Table of Contents
Assam Issue (Internal Security)
This article deals with the ‘Assam Issue (Internal Security) .’ This is part of our series on ‘Internal Security’, an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Introduction
Assam is the land of Ahoms (also called Shans), who invaded and settled here in the 13th century. The land of the Ahoms thus came to be called Asama. Word Assam is the anglicised form of the word ‘Asama’.
The burnt of invasion was suffered by the original inhabitant tribes. Bodos form the most important group of this race.
Later, Ahoms were defeated by the Burmese, who entered through the eastern borders. Finally, in 1826, Assam became Britain’s protectorate under the Treaty of Yandabu, signed between Burma and Britain after the defeat of Burma in the Anglo-Burma Wars.
In Assam, there are two main issues wrt Assam. These include
- Migration of Outsiders in Assam
- Bodoland Issue
Issue 1: Migration of Outsiders in Assam
The first issue that we will deal wrt Assam is the issue of the migration of outsiders in Assam. This has led to agitations. The main insurgent organization involved with this issue is ULFA.
Migration of outsiders to Assam
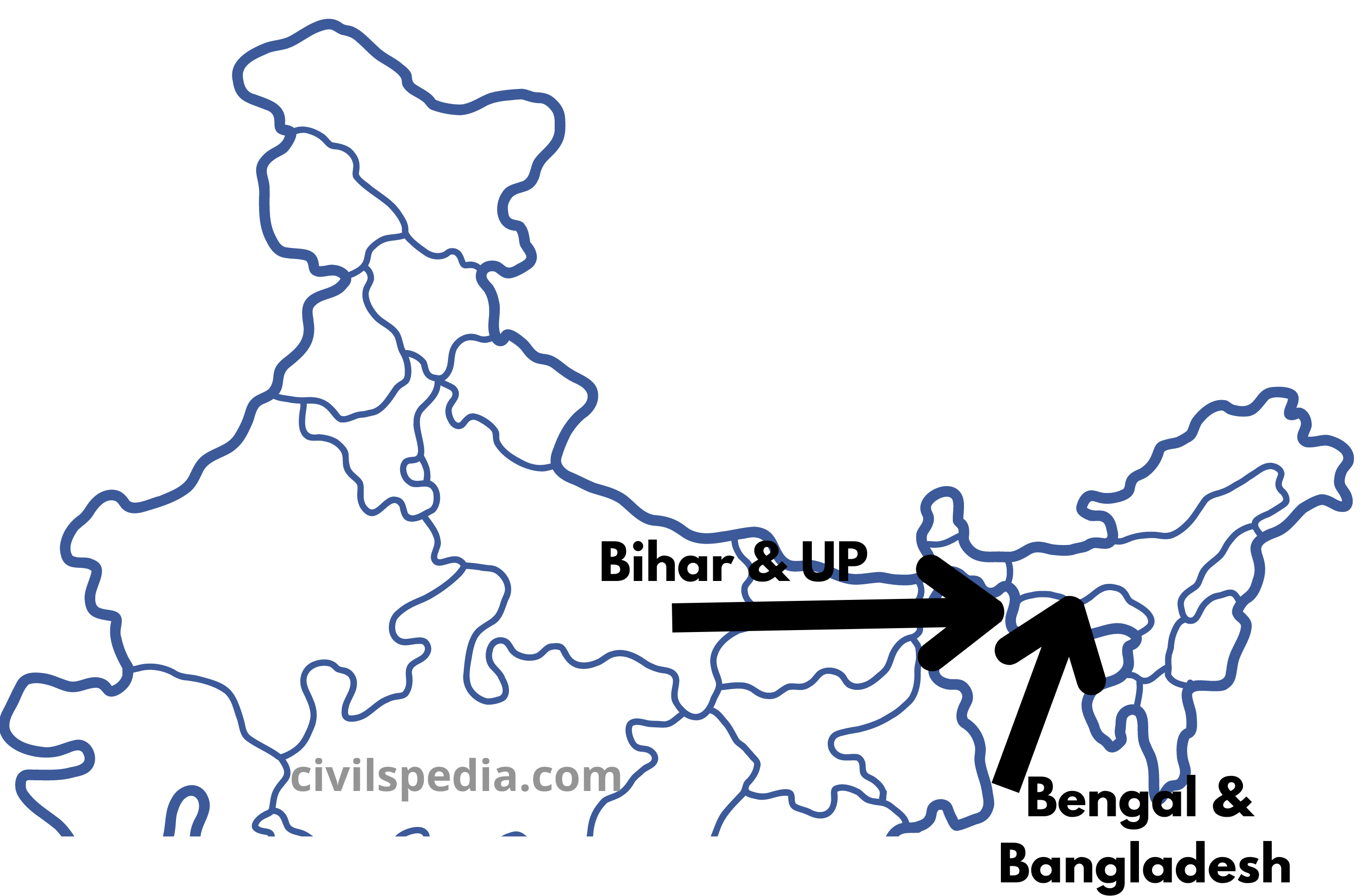
- Britishers developed the tea industry in Assam. They imported labour from Bihar & other Indian provinces to work in tea gardens.
