Table of Contents
Indian Ocean Region
This article deals with the ‘Indian Ocean Region.’ This is part of our series on ‘International Relations’ which is an important pillar of the GS-2 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
What is Indian Ocean Region (IOR)?
- The region containing and surrounding the Indian Ocean is known as Indian Ocean Region.
- Indian Ocean Region has 51 coastal and landlocked states. Hence, it is a vast region.
Reasons behind the increased importance of the Indian Ocean
- The Indian Ocean has become the lifeline of world trade (& has been so since time immemorial). The Indian Ocean is important for commerce as
- 2/3rd of world oil shipments pass through the Indian Ocean.
- 1/3rd of bulk cargo passes through the Indian Ocean.
- It hosts nearly 40% of the world’s population.

- The Indian Ocean has the world’s most important choke points, notably the Straits of Hormuz, Malacca and Bab el Mandeb. As these choke points are important for global trade, a number of extra-regional states maintain a naval presence in the Indian Ocean. Eg
- US: 5th Fleet in Bahrain & uses the island of Diego Garcia as an air-naval base.
- France: Naval bases in Djibouti, Reunion Island and Abu Dhabi
- Growing Economies: The economies of many Indian Ocean countries, such as India, Malaysia, and Tanzania, are growing rapidly and are attracting huge investments.
- Indian Ocean Region (IOR) is rich in natural resources containing
- World’s 40% oil exploration
- Nearly 15% of total fishing in the world
- Mineral and natural resources like iron, copper, Zinc, manganese, gold and silver
- China’s aggressive soft power diplomacy and Maritime Silk Road (MSR) Policy have been the most crucial element in shaping the Indian Ocean strategic environment. The US and other nations like Japan, India and Australia are also trying to counter Chinese initiatives.
- Security issues: Indian Ocean Region (IOR) faces many security issues, such as piracy, illegal migration, drug trade etc.
Changed attitude of India towards Indian Ocean
- Indian Ocean Region is the centre stage of 21st-century politics & India stands geographically right in the middle. South Africa, Iran, Indonesia & Australia are also part of the Indian Ocean RIM family, but none has centrality & attraction like that of India.
- India is positioning itself as the “net security provider” in the broader Indian Ocean region.
- Due to its strategic location and capabilities, India can play a pivotal role in this region. Till now, India has played a positive role and, in the time of need, has readily helped smaller countries of the region such as Maldives (Operation NEER), Srilanka, Bangladesh etc.
Importance of IOR for India
1. Geostrategic Importance
- India is situated right in the middle of the Indian Ocean.
- It is important to secure Indian Ocean Region to protect Indian ships from piracy and stop human trafficking and drug smuggling.
- 90% of Indian trade passes through the Indian Ocean. Hence, it is vital to protect our Sea Lines of Commerce (SLOC).
- Energy Security: Most of our oil supplies come from Indian Ocean Rim countries.
2. Protection of assets and islands
- Its security is important to
protect Indian assets and islands situated in the Indian Ocean
- Islands: Andaman & Nicobar and Lakshadweep
- Assets: Like Bombay High
3. Economic Importance
It is the source of resources like
- Fishing and aquaculture
- Deep sea mineral exploration
- Petroleum reserves like Bombay High
4. Cultural Importance
- India has cultural relations with IOR countries dating back centuries.
- India has been the centre stage of Indian Ocean trade, corroborated by texts like Periplus Maris Erythraei, Jataka Stories, Sangam Poetry etc.
5. Diaspora
- A large Indian diaspora lives in Indian Ocean Rim Countries and Small Island Nations like Mauritius, Maldives, South Africa etc.
6. Countering China’s influence
- China’s aggressive soft power diplomacy has been seen as arguably the most critical element in shaping the IOR environment, transforming the entire region’s dynamics.
7. Other
- Monsoon Mechanism: The Indian Ocean plays a vital role in keeping the Monsoon mechanism in favour of India.
