Table of Contents
Disabled Persons
This article deals with ‘Disabled Persons ’. This is part of our series on ‘Society’ which is an important pillar of the GS-1 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.

These people told the world that it is not the disability but one’s ability that counts.
Introduction
Persons with Disability Act recognises 21 types of disabilities like
- Blindness
- Low vision
- Leprosy cured
- Hearing impairment
- Locomotor disability
- Mental retardation
- Mental illness
- Acid Attack victims
- Dwarfism
2011 Census says 2.21% of the Indian population is disabled (which is an underestimation).
Issues with Disables
- Disability is not measured correctly in India. Census depends on self-reporting of disability, and many don’t report owing to social stigma.
- India looks at disability from a medical or pathological angle only. Most developed countries look from a social angle.
- Lack of Institutional and Infrastructural Support for the disabled in India.
- Lack of schools for disabled
- Physical infrastructure is not disabled-friendly.
- Under the new GST regime, almost all disability aids and appliances are to be taxed at the rate of 5% or 12%.
- Employment: Private sector is reluctant to employ the disabled.
- Inaccessible Infrastructure: Physical accessibility in buildings, transportation, access to services etc., remains a challenge for the physically disabled.
Rights of Person with Disability Act, 2016
- The act was brought to fulfil obligations under the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD) ratified by India in 2007.
Provisions
- Types of disabilities have been increased from existing 7 to 21, including Acid Attack Victims, Dwarfism, etc
- Reservation in government jobs has increased from 3% to 4%.
- Every disabled child in age group 6 and 18 years has the right to free education.
- Ensure accessibility in public buildings (both Government and private).
- Special Courts for handling cases concerning violation of rights of PwDs.
Benefits
- Right based approach: This will help to move the discourse away from charity.
- Broader coverage: The list of disabilities is expanded from 7 to 21.
- Provides reservation and hence will help in Socio-Economic development.
Criticism
- Reservation: Reservation was 5% in the 2014 proposed bill but reduced to 4% in this act.
- There is no provision regarding insurance companies that they cant charge higher premiums from Disabled persons.
Marrakech Treaty and blind
- Under Marrakech Treaty, copyrights don’t apply if the book is reproduced for the visually challenged.
- India has ratified this treaty in 2014.
- India has launched Sugamya Pustkalya in line with the treaty.
Sugamya Bharat Abhiyaan (Accessible India Campaign )
- Sugamya Bharat Abhiyaan is aimed at creating a barrier-free environment for the disabled.
- The scheme draws inspiration from United Nations Convention on Rights for Persons with Disabilities (2007) and Incheon Strategy.
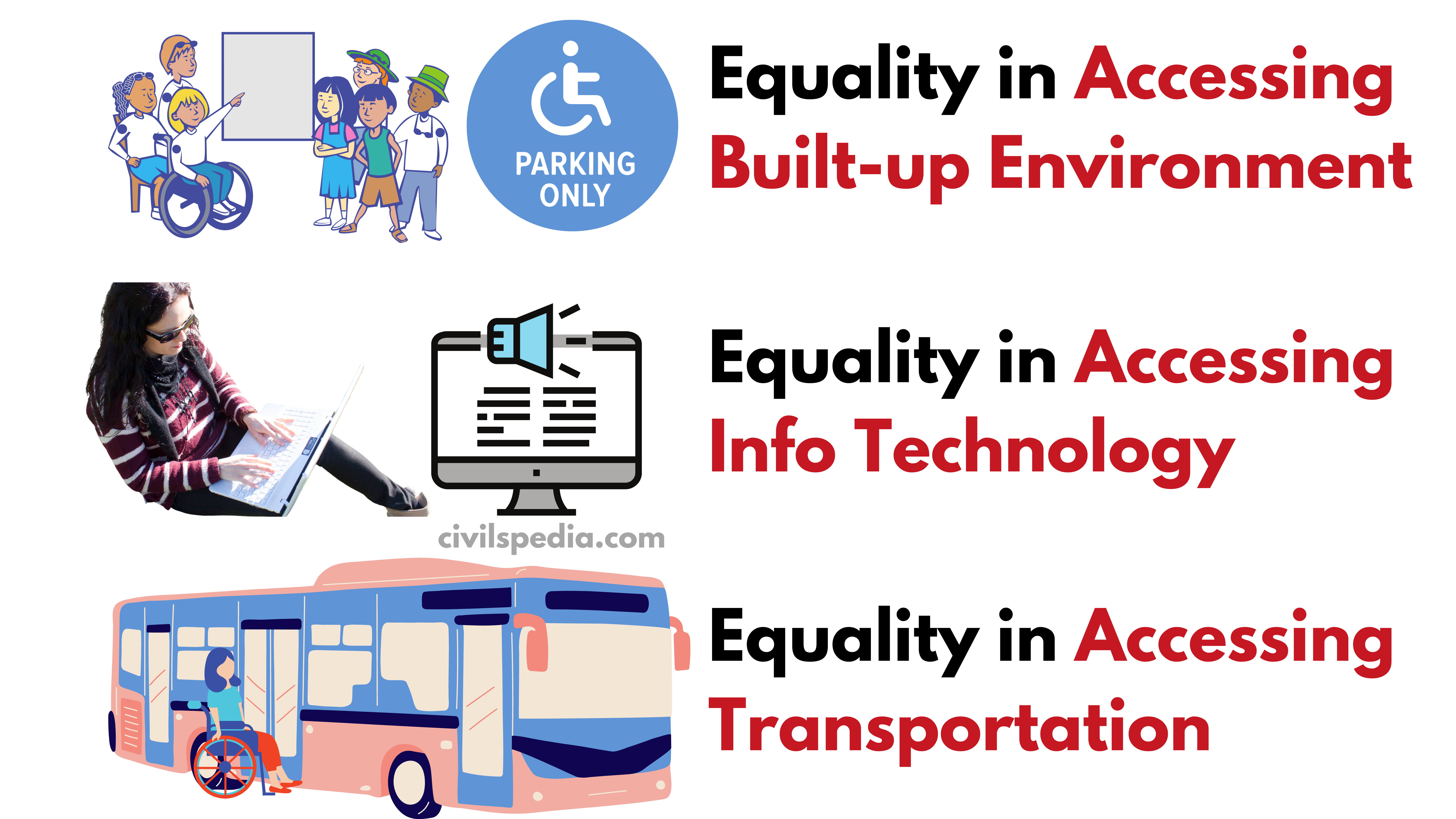
- The campaign targets three separate verticals for
- Equality in Accessing built-up environment (i.e. Disable friendly buildings)
- Equality in Accessing Information and Communication
- Equality in Accessing Transportation
Mental Healthcare Act, 2017
- The act defines “mental illness” in line with the UN Convention on Rights of Person with Disability.
- The right to confidentiality has been given to persons with mental illness.
- Central Mental Health Authority and State Mental Health Authority has been set up to register psychologists, mental health nurses etc.
- Suicide has been decriminalised (IPC Section 309) & presumed to be suffering from mental illness.
- It has prohibited electro-convulsive therapy without the use of muscle relaxants and anaesthesia.
