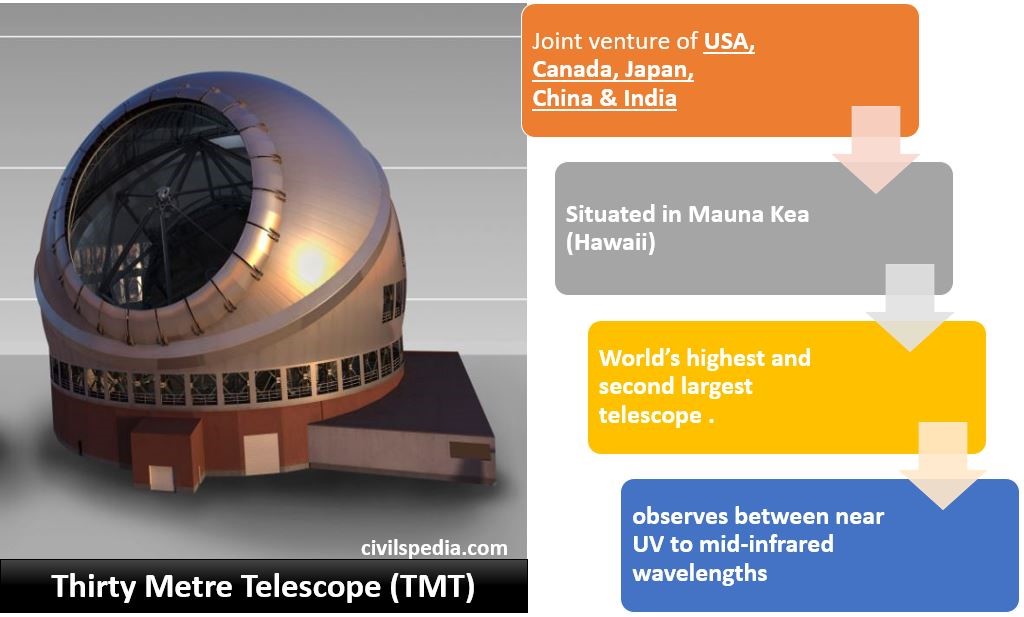
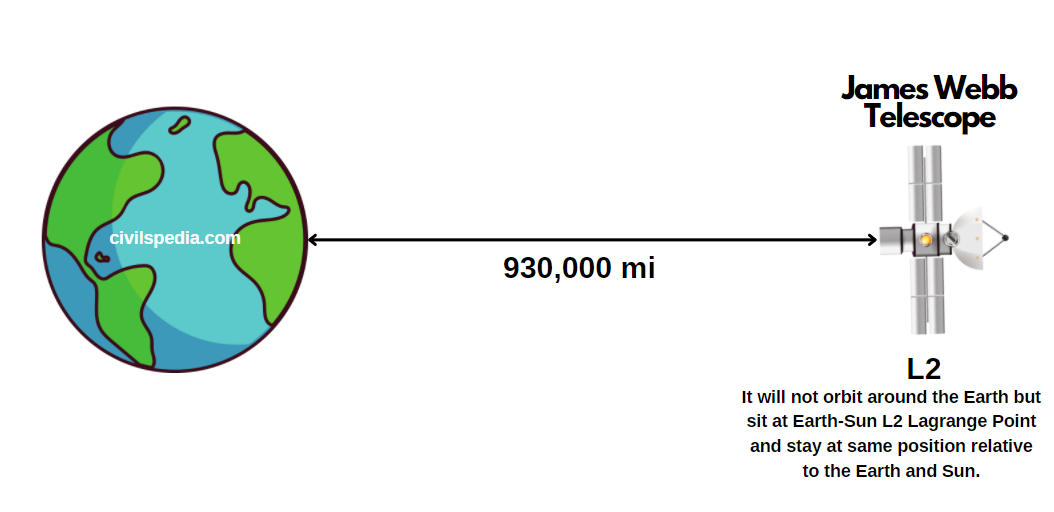
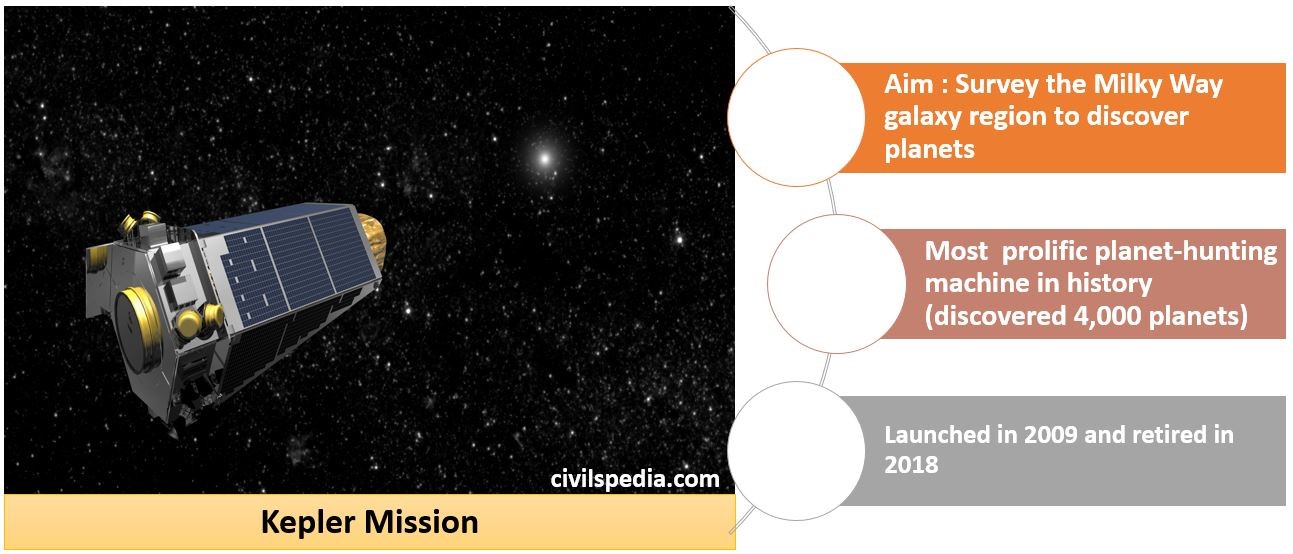
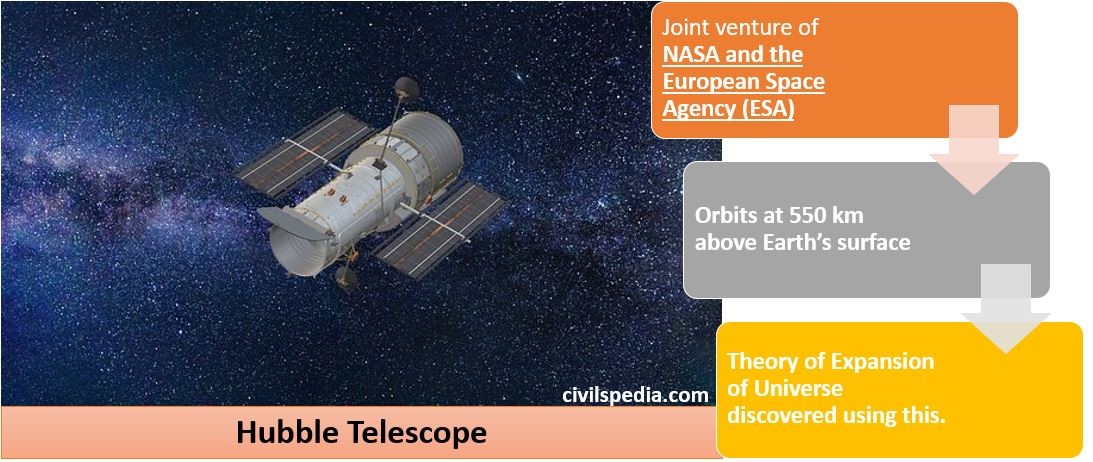
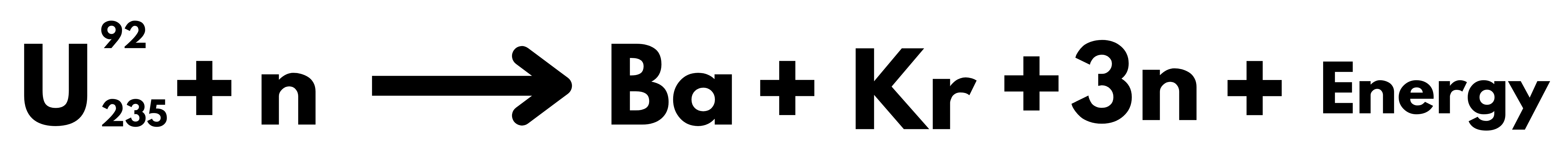Nuclear Energy in India