Chinese threat & String of Pearls
China’s Malacca Dilemma
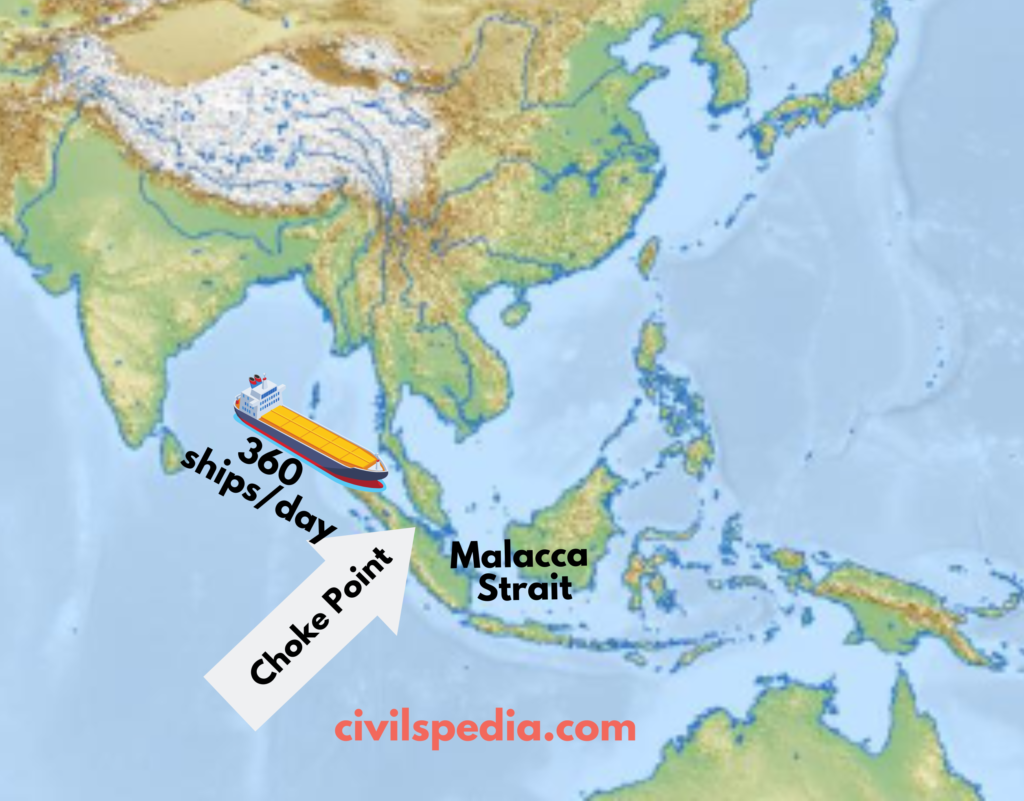
- Nearly 360 ships per day pass through the Strait of Malacca.
- If there is any blockade by a human or natural disaster, it will cause problems for China because 80% of its oil & gas imports & almost 60% of exports pass through this region.
- Singapore is located on the Malacca Strait and hosts a huge US naval base.
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands are situated near Malacca and can be used to choke the Straits.
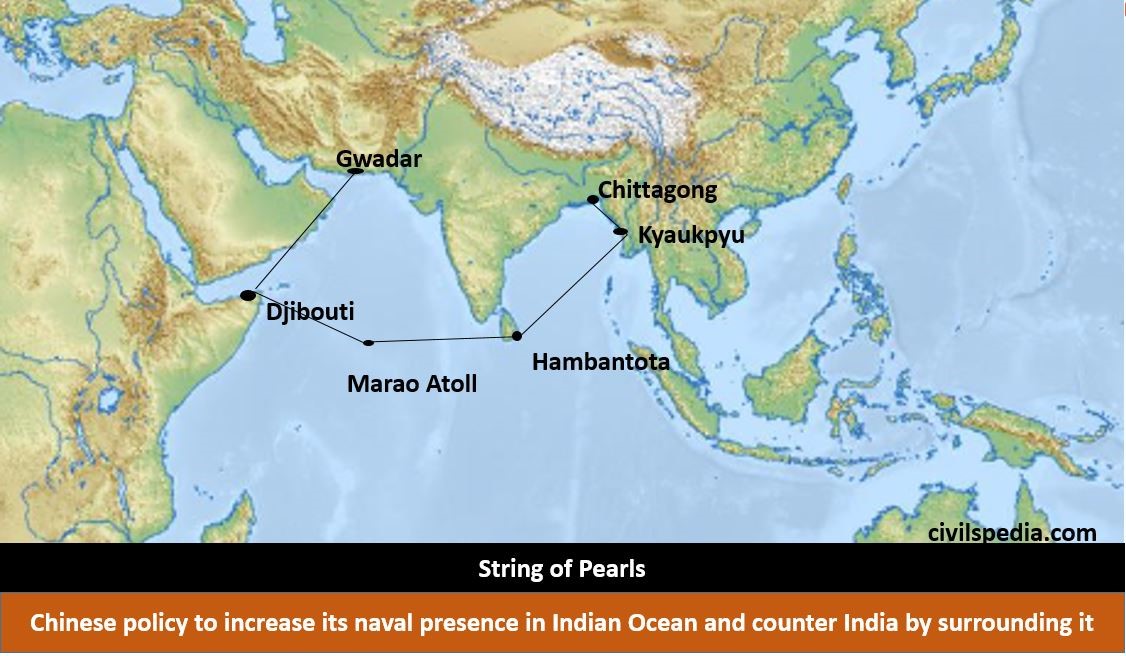
- To counter Malacca’s Dilemma, China has opted to go for an ambitious String of Pearls strategy.
