Cryptocurrency – Issues and Regulation
This article deals with ‘Cryptocurrency – Issues and Regulation.’ This is part of our series on ‘Economics’ which is an important pillar of the GS-2 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
The genesis of Cryptocurrency
- During the Subprime Crisis, the Central Bank of the US & other developed countries adopted Easy Money Policy & as a result, the purchasing power of $ decreased. The leading cause of the Subprime Crisis was the loans given by banks to subprime borrowers. Hence, anarchists argued that banks earned by charging interest and fees. But when loans turned bad due to their mistake, governments made common people suffer by following Easy Money Policy and reducing the purchasing power of their hard-earned money.
- Cyber Anarchists decided to withdraw from Banking System and start a currency that would not depend on any country’s Central Bank.
- Hence, bitcoin can be considered a political movement rather than a technological movement.
Timeline
- 2008: Satoshi Nakamoto (the name of the online user, but nobody knows who he is) issued an online paper.
- 2009: The operation of Bitcoins started.
- 2015: Ethereum, the second most popular cryptocurrency after Bitcoin, was launched.
- 2020: The price of Cryptocurrencies started to rise amidst the Corona crisis due to fear that governments would print money in excessive amounts to cover the fall in tax collections and cover unemployment benefits.
- 2021: In the private sector, the acceptability of Bitcoins started increasing. E.g., Elon Musk and Jack Dorsey (founder of Twitter) are investing in Bitcoin.
- 2022: The price of all Crypto-currencies, including Bitcoin, fell sharply.
What is Cryptocurrency?
- Cryptocurrency is a digital currency created, stored and transacted using blockchain technology.
- Examples of Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin, Dogecoin, Litecoin, Ethereum etc.
- Bitcoin, invented by Satoshi Nakamoto (anonymous), is the most popular.

How Bitcoins Work?
Technically Incorrect Example
- Suppose there is a gold mine, and a person starts to mine it with tools. All the mined gold is converted to coins with a serial number on it by the person sitting at the exit of the mine and registered in Ledger.
- The coin that is produced can be broken into smaller coins to pay for smaller transactions. But each time the bigger coin is broken into smaller coins, a separate Registration number is given to it, and it is registered in Ledger again.
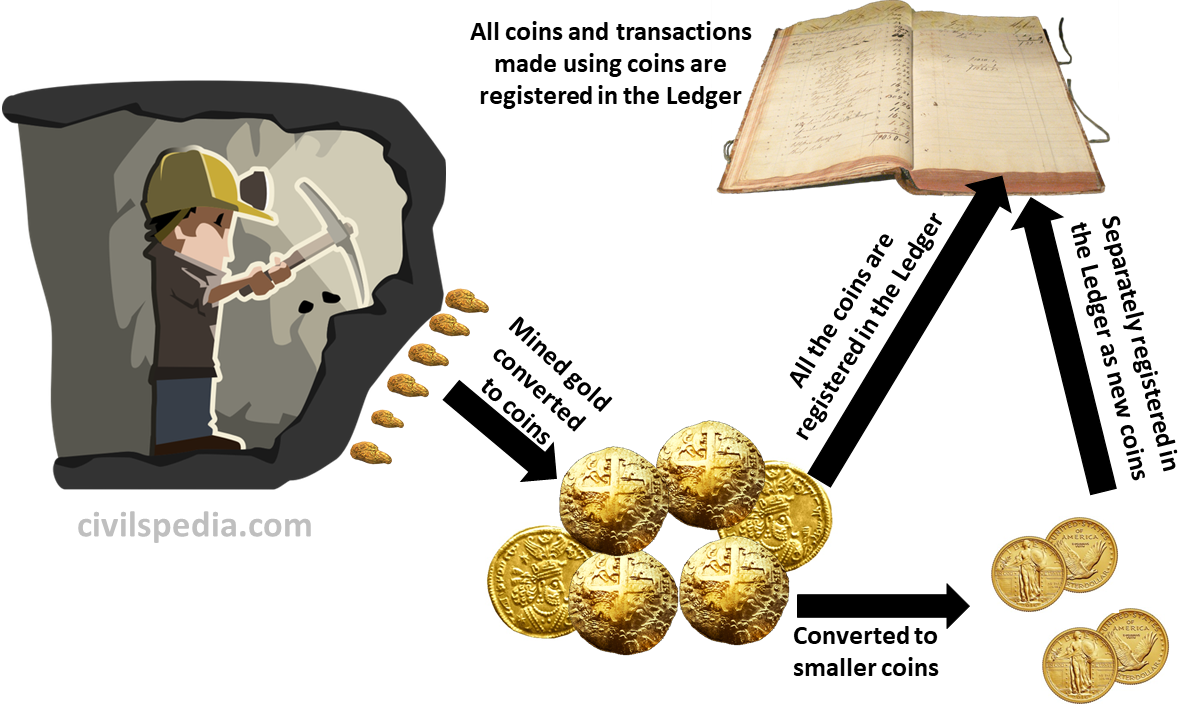
Working of Bitcoin
- Instead of Gold Mine, Satoshi Nakamoto has created a Cryptographic’ Data Cube’. This Cube can be mined using a computer. When the whole of ‘Data Cube’ is mined, 21 million bitcoins will be generated.
