Table of Contents
BRICS Bank
This article deals with the ‘International Monetary Fund .’ This is part of our series on ‘Economics’ which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
What is BRICS?
- 2001: The term ‘BRIC’ was coined by Jim O’Neil of Goldman Sachs to describe the growing prominence of Brazil, Russia, India and China
- 2009: BRIC country leaders started meeting as a bloc (immediately after Sub Prime Crisis). South Africa joined them later.
- BRICS account for
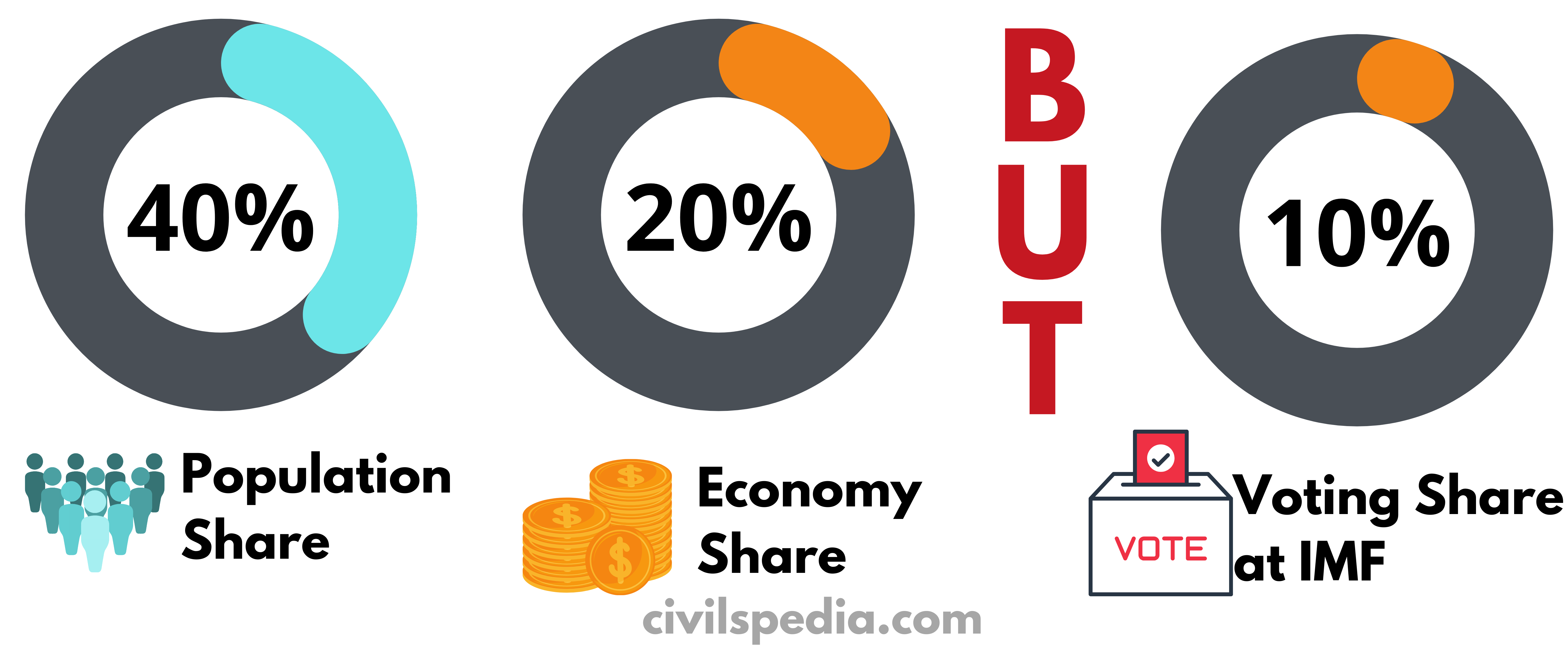
- Developed countries such as the US, Japan, Germany, U.K. and France hold 40 % voting power.
Information at Glance
| Formed at | 6th BRICS summit held in Fortaleza, Brazil (through Fortaleza Declaration) |
| Year of Formation | 2014 |
| Headquarters | Shanghai, China |
| Members | 5 (BRICS, i.e. Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) |
| Subscribed Capital | $50 billion—equally shared by the five nations |
| Contingent Reserve | $100 billion (to provide liquidity protection to members during the balance of payments problems) |
| Voting power | One-nation one-vote principle (unlike World Bank and IMF) |
| Purpose | – Loans for infrastructure and sustainable development projects (75% of funds will fund sustainable development funds) – Helping the countries facing the balance of payment (BoP) crisis. |
Why was BRICS Bank born?
BRICS countries decided to form a development bank, whose purpose will be to “mobilise resources to set up infrastructure and ensure sustainable development” in BRICS countries and in other emerging economies.
- BRICS block emerging as a new economic powerhouse with 20% global GDP & 40% population. Hence, to solidify and demonstrate their strength BRICS Bank has been formed by these nations.
- Disenchantment with Bretton-Woods institutions viz World Bank & IMF: Since its inception in 1944, the IMF and World Bank have not reformed their governance structure. The USA dominates both are out of sync with new world dynamics.
- Exchange Rate Volatility: It will help defend these five economies from volatility in the dollar exchange rate.
- Making an alternative to the US Dollar: BRICS Bank will make the Chinese Yuan an alternative to US Dollar in the long run.
- In the BRICS bank, the First chairman of the board of governors will be a Russian. The first President of the bank will be an Indian (KV Kamath). It is difficult in the World Bank and IMF, given the lobbying and uneven voting power.
It has to be noted that BRICS Bank is not an isolated initiative. Similar initiatives have been started in the past to blunt the might of Bretton-Woods institutions. These include the Development Bank of Latin America ( by Andean nations) in the 1960s, the Chiang Mai Initiative in the early 2000s (of 10 ASEAN nations plus China, South Korea and Japan) and Bank of South by Latin American countries in 2009.
Counterview about BRICS Bank
- It will allow Beijing to invest overseas in developing nations through a neutral mechanism and avoid criticism of Chinese neocolonialism.
- It will become difficult for India to balance a scenario in which China will provide funds for its OBOR through BRICS, especially because India is not part of the project.
