Last Updated: May 2023 (Indian Air Force)
Table of Contents
Indian Air Force
This article deals with the ‘Indian Air Force.’ This is part of our series on ‘Science and Technology’ which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Airforce
- Indian Airforce with 1.27 active personnel defends the Indian airspace.
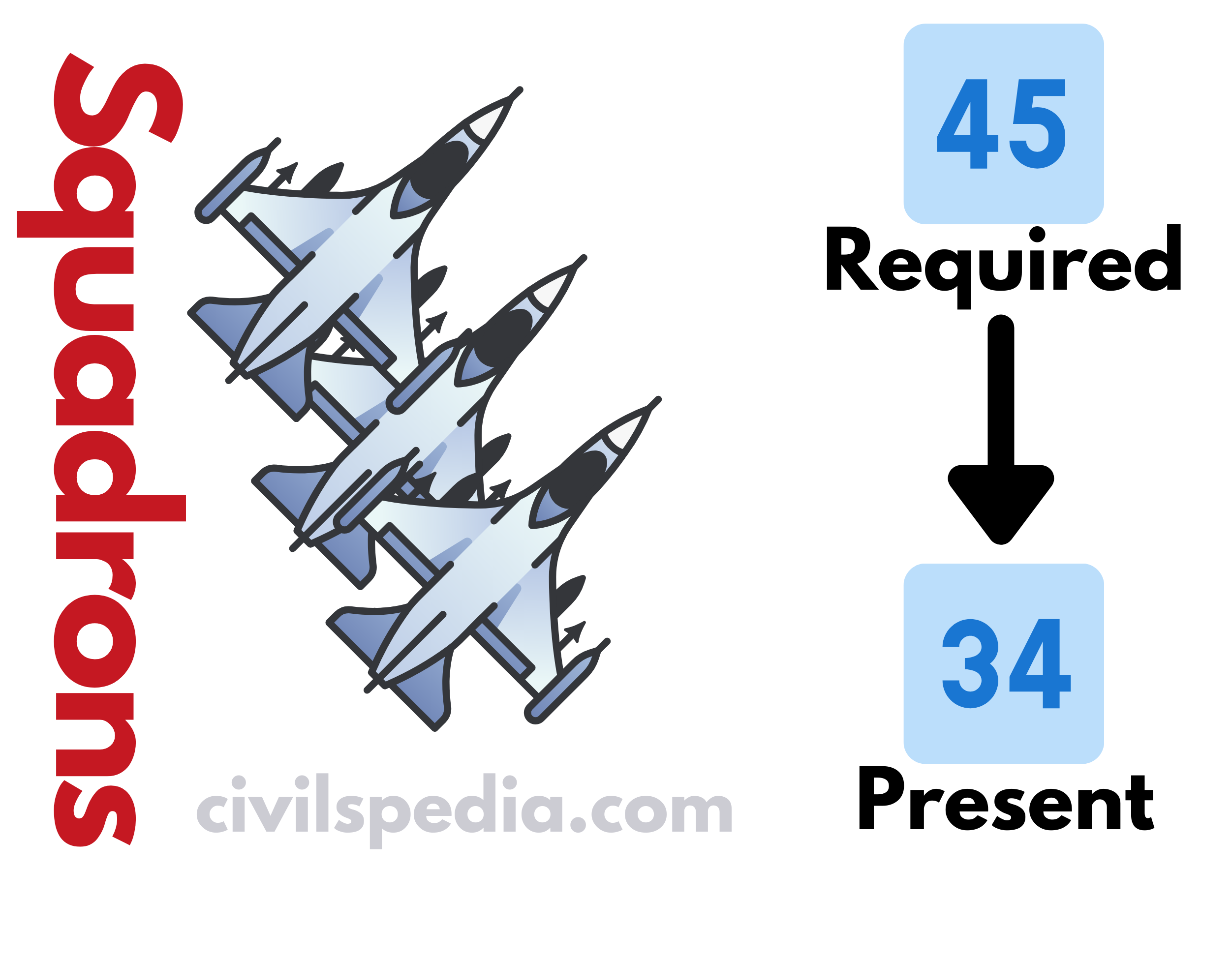
- At present, the Indian Airforce (IAF) has 34 fighter squadrons. But to be effective against China and Pakistan, India needs at-least 45 squadrons.
