Table of Contents
Eutrophication and Algal Bloom
This article deals with ‘Eutrophication and Algal Bloom – UPSC.’ This is part of our series on ‘Environment’ which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles on Science and technology, you can click here
What is Eutrophication?
- The syndrome, in response to the addition of artificial or natural substances such as nitrates and phosphates through fertilizers, sewage, etc., fertilizes the aquatic ecosystem, causing algal bloom, which ultimately results in the death of aquatic plants and animals.
- It is primarily caused by the leaching of phosphates or nitrates containing fertilizers from agricultural lands to lakes or rivers.
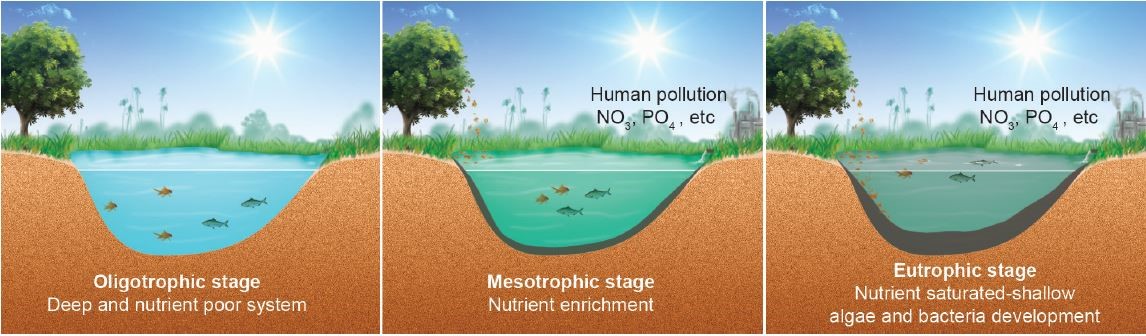
Algal Bloom
- The sudden growth of algae, especially in shallow water bodies, which causes the blocking of sunlight, is known as an algal bloom.
- Algal blooms increase the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) as they produce toxins causing anoxic conditions and death of the lakes.
- But sometimes, algal and phytoplankton blooms are helpful because they form the base of the food chain providing food to marine organisms.
Causes of Algal Bloom
- Nitrates and phosphorus fertilization due to excessive use of fertilizers in the agriculture
- Excessive dumping of biological waste in the water bodies
- Direct sewage disposal in the water bodies
- Disposal of industrial waste in the water bodies
- Aquaculture (i.e. technique of growing fish in an artificial atmosphere as it involves a direct application of nutrients)
- Natural events such as floods which take excessive nutrients due to enhanced weathering and erosion
Solutions
- Reducing the use of fertilizers by using Nutrient Management Policy
- Switching to composting in which organic matter is converted to manure. The nutrients present in the compost are deficient in nitrates and phosphates because the essential elements are broken down, thus stopping the cycle of eutrophication.
- Precision agriculture, i.e. the use of information communication technology in crop and farm management to provide agro-inputs according to the specific requirement of the different parts of the farm.
- Strengthening the laws and regulations for the point and non-point sources of water pollution.
- Construction of riparian buffers and restoration of wetlands as the riparian buffer acts as a transition water-body or wetland between surface runoff and main water body.
Effects of Eutrophication and Algal Bloom
1. Changes in ecosystem
- The waterbody is eventually reduced to a marsh.
2. Decreased biodiversity
- It results in the death of flora and fauna.
3. New species invasion
- It may make the ecosystem competitive by transforming the normal limiting nutrient to an abundant level. It causes shifting in the species composition.
4. Toxicity
- Neuro or hepatotoxic released by some algal blooms
- Loss of corals
- Colour smell & water treatment problems
Mitigation
- Minimize non-point pollution, especially from agriculture.
- Treat industrial effluents before dumping.
- Treatment of sewage before dumping.
Case Study: Sea of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara faces the issue of sea snot. Sea Snot is characterized by a large amount of algae formed due to nutrients from untreated waste (from Istanbul), and agricultural runoff is drained straight into the sea. It has also resulted in mass deaths among the fish population
Side Topic: Dead Zones
Dead zones or Hypoxic zones are regions in the ocean or lakes where the oxygen level falls to such a low level that marine life can’t even survive in them.
Causes
There are two leading causes
- Rising sea temperatures: Temperature rise reduces the solubility of oxygen in the water.
- Eutrophication: The algal bloom results in the reduction of oxygen levels.
Note – Dead zones are reversible if their causes are reduced or eliminated.
Impact
- Impact on Global Warming: It triggers the release of chemicals like nitrous oxide, which have high GHG potential.
- Impact on Corals: The low levels of oxygen in the aquatic ecosystem results in the death of coral reefs.
- Impact on food security: It results in the loss of marine food resources.
