Governance & Administrative Reforms in Banking Sector
This article deals with ‘Governance & Administrative Reforms in Banking Sector – UPSC Notes .’ This is part of our series on ‘Economics’, which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Introduction
The government is trying to recapitalize the Public Sector Banks and helping them to cleanse their stressed Balance Sheets. But, if nothing much is done regarding the Governance & Administration of the Public Banks, then Banks nothing will change, and banks will carry on their operations as usual. Hence, the government has brought various Governance & Administrative reforms along with the recapitalization of banks.
1. Gyan-Sangam-I, 2015
- Finance Ministry organized a workshop for financial regulators, Public Sector Bank, Insurance Companies etc., called Gyan Sangam.
- It resulted in the following outcomes.
- PSBs’ CMD post is bifurcated into a separate 1) chairman and 2) separate MD (CEO) to ensure Separation of Power and make them more accountable and transparent.
- An autonomous body called Bank Board Bureau (BBB) will be set up to select the MD, Chairman, Directors and other top officials of PSBs (Earlier, the Government was selecting top officials of Banks, leading to the politicization of posts.)
2. Mission Indradhanush
- Governmental reforms in Banking Governance under 7 Pillars (ABCDEGA)
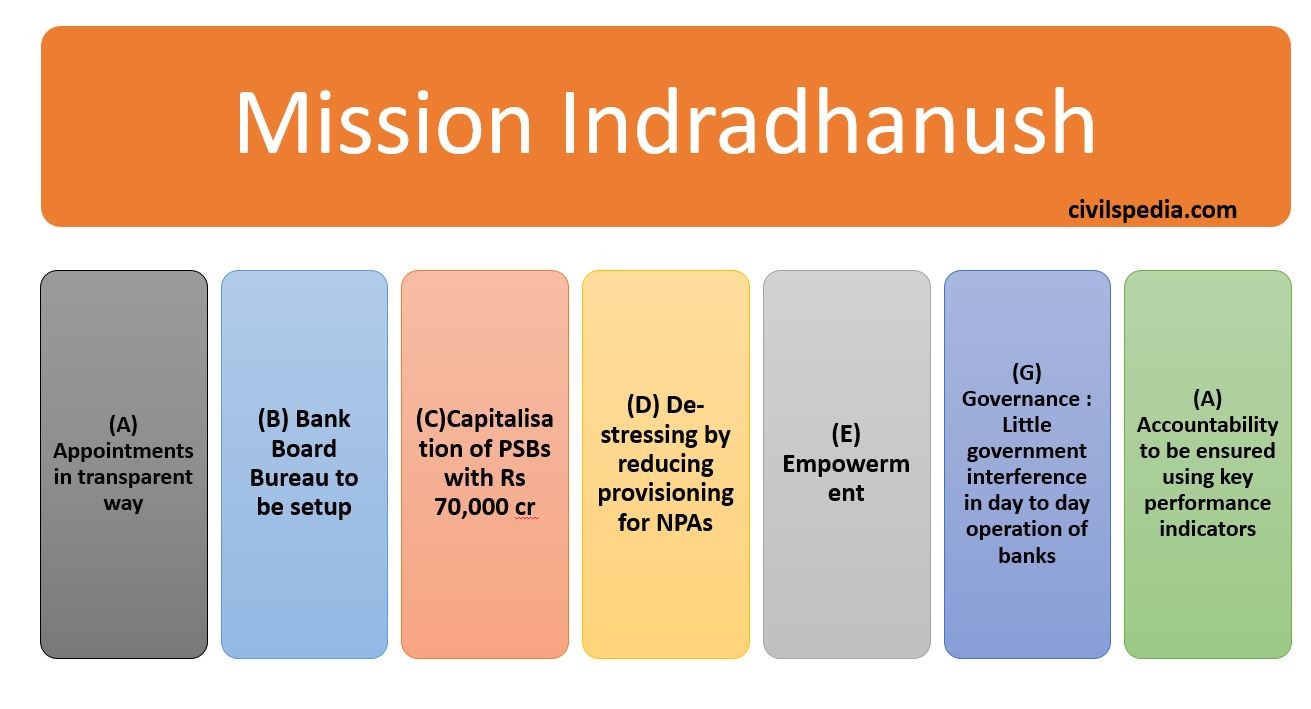
(as such, it has become an old topic, and just an infographic will suffice)
Side Topic: Bank Board Bureau (BBB)
- Earlier Government was selecting top officials of Banks, leading to the politicization of the posts. To deal with this issue, BBB was set up on the recommendations of the PJ Nayak Committee.
- BBB’s primary function is to select top officials for PSBs, LIC and other public sector financial institutions.
- BBB also helps the banks in governance reforms, raising capital for BASEL-III etc.
- BBB has 1 Part-Time Chairman, 3 Part-Time Members, and 3 Ex-officio Members (from Govt & RBI side)
- In 2018, Bhanu Pratap Sharma (retd. IAS) replaced Vinod Rai (ex-CAG) as the new chairman of BBB.
3. EASE Agenda
When Government announced ₹2.11 lakh crore package for the recapitalization of PSBs, at the same time, it started EASE Agenda so that employees don’t become lazy thinking that all their problems have been solved. Additionally, PSBs will have to change their arrogant and carefree attitude and focus on the 6 pillars listed below.

4. Other Steps
- RBI has laid down instructions for Private Sector Banks that the same person can’t hold the post of MD, CEO and Whole-time Director for more than 15 years to improve Corporate Bank Governance and reduce the concentration of power.
Further Suggestions
- Employee Stock Option Plans (ESOPs)
- ESOP is a type of benefit plan wherein employees are given some shares of the company apart from regular salary (companies like Facebook, Google, and many other Startups already use ESOPs).
- Existing salary-based compensation mechanism encourages employees to prefer safety and conservatism over risk-taking and innovation. But giving them some shares via ESOP may encourage risk-taking and a possible change of mindset from an employee to an owner.
- Allow lateral entry into higher management.
- Allow campus recruitment of some specialists from institutions like IITs, IIMs etc.