Aircrafts of India
Combat Aircraft
| Dassault Rafale | 26 |
| Sukhoi Su-30 MKI | 272 |
| HAL Tejas | 22 |
| Mig-29 | 66 |
| Mirage 2000 | 49 |
| Jaguar | 120 |
| MiG-21 Bison | 107 (retire in 2025) |
Reconnaissance Aircraft
| Boeing 707 | 1 |
| Global 5000 | 2 |
| Gulfstream | 2 |
Tanker Aircraft
Il-78 : 6
Transport Aircraft
| Ilyushin IL-76 | 17 |
| Boeing C-17 Globemaster | 11 |
| C-130J Super Hercules | 12 |
| Antonov A-32 | 104 |
| Dornier 228 | 50 |
Helicopters
| HAL Light Combat Helicopter | Attack Helicopters |
| HAL Rudra | Armed |
| HAL Dhruv | Utility |
| Boeing Apache | Attack Helicopters |
| Mi-24 | Attack Helicopters |
| Chinook | Heavy Transport |
UAVs
| Harop | Loitering Munition |
| Heron | Surveillance |
| Searcher | Surveillance |
| DRDO Lakshya | Target Drone |
Side Topic: Generations of Aircrafts
| Period | Features | Examples | |
| 1st Gen Fighters | 1940s-50s | – Turbojet Engines | Mig-15 and Mystere-IV |
| 2nd Gen Fighters | 1950s-60s | – Delta Wings – Guided and Beyond Visual Range Missiles | Mig-21, Su-7 and F-104 |
| 3rd Gen Fighters | 1960s-70s | – Improved Radars, Missiles and Avionics | Mig-25 and F-4 Phantom |
| 4th Gen Fighters | 1970s-90s | – Fly by wire controls – Multi-role capabilities | Mirage-2000, Mig-29, Su-27, F-16 Fighting Falcon |
| 4.5th Gen Fighters | 1990s onwards | – Some stealth features – Advanced avionics | Su-30 MKI, Rafale, Eurofighter Typhoon, F-16 Desert Falcon |
| 5th Gen Fighters | In development | – Advanced Stealth – Highly sophisticated avionics – Thrust Vectoring – Supersonic cruise without the use of afterburners | F/A-22 Raptor, F-35 and Sukhoi T-50 |
Detail of Combat Aircrafts in news
1. Rafale & MMRCA
Rafale is 4.5 generation Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft (MMRCA) aircraft made by Dassault Aviation of France.

Main features of Rafale
- 4.5 generation Multirole combat aircraft, i.e. can be used for ground support, in-depth strike, and anti-ship strike.
- Rafale is capable of carrying nuclear weapons.
- Equipped with precision air to air and air to surface missiles.
- Range: 3,700 Km
- Max Speed: 1,389 Km/hr
- Load Carrying Capacity: 9,500 Kg
Rafale Acquisition: Chronology of Events
| 2007 | Tender for MMRCA was invited, and various bidders such as Eurofighter (of British Aerospace), F-16 (of Lockheed Martin), MiG-35 (of Russia) and Rafale (of Dassault (France)) applied for the bids. |
| 2011 | Rafale was shortlisted. It was decided that India would buy 126 Rafale. In this, 18 were to be purchased in fly-away condition, and the rest 108 were to be made by HAL under Transfer of Technology. |
| 2015 | But the issue was Dassault was not prepared to guarantee the performance of aircraft manufactured in India. The plan was changed, and the government decided to buy 36 Rafale in the ready-to-fly condition given to India in two years. |
| 2018-19 | The case went to Supreme Court to increase the cost per aircraft and give offset contract to Reliance instead of HAL. |
| 2020 | Delivery of Rafales started. The first batch of 5 aircraft was delivered to India. |
Issues
- The stealth system of Rafale is outdated compared to other competitors in the same class.
- Rafale doesn’t have STOVL (Short take-off and vertical landing) capability, present in other competitors.
- Brazilian Airforce was earlier interested in buying Rafale but later changed to Swedish Gripen jet.
2. Tejas / HAL’s LCA
- HAL Tejas or Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) is a 4th Generation fighter aircraft made by India.
- It is manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautical Limited (HAL).