This article deals with ‘Nuclear Energy in India.’ This is part of our series on ‘Science and Technology’ which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here
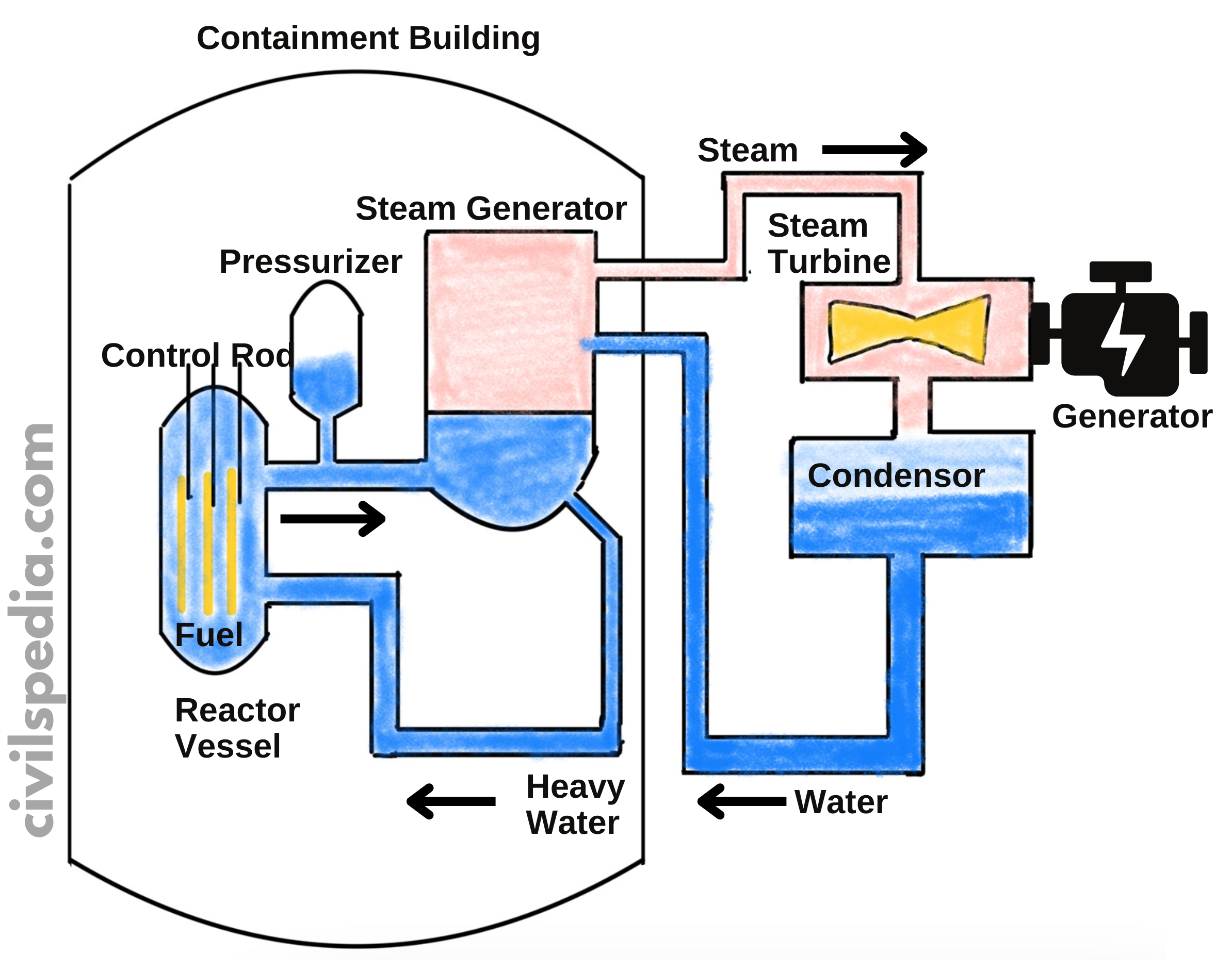