- The primary condition is the same here as well. Every coin that is generated has to be registered in Public Ledger (called Blockchain).
- Bitcoin is divisible up to 10^8 Satoshi. But each time Bitcoin is divided, it has to be registered in Public Ledger. Hence, every transaction is registered in Public Ledger (Blockchain) (more on this later).
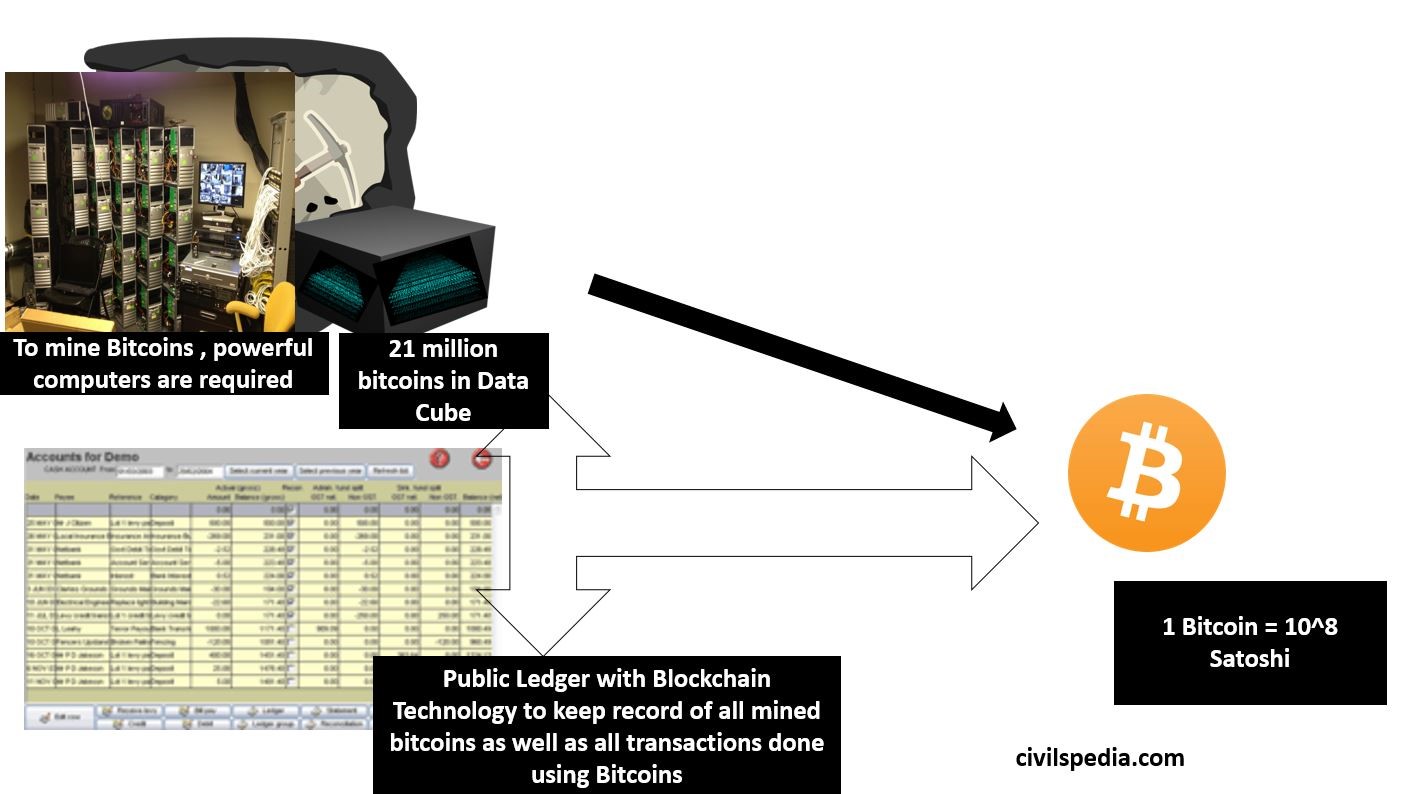
How are cryptocurrencies bought?