String of Pearls
- It is the theory that China is trying to increase its naval presence in the Indian Ocean and counter India by surrounding it.
- It is developing a string of ports around India for this purpose.
| Kyaukpyu | Myanmar |
| Chittagong | Bangladesh |
| Hambantota | Srilanka |
| Marao Atoll | Maldives |
| Gwadar | Pakistan |
| Djibouti | First Chinese Overseas Military Base (overlooks Bab el Mandeb) |
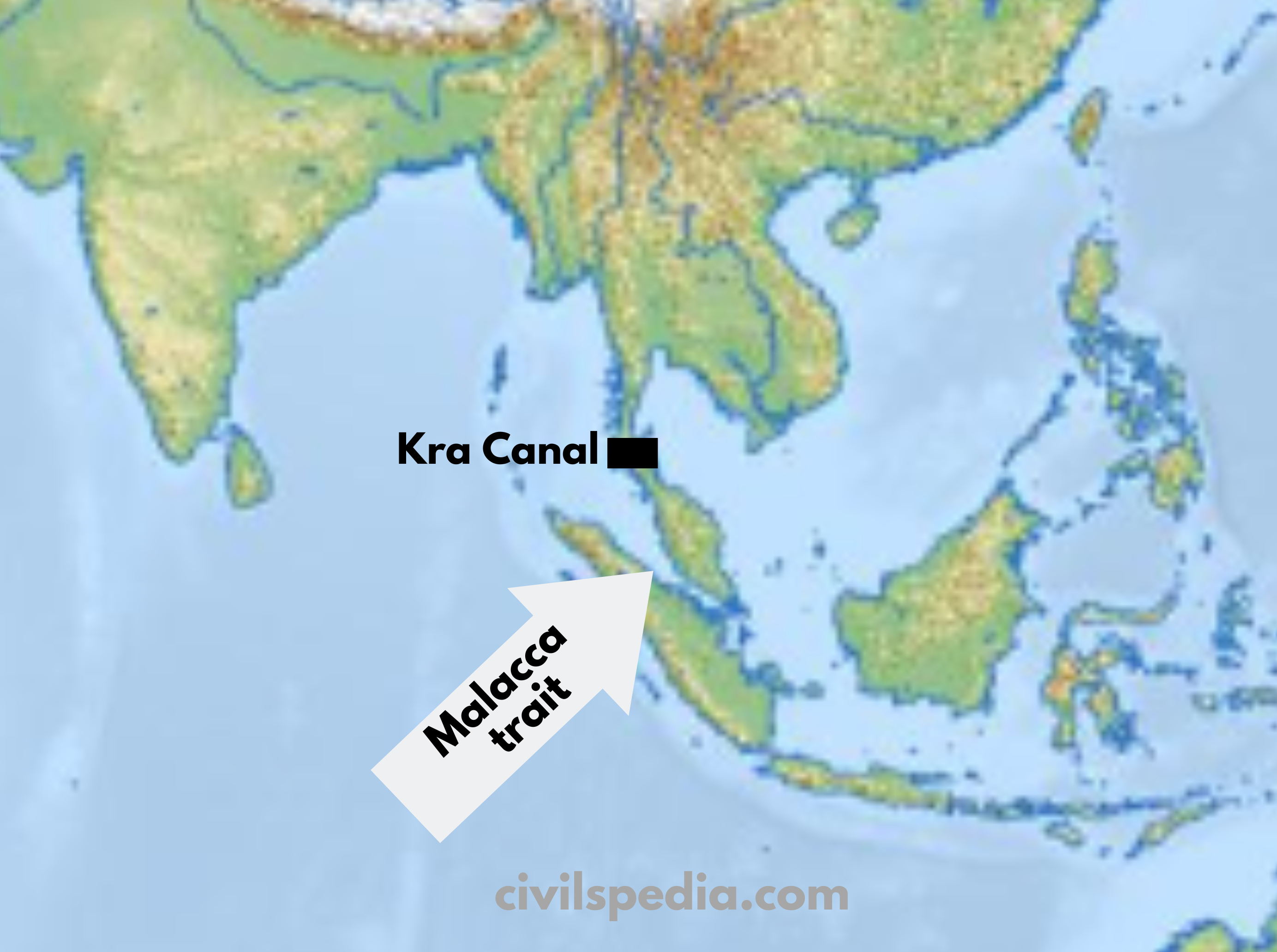
Side Topic: Kra Canal
- The Kra Canal aims to address China’s Malacca Dilemma.
