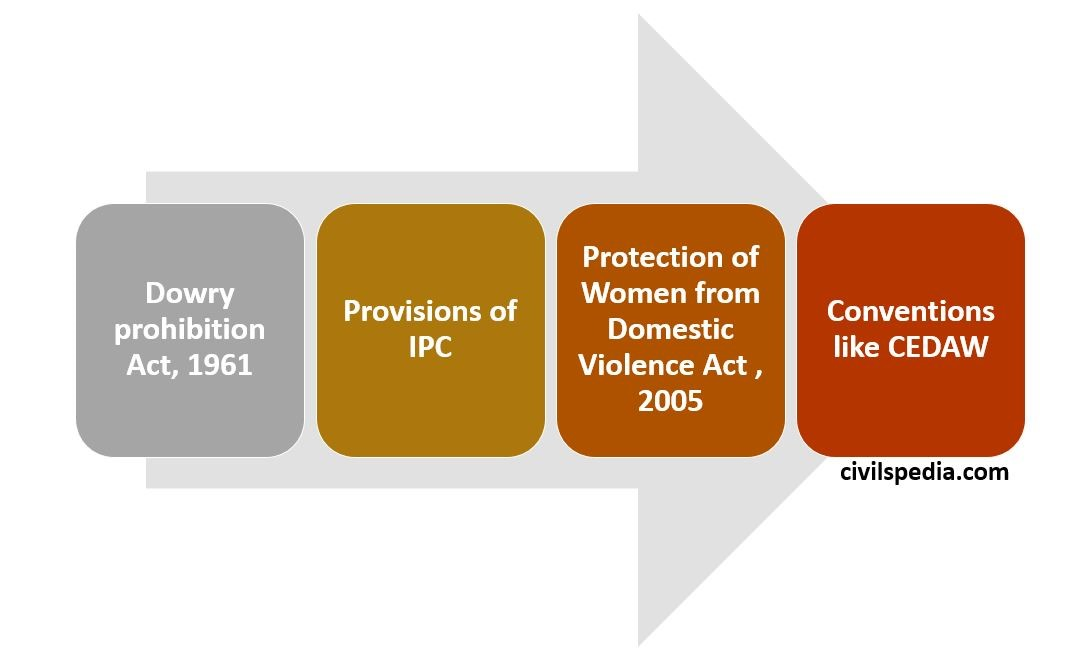
1. Dowry (Prohibition) Act, 1961
- Under the provisions of the act, demanding & giving dowry has been made punishable by 6 months or a fine.
- The issue with the Act: “Dowry” is defined as the gift given or demanded as a condition for marriage. Gifts given without condition are not considered dowry and are not punishable.
2. Section 304 B of IPC
- Section 304 B deals with dowry death-related cases.
- It has the provision of imprisonment of 7 years to life term.
3. Section 498 A of IPC
- Dowry-related cases are non-bailable and non-compoundable.
4. Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005
- Dowry often leads to domestic violence against women. Protection of Women from Domestic Violence protects women from such violence.
5. Conventions
- Convention on Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) is against all types of discrimination against women, including dowry.
Issues with Dowry related provisions of IPC
- Section 406 of IPC doesn’t demarcate the boundary between ‘Dowry’ & ‘Streedhan’. This ambiguity has been misused in demanding dowry. (according to Justice Malimath Committee) .
- Section 498 A of IPC is problematic
- The husband or his family members are presumed to be guilty until they prove their innocence => this provision is misused by the women.
- Dowry-related cases are non-compoundable (can’t compromise while the case is going) and non-bailable. According to Justice Malimath Committee, it kills any effort of conciliation.
- In Rajesh Sharma vs the State of UP (2017), the Supreme Court accepted that Section 498A of the IPC is misused. As a safeguard, Supreme Court ordered to set up of 3 membered ‘family welfare committees in all districts. The committee will look into every complaint within a month & no arrest can be made till that time. Supreme Court, however, has stated that these directions do not apply to cases in which the wife has suffered tangible physical injuries or Death.
How to end dowry?
- Attitudinal Change: Government should use peer pressure to bring attitudinal change in society.
- Amend Sections 406 and 498A of IPC as suggested by Malimath Committee.
- Government should enforce the laws strictly.
- Dowry-related cases should be fast-tracked in the courts.
- Government should promote “Adarsh Marriage” & “Mass Marriage”.