There are two ways
- Mining: One can mine cryptocurrency coins using computers.
- Buy from someone: One can also buy cryptocurrency. This buying can also happen in two ways
- Peer-to-Peer Transactions: Buying directly from someone who owns that cryptocurrency.
- Exchange facilitated transactions through exchanges such as Kuber, WazirX etc.
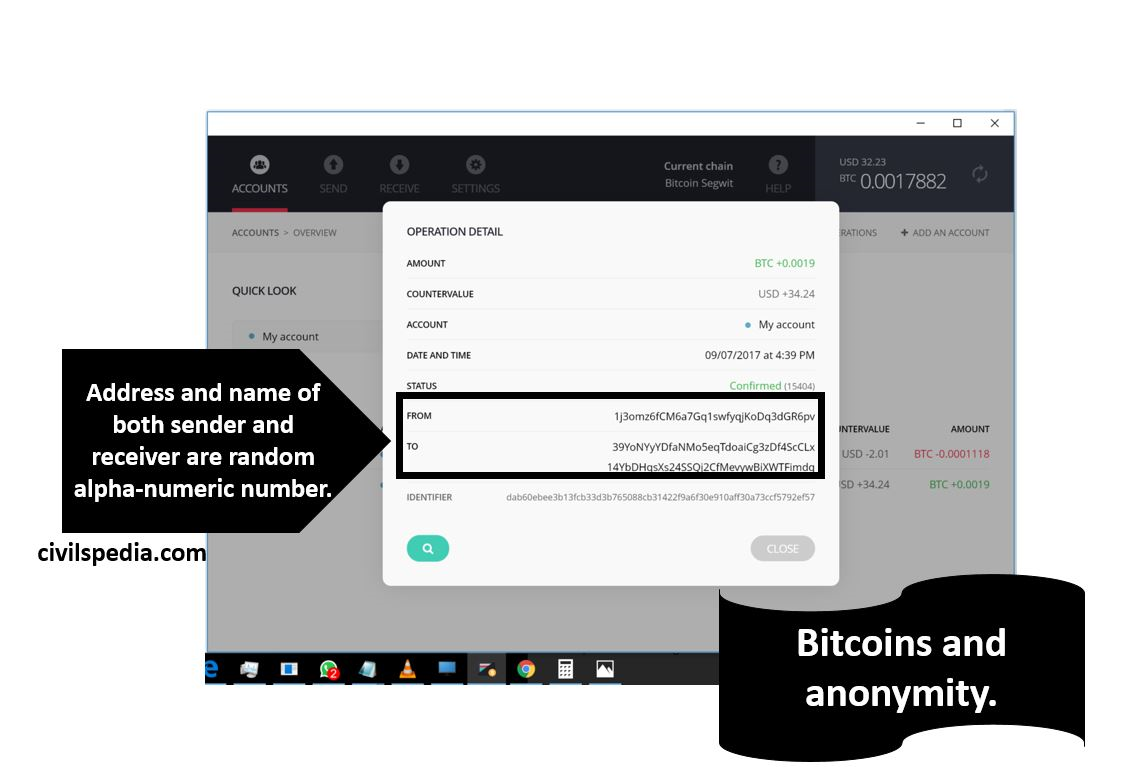
Bitcoin Wallet
- Bitcoin Wallet looks like other Wallets (like Paytm Wallet). One can send money to any person using his Bitcoin wallet’s Address and Password (Wallet address is random alpha-numeric)
- But there is no requirement for Name, Mobile Number and KYC Norms. One can send Bitcoins to another person without knowing the identity of the other. Hence, it is very anonymous.
Benefits of Cryptocurrency
- Cost-effectiveness in International Use: Electronic transactions to other countries are expensive due to currency conversion & processing fees levied by banks. Cryptocurrencies solve this problem, as they have a single valuation globally.