- The program to build indigenous Indian combat aircraft started way back in the 1980s. After long delays, the first Tejas was delivered to the Indian Airforce in 2015. In 2021, the Indian government announced to procure 83 Tejas.
- Tejas is going to replace India’s ageing MiG 21 aircraft.
- Features of HAL Tejas
- It has ~60% indigenous content.
- Maximum Speed: 1,350 Kmph.
- Its radius of action is 400 Km without refuelling.
- It can carry a weight of up to 12 tonnes.
- Delta wing configuration
- Numerous integrated technologies like Fly by wire flight control system, advanced digital cockpit, digital avionics, advanced composite material structure etc.
- It is equipped with operational capabilities like Beyond Visual Range Missile and Air to Air Refueling.
- It has STOBAR (Short Takeoff But Arrested Recovery) capability.

Side Topic: (LCA) Kaveri
- Kaveri is the name of Tejas’s engine that was to be used, but India couldn’t make it on time to be used in the plane.
- It would have been India’s first indigenous gas turbine engine.
3. Sukhoi T-50 (Fifth Generation)
Sukhoi T-50 is an Indo-Russian collaborative project to make 5th generation fighter aircraft. It is a joint venture of Russia’s Sukhoi and India’s HAL.
It will have the following characteristics
- Stealth features like specially designed airframes, engines intakes, and radar absorbing material
- Thrust vectoring nozzles
- One or two seated
- 30 mm cannon
- Eight weapon internal points and eight external points.
- Max speed of 2 Mach.
- Fuel capacity of 10,300 kg.
But in 2018, India has conveyed its unwillingness to Russia to go ahead with this project due to the high costs involved.

Detail of Transport Aircrafts in news
1. C-17 Globemaster
- It is a large military transport aircraft of US origin developed by Boeing.
- Indian Airforce has 11 Globemasters.
- It can be used for
- Transporting troops.
- Maintaining supplies and carrying equipment to small airfields in remote and harsh terrain (E.g., Ladakh)
- Its main features include
- Ability to take off from very high altitudes
- Land on paved as well as unpaved airfields during day and night.

Helicopters
Important Made in India Helicopters
1. Dhruv (ALH)

Dhruv features of this helicopter
- Dhruv was designed for the military as well as civilian purposes.