- Assamese people living mainly in Upper Assam were not interested in expanding the cultivation in hitherto uncultivated land. Therefore, the British encouraged Bengali Muslim peasants from present Bangladesh to move into Lower Assam to put virgin land under cultivation.
- Later during the 1971 crisis, a large number of Bangladeshi Muslims (and Hindus) came and settled in Assam. This pattern is going on even after that.
As a result, the Assamese people started the Socio-political movement in 1979 to evict illegal Bangladeshis. It ended in the famous Assam Accords in 1985.
Reason for Migration from Bangladesh
- Increasing pressure on land and mounting unemployment in Bangladesh due to rapid population increase.
- Bangladeshi Hindus migrate to Assam or other parts of India due to religious persecution in Bangladesh.
- Large segments of Bangladesh’s population are uprooted by severe floods and cyclones which migrate to Assam (or other parts of India).
- Porous India-Bangladesh border also facilitates this trend.
- Economic conditions of India is relatively better than that of Bangladesh.
ULFA (United Liberation Front of Asom)
- ULFA was formed in 1979 against the backdrop of the All Assam Student Union’s agitation against foreigners under the leadership of Arbinda Rajkhowa, Pradip Gogoi, Paresh Barua etc.
- They aimed to create an Independent and Socialist Assam through arms struggle. It seeks to bring back the glorious times of the Ahom kingdom. ULFA claims that Assam was never a part of India as the Treaty of Yandabu was signed between two imperial powers (i.e. Burma and Assam) without the involvement of the Assamese people.
- It established a close relationship with organizations such as the NSCN of Nagaland and the Kachin Independence Army (KIA) of Myanmar to acquire arms and train recruits. ULFA has also established links with the ISI of Pakistan.
- It conducted several terrorist activities throughout the 1990s. Hence, it was declared a Terrorist Organisation under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (i.e. UAPA) in 1990.
- Bangladesh has also helped cracking down on the ULFA rebels.
- In 2009, India was successful in getting the chairman of ULFA into custody
- In 2011, Tripartite Agreement was signed between the Union Government, the State of Assam and ULFA for the suspension of operations of ULFA. Currently, ULFA is divided into two factions – ULFA (PTF) and ULFA (ATF), i.e. Pro and Anti Talk Faction. ULFA (PTF) has suspended the operations and is engaged in peace talks. On the other hand, ULFA (ATF) is continuing its previous modus-operandi.
Security Challenge
- Agitations in which public property is damaged: Government failure to respond to illegal migration leads to the uproar by Assamese and damage of public property on a large scale.
- Illegal Voters: Most illegal Bangladeshis have their names enlisted in the voting list, thereby claiming themselves as state citizens. The immigrant population acts as a vote bank for the political parties in Assam.
- Issue of terrorism: Pakistan’s ISI has been active in Bangladesh, supporting militant movements in Assam. Among the illegal migrants, there are also militants.
Way Out
- Diplomatic Effort: India has to make a diplomatic effort to get Bangladesh to cooperate, as illegal migration cannot be solved unless sending country cooperates.
- Better Border Management: Fencing, construction of border roads and proper border management will make a difference
- Bar from voting rights: Illegal migrants should not be allowed to vote, which will diminish their ability to influence government decisions by being a political force.
Issue 2: Bodoland Issue
- Bodoland is a state demanded by a tribal community called Bodos in Assam, comprising 5%-6% of the state’s population.
- National Democratic Front of Bodoland (NDFB), an ethnic insurgent organization, has been leading the charge in demand for a separate state.
- Reasons for the demand for Bodoland include
- Massive Illegal Immigration from Bangladesh and their inclusion in the voter’s list has turned Bodos into a minority in their land
- Failure of The Bodo Territorial Council (BTC) due to weak administrative institutions and divisive politics
NDFB
- National Democratic Front of Bodoland (NDFB) was established as Bodo Security Force in 1986 and was later rechristened as NDFB in 1994.
- They want a sovereign state of Bodoland in the areas lying North of the Brahmaputra river in Assam.
- NDFB though claim to represent the Bodo people, in reality represent the Christian minority and not the indigenous Bodos.
- It has training camps in south Bhutan, and the Indian Security Forces, with the help of Bhutan, has launched operations to destroy these training camps.
Other Insurgent Groups active in Assam
- Hmar People’s Convention (for the creation of the Hmar state consisting of Hmar’s living in Mizoram, Assam and Manipur)
- United Liberation Front of Barak Valley
- Karbi People’s Front
- Kamtapur Liberation Organisation (KLO)
- Muslim United Liberation Tigers of Assam (MULTA)
- Black Widow