- It is a 100-km canal cutting Thailand into two parts. Kra Canal will link the South China Sea to the Andaman Sea, bypassing the Malacca Strait.
- It has the added advantage of saving time.
- Experts believe Kra Canal could benefit India and other economies by taking pressure off the overcrowded Malacca Straits.
Indian steps wrt IOR
To counter String of Pearls, India is also making ports
| Andaman & Nicobar Islands | It can act as an Iron choke to Malacca 1. Malacca strait is overlooked by Andaman & Nicobar islands. 2. India has established a naval air station here called Baaz. |
| Chabahar Port | India is developing the Chabahar port in Iran. |
| Duqm port | India has signed an agreement with Oman to provide military and logistics support to Duqm Port. |
| Seychelles | India has given a proposal to lease the Assumption Islands from Seychelles. |
| Myanmar | India is investing in Sittwe port as part of its Kaladan Multimodal project. |
| Mauritius | India has developed infrastructure on Agalega Island in Mauritius. |
| Srilanka | India is developing Kakesuthai & Trincomalee ports. |
| France | India and France signed the “reciprocal logistics support” agreement as part of which warships of both nations would have access to each other’s naval bases. |
Making Alliances
Apart from that, India is trying to contain China by making alliances with like-minded nations. These include
- Making an alliance with Vietnam (Vietnam, too, has issues with China in the South China sea).
- Malabar practice with US & Japan.
- Formation of Quad by USA, Japan, Australia and India.
Military Modernisation
- Agni, Sukhoi, Nuclear submarines, and Aircraft Carriers-Vikramaditya and Vikrant, are not meant for Pakistan but to fight against a powerful nation like China.
Iron Curtain Policy to counter Chinese String of pearls
- It is the term given by naval analyst Zang Ming according to which Andaman & Nicobar islands can be used as a metal chain to block Chinese access to the Strait of Malacca.
- Japan is also helping India to develop Andaman and Nicobar.
Project Mausam
- It was launched in June 2014.
- It is a Ministry of Culture project.
- Aim :
- The project tries to see how the monsoon winds helped maritime trade historically between Indian Ocean-connected countries.
- How winds influenced local economies, scientific quests, modern statecraft, religion, politics and cultural identity
Cotton Route
- ‘Cotton Route’ has been started to strengthen economic ties between countries in the Indian Ocean rim.
Spice Route
- The Spice Route has been started to revive old links between 31 countries in Asia and Europe with India, particularly spice-rich Kerala.
SAGAR Initiative
- Announced by the PM of India, the Sagar initiative aims at Security And Growth for All in the Region.
Challenges to India’s role as a net security provider in IOR
- The capacity of the Indian defence industry to supply naval and military equipment to India and its allies is challenged by the experts. Achieving the status of net security provider can put enormous strain on the country’s finite resources and calls for a manifold increase in existing military hardware.
- More focus on territorial boundaries: Due to its pending territorial disputes with China and Pakistan, India is forced to focus on its territorial boundaries.
- China challenges India’s status in the Indian Ocean through its Belt and Road Initiative and String of pearls.
- Opposition from other countries. E.g.:
- Seychelles parliament has opposed the lease of Assumption Island to India.
- Past Experience of Overseas Deployment of Armed Forces: The recipe of net security provider does encompass ‘Overseas Deployment’ as a vital ingredient. However, the experiences in Sri Lanka continue to have a dragging effect on any thought process involving overseas deployment.