- It is manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- It can play multiple roles: logistics, rescue and attack for Army, Navy, Airforce and Coast Guard.
History
- The project was first announced in 1984 & was designed in assistance with MBB of Germany.
- First flew in 1992 but developments prolonged due to budget restrictions and various restrictions placed on India after Pokhran 2 in 1998.
- Entered into service in 2002.
- First exported to Nepal & Israel & is on order by several other countries.
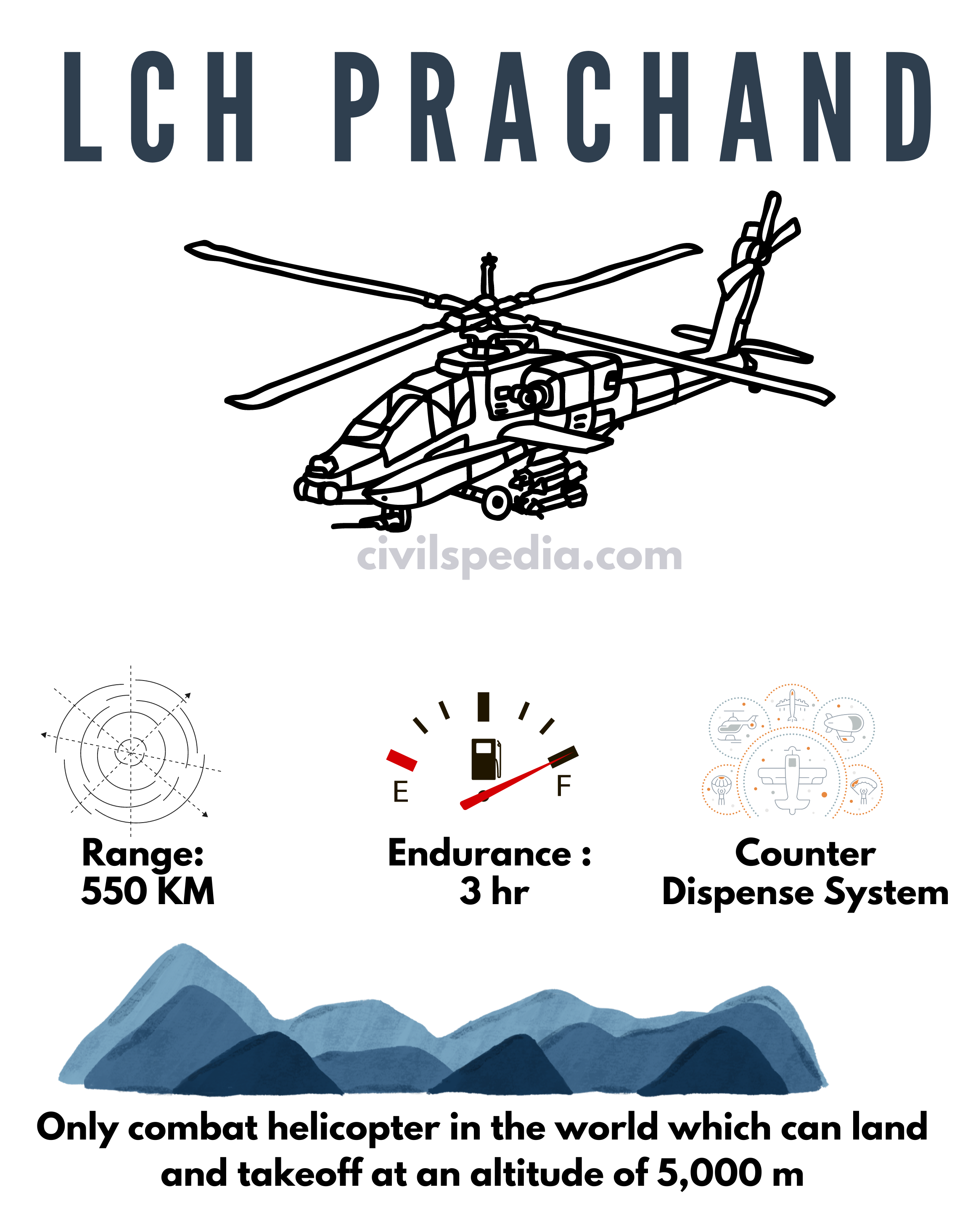
2. LCH Prachand
- LCH Prachand is indigenously developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd.
- It is a multi-role combat helicopter. With this, India has become the seventh country to make attack helicopters.
- Features of LCH Prachand
- Range: 550 Km
- Endurance: 3 hours
- Maximum height at which it can fly: 6.5 Km
- It is the only combat helicopter in the world which can land and takeoff at an altitude of 5,000 m.
- Equipped with a ‘COUNTERMEASURE DISPENSE SYSTEM‘ to protect it from enemy radars and missiles.
Foreign Helicopters bought by India
1. Chinook

- Chinooks are the heavy-lift helicopters used by the US Army.
- India decided to buy 15 Chinook helicopters from the USA in 2016, and the first batch was delivered in 2019.
- Features of Chinook Helicopters
- Twin Engine with Tandem Rotor.
- Can carry up to 35 troops or 24 stretchers with 3 attendants or 10,500 kg payload.
- Advanced Avionics.
- Advanced M240 Machine Gun
2. Apache
- Apache is USA’s most advanced ‘attack helicopter’.
- India has bought 22 Apache Helicopters.
- Features of Apache Helicopters
- Twin Turboshaft Engines
- Armed with missiles like Hellfire, Spike and Stinger missiles
- Armed with advanced M230 Chain Guns
- Night vision systems
- Advanced avionics
3. Mi-17
- Mi-17 is a Russian origin transport helicopter manufactured by Kazan Helicopters.
- It is one of the most advanced transport helicopters equipped with advanced features such as
- Advanced self-defence system equipped with 23 mm cannon and heat-seeking missiles
- Twin-engine single rotor
- Highly sophisticated navigation and avionics system
- Maximum speed of 250 km/hr
- Range of 675 Km
- Payload capacity of 4,000Kg
- Capacity to transport up to 36 troops.
- It is used for the transportation of VVIPs, including PM and army chiefs.