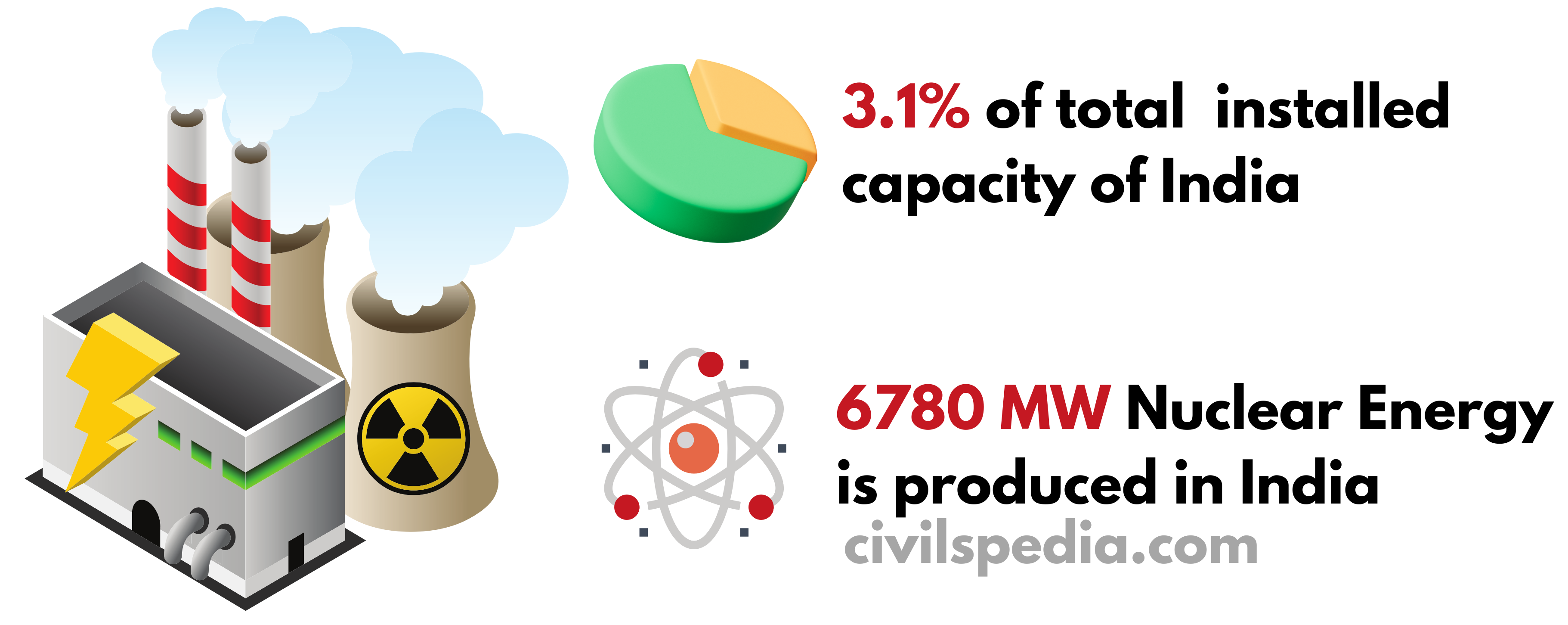
Installed capacity of Nuclear Power in India
India has been actively pursuing nuclear power as a part of its energy mix to meet its growing electricity demands and reduce its dependence on fossil fuels.