- Privacy Protection: Using pseudonyms conceals the parties’ identities, information, and transaction details.
- They are difficult to counterfeit compared to physical currency because they use Blockchain Technology.
- Immunity from Government’s Financial Retribution: For citizens in repressive countries, where governments can easily freeze or seize bank accounts, cryptocurrencies are immune to any such seizure by the state.
Problem with Cryptocurrencies
- Used in carrying out Illegal Activities because of anonymity, it offers
- Various sites selling Drugs and other banned substances through Bitcoins, like Silk Road, came up.
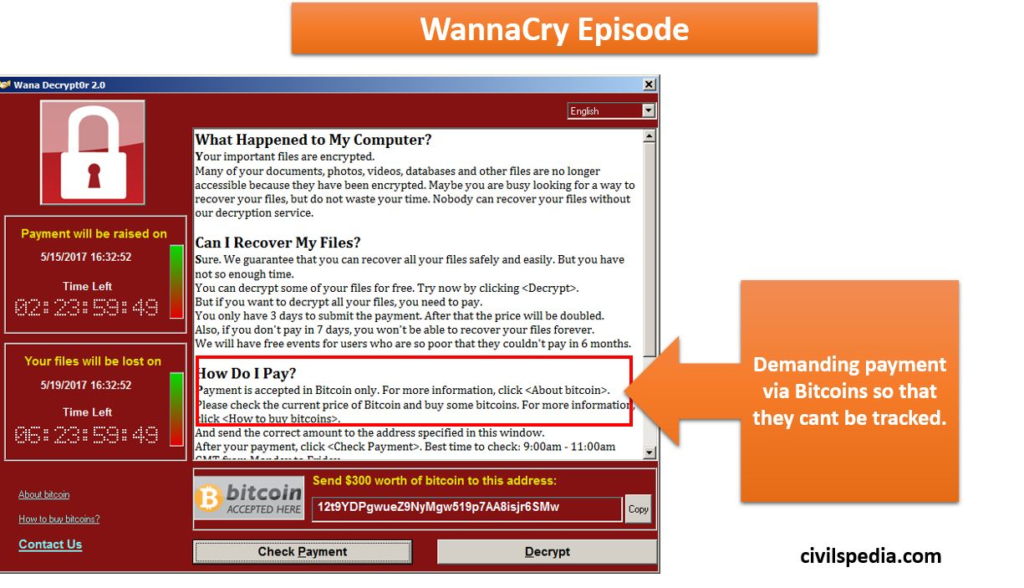
- Criminals use Bitcoins in case of cyberattacks—E.g. Wannacry episode.
- Crypto-Exchanges are prone to Scams: The crypto exchanges used by ordinary people to buy, sell and store cryptocurrencies are also prone to scams. For example, FTX Exchange, based in Bahama, indulged in the scam, and more than Rs. 10 lakh crore of investors are stuck due to the fraud.
- Money Laundering: The cryptocurrency market isn’t universally protected or regulated like Banks. Thus, it is increasingly used to launder money. In 2019, criminal entities laundered approximately $2.8 billion through crypto asset exchanges.
- The government is deprived of its taxes. E.g., On selling gold, government charges Capital Gains Tax, but Bitcoin transactions are difficult to trace.
- Climate Change: Experts estimate that cryptocurrency mining-related electricity consumption generates 38 megatons of CO2 annually (equal to that of Mumbai and more than Austria and Bangladesh).
- Countries like Iran and North Korea are using cryptocurrencies to bypass economic sanctions.
- Uncertainty over Consumer Protection and Dispute Settlement Mechanisms: as Cryptocurrencies are decentralized.
- Highly Volatile: Explained below.
- No intrinsic value: Explained below.
Bitcoin Bubble / High Volatility?