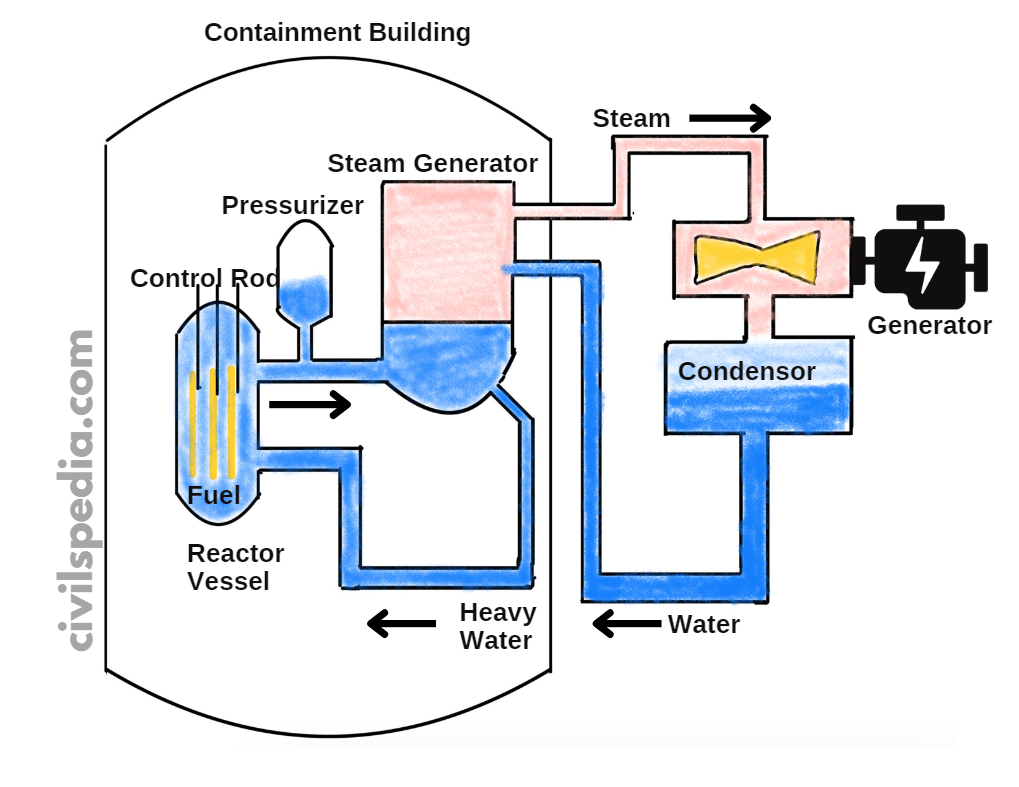
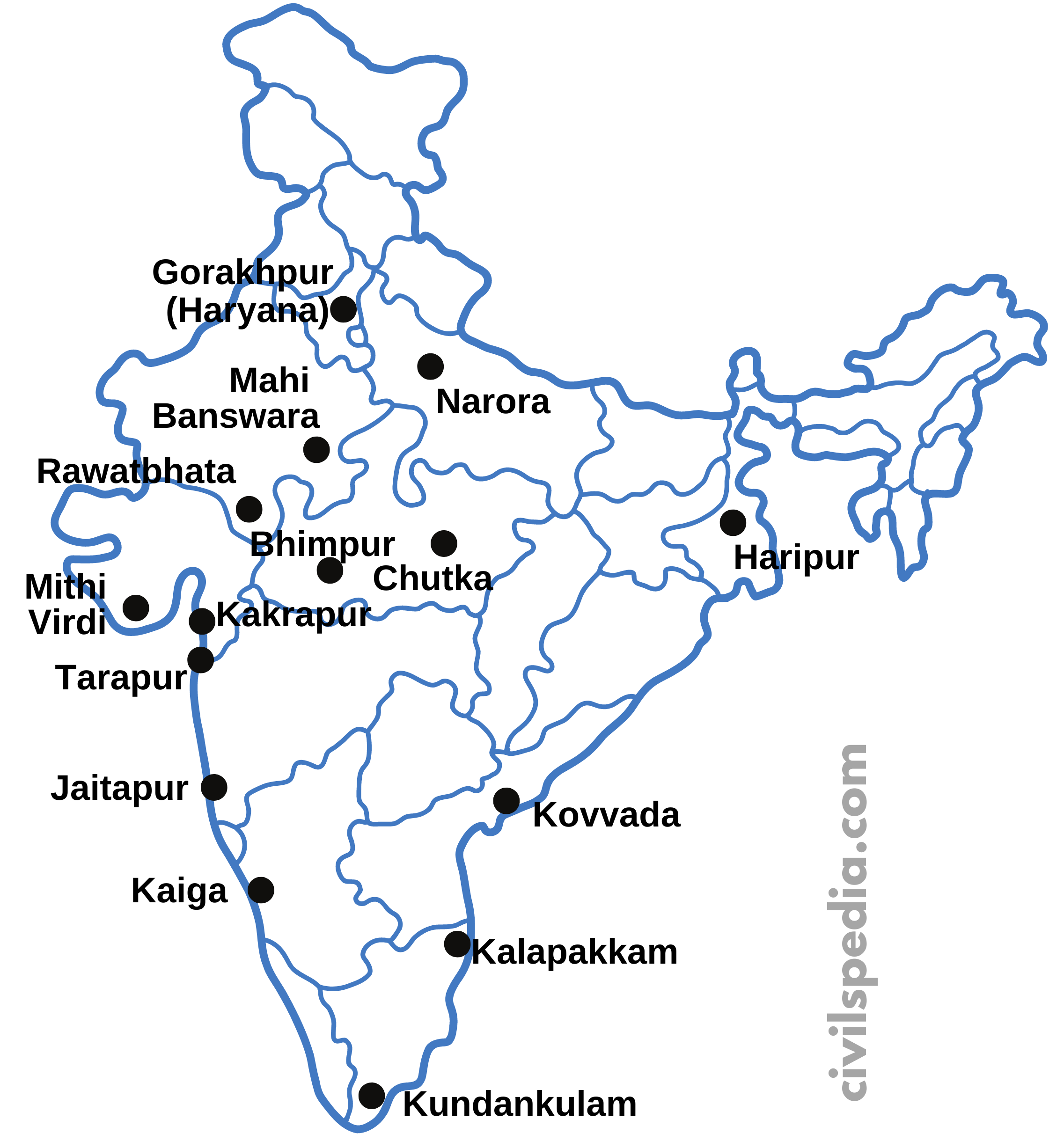
Nuclear Plants in India
Problems with India’s Nuclear Power
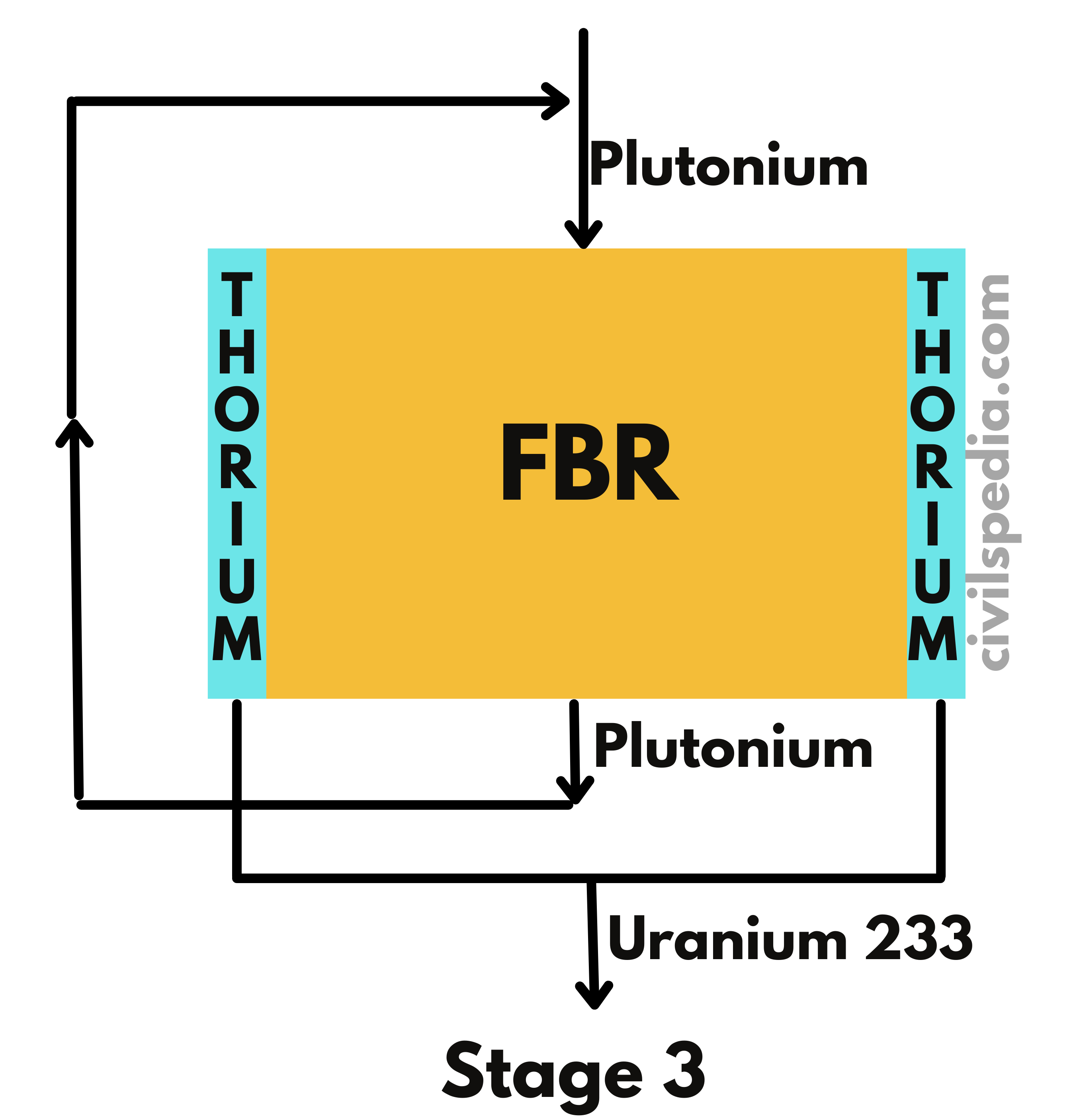
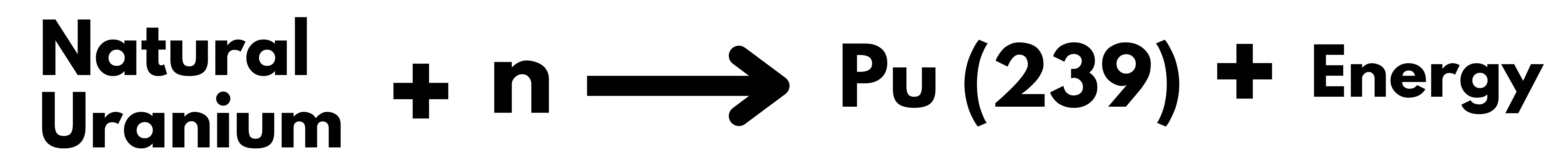
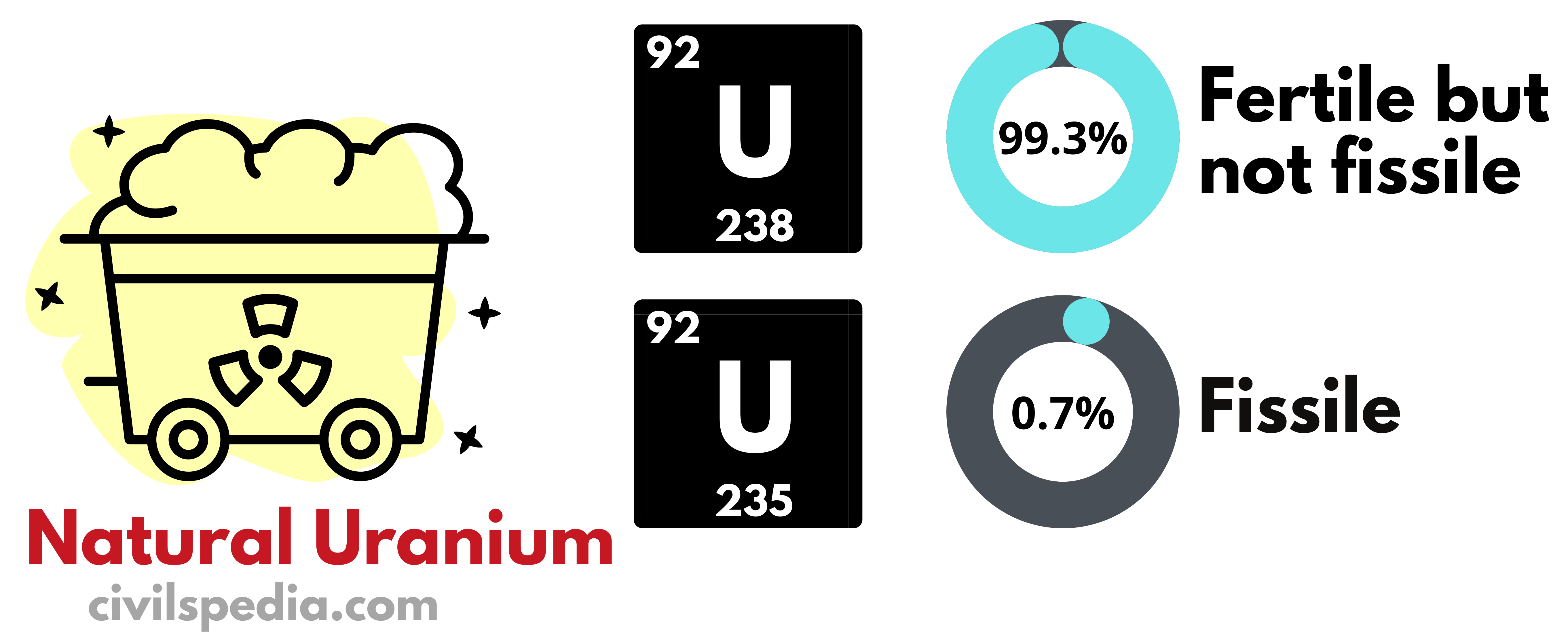
India’s domestic Uranium Reserve can support only 100 GW of energy.
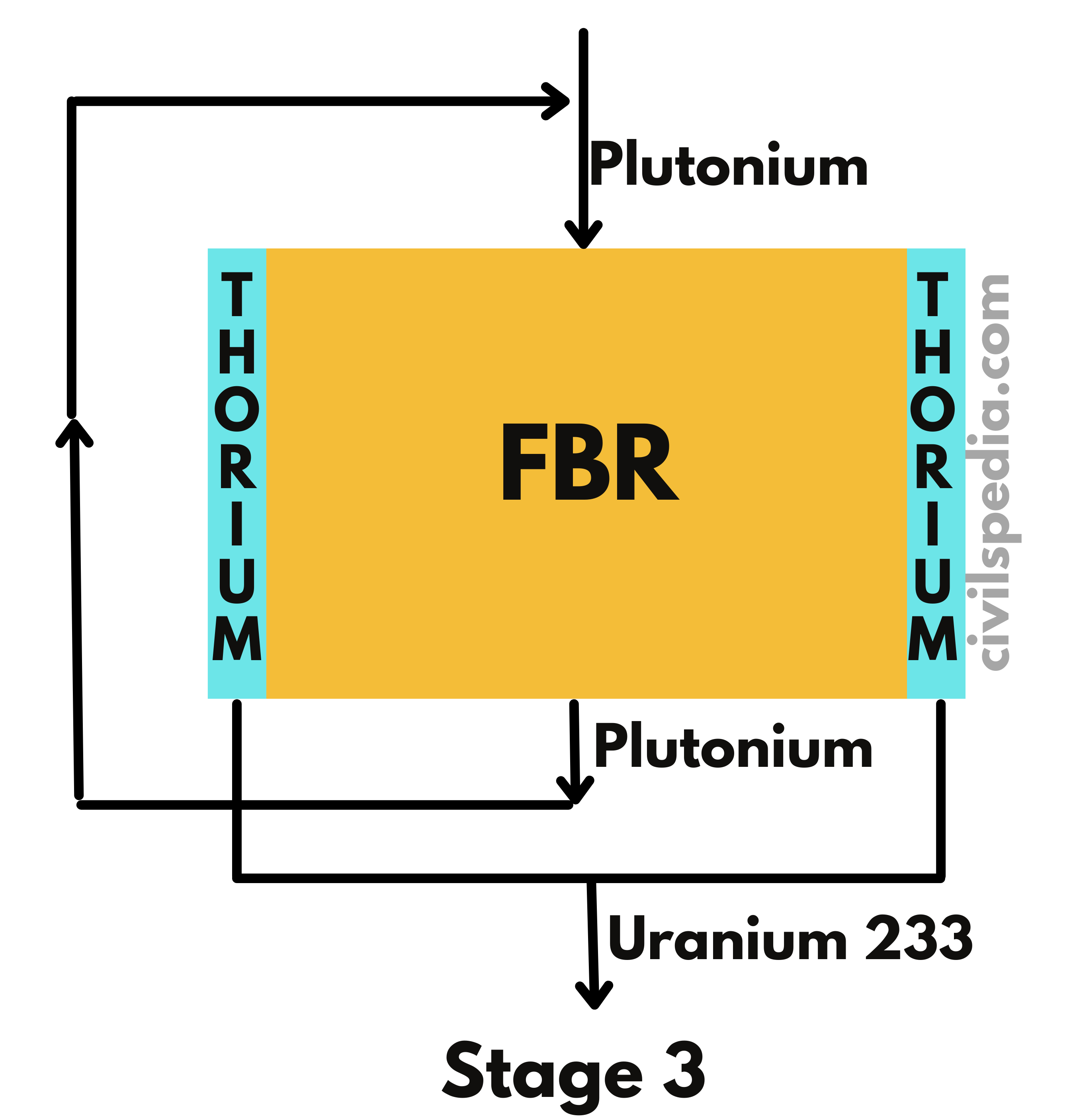
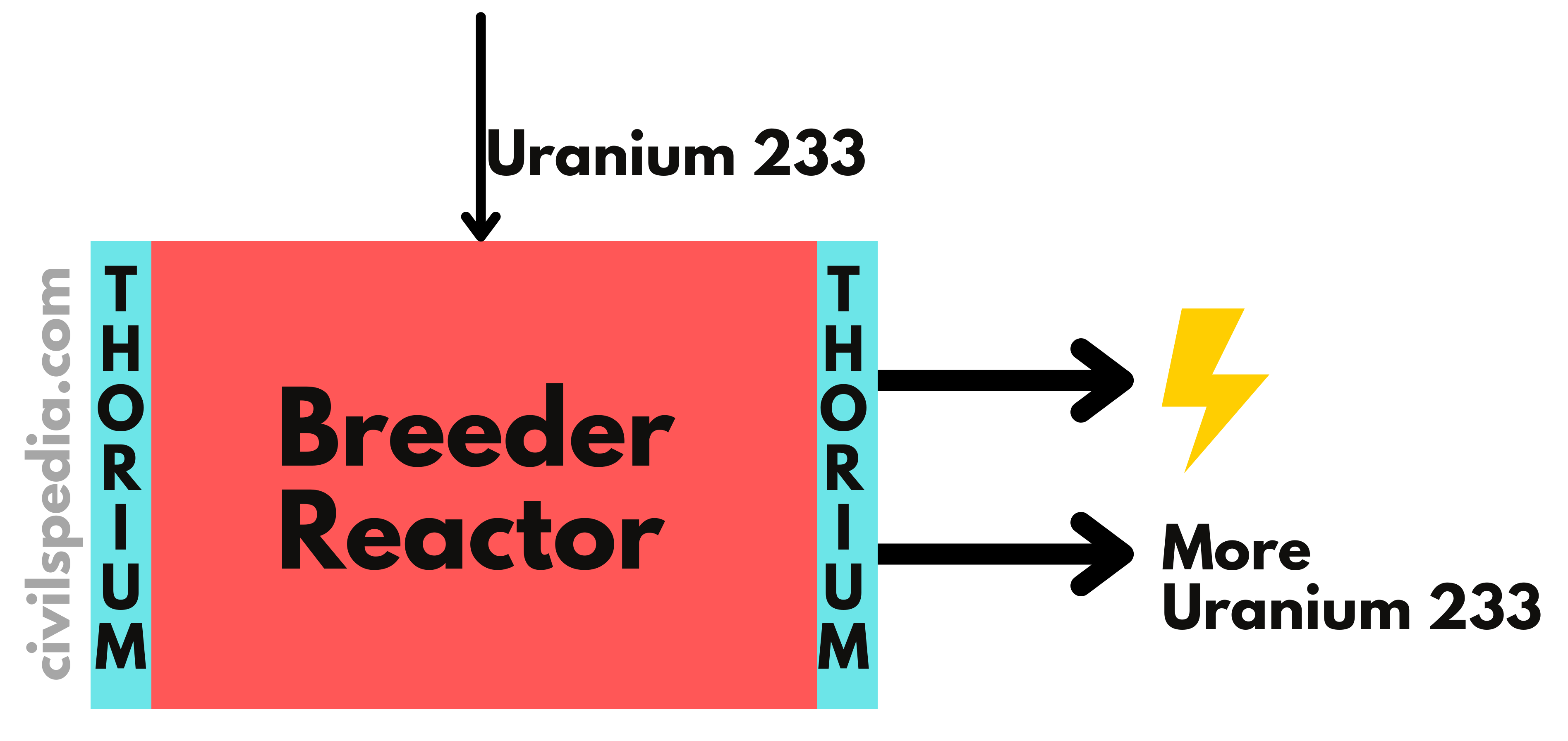
- Our future depends upon the development of the third stage of the Nuclear Program, without which it will remain dependent on imported Uranium, as it is the case with Oil currently.
High Cost
- Increased Cost due to New Safety Regulations: Due to new safety regulations following the Fukushima tragedy, nuclear reactors now cost substantially more per MW than thermal, solar, and wind plants. E.g., the Jaitapur plant (AREVA) is expected to cost 20 crore/ MW in comparison other sources cost 4 crore/ MW.
- Some argue that the Total costs of a Nuclear Lifecycle, which involves the mining of Uranium, transportation, handling of waste generated etc., is significantly more than the economic value generated during the lifetime of the functioning of the plant
Alternative Energy Options
- Experts opine that India should focus on renewable energy like solar and wind, which are considered safer, environmentally friendly, and have rapidly declining costs. Investing in renewables can also help address energy access issues in rural areas and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Public Opposition and Social Concerns
- Nuclear power projects often face opposition from local communities and environmental groups due to concerns about radiation risks, potential accidents, and the long-term impact on public health and the environment.