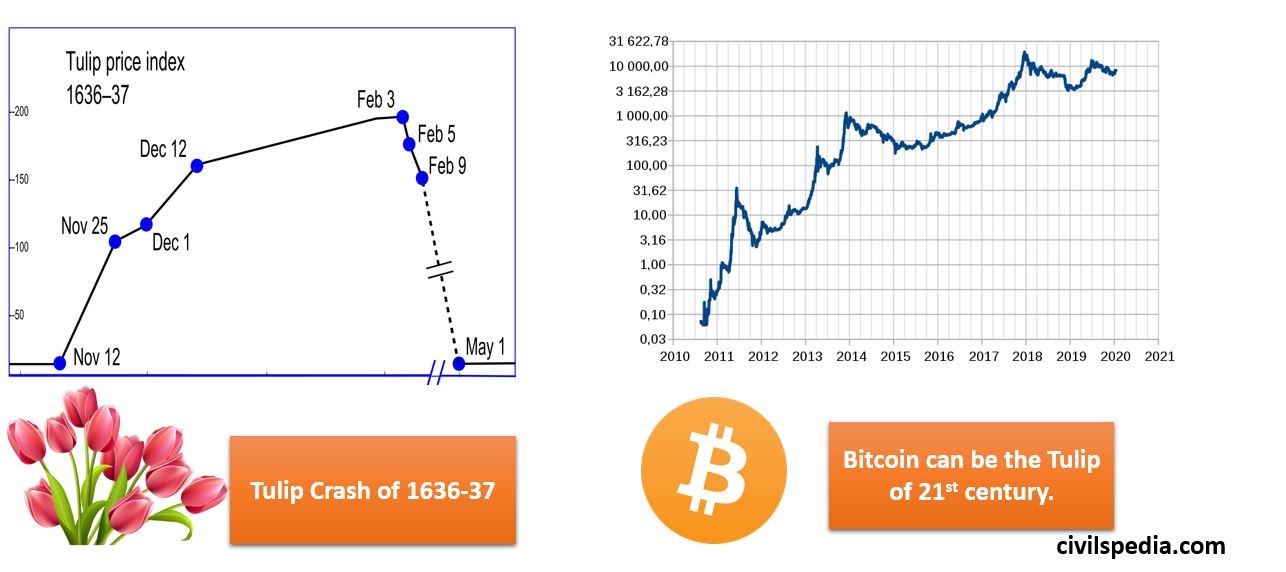
Whether this is Bubble or not?
- Cryptocurrencies like bitcoin, according to its advocates, are quickly becoming accepted forms of payment that will pose a severe threat to the national currencies issued by central banks. They, therefore, consider the increase in bitcoin’s acceptability only a reflection of its promising future as a stateless currency.
- Sceptics have cited the 17th-century tulip bubble and the late-1990s Internet stocks as cautionary tales. Bitcoins lack inherent value, and emotion rather than value drives their exponential growth.
India and Cryptocurrencies
- Budget 2022: Budget 2022 placed the transactions in the Virtual Digit Assets (i.e. cryptocurrency, NFT etc.) under tax provisions
- 30% tax has been placed on the income earned from the transactions in the cryptocurrency.
- The losses can’t be offset by the profits.
- Gifting the cryptocurrency will also be taxed.
- 1% TDS will be deducted for payment made above a certain threshold in relation to the trade of Virtual Digital Assets.
- RBI on Cryptocurrencies
- RBI has notified all the regulated entities (like Banks, Card Companies etc.) that they can’t help anyone to buy/sell bitcoins or any other Virtual Currency
- 2020: But this ban was declared illegal by Supreme Court. But this ban was declared illegal by Supreme Court.
Virtual Currencies & World
Some countries have restricted and prohibited Virtual Currencies (India, China, Bolivia etc.), while others allow their use in regulated forms (Japan, the US, Australia, South Africa etc.).
Virtual currencies and Blockchain-based things started by various countries
1. China
- 2019: People’s Bank of China announced they would launch their own Crypto-currency.
- 2021: China’s crackdown on Cryptocurrencies led to a significant downfall in the value of almost all cryptocurrencies.
2. El – Salvador
- El-Salvador has become the first country to accept Bitcoin as legal tender in 2021.
3. UNICEF and Bitcoins
- In October 2019, UNICEF announced that they would accept donations through Bitcoins and all the other sovereign currencies of the world.
4. Petro
In 2018, President Nicolas Maduro announced the following:
- The government of Venezuela decided to issue 100 million Petro coins – a type of cryptocurrency.
- Price of 1 Petro coin = market price of one oil barrel from Venezuela.
5. Libra
- Cryptocurrency announced by Facebook.
- Unlike other Cryptocurrencies, Mark Zuckerberg has announced that it will be backed by assets in reserve.
- But countries like France have openly rejected Libra as it will set a precedent of currencies of MNCs and challenge the sovereignty of nation-states.