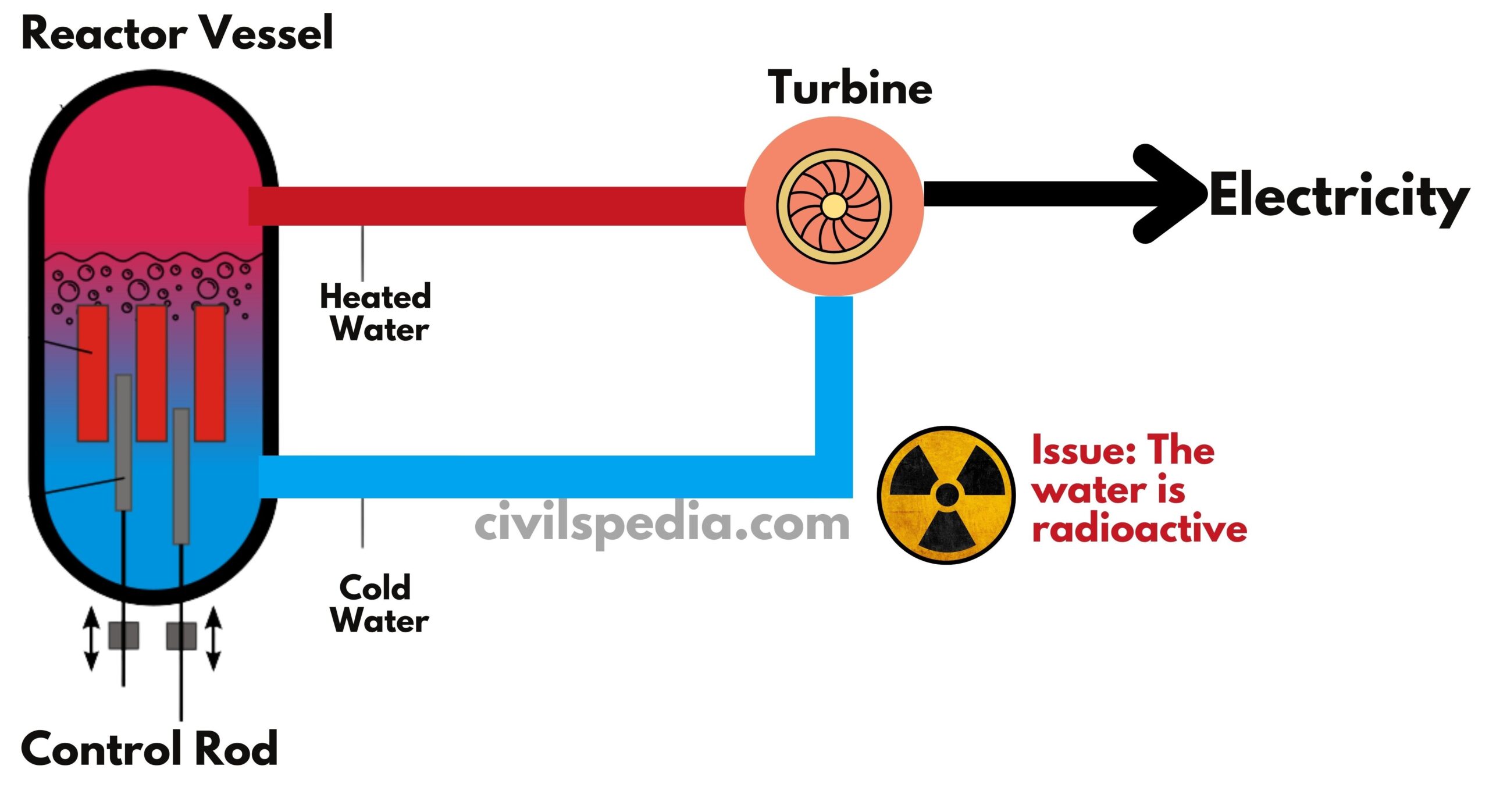
Current Nuclear reactors consume a significant amount of water
- Hence most of upcoming plants will be set up near sea coasts. It will put pressure on the coastline & Western Ghats.
Long Gestation Period
- There are long gestation periods which increase the costs of the plant significantly.
Non-proliferation and international obligations
- India hasn’t signed the NPT and has faced scrutiny regarding its nuclear weapons program.
Target of Terrorists
- Nuclear installations will be the favourite targets of terrorists, which can cause irreversible damage to people.
Should Nuclear Energy be used?
Strong arguments which justify the use of nuclear energy are
- No GHG are emitted in Nuclear Power generation, a significant contributor to climate change. Hence, it helps to fight Global Warming.
- Nuclear Energy is helpful in achieving Paris Pledge. India has also pledged to generate 40% of its energy from Non-fossil sources.
- Energy security and independence: Nuclear energy reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security for countries.
- Job creation and economic benefits: Nuclear power plants require skilled workers for operation, maintenance, and construction, thus creating employment opportunities.
- Increases the image of the country as a technologically advanced nation
- Non-fluctuating sources of renewable energy as Solar and wind energy, depend on sunshine, wind speed etc. On the other hand, Nuclear power plants provide a continuous and reliable source of electricity.
- Baseload power and grid stability: Nuclear power provides a stable and consistent baseload power supply, essential for maintaining grid stability. It can complement intermittent renewable energy sources,
- It generates very limited waste in quantity (although far more hazardous in quality).
Arguments against use of Nuclear Energy
While there are strong arguments in favour of nuclear energy, there are also valid concerns regarding high cost, waste disposal, potential accidents, the proliferation of nuclear weapons, and the high cost of building and decommissioning nuclear plants.
- Costs of power from new nuclear reactors are increasing significantly post Fukushima Disaster. New PHWR power costs between Rs. 6.2-6.5/Unit
- In case of any nuclear leakage & accident in nuclear power plants, the damage is immense & incurable.
- Nuclear projects face opposition from local communities and environmental groups due to land acquisition issues, the need for large water reservoirs for the reactors, & concerns about a possible tsunami scenario
- Major Nuclear Companies like Toshiba-owned Westinghouse, Areva etc., are on the verge of Bankruptcy, pointing towards the fact that Nuclear Energy has become unviable.
- Investing in Solar and Wind Energy is a better option. The cost of Solar Energy has decreased to around ₹4.5 / kWh compared to ₹6.5 kWh of Nuclear Energy.
- Uranium contamination of groundwater due to mining. E.g.,: in Rajasthan