Last Updated: June 2023 (Reproductive Technologies)
Table of Contents
Reproductive Technologies
This article deals with ‘Reproductive Technologies – UPSC.’ This is part of our series on ‘Science and Technology’, which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Reproductive Technologies
1. In-vitro Fertilization (IVF)
- IVF is the process of fertilization of an egg and sperm outside the mother’s body. The baby thus produced is known as Test Tube Baby.
- In this process, a child is conceived outside the women’s body in vitro (i.e. lab). Eggs removed from the mother’s ovary are incubated with the sperm from the father. Now, they are allowed to divide until the Blastula stage (64-128 cell structure), which usually takes 3-4 days, which is then transferred to the mother’s or a surrogate’s uterus to develop normally.
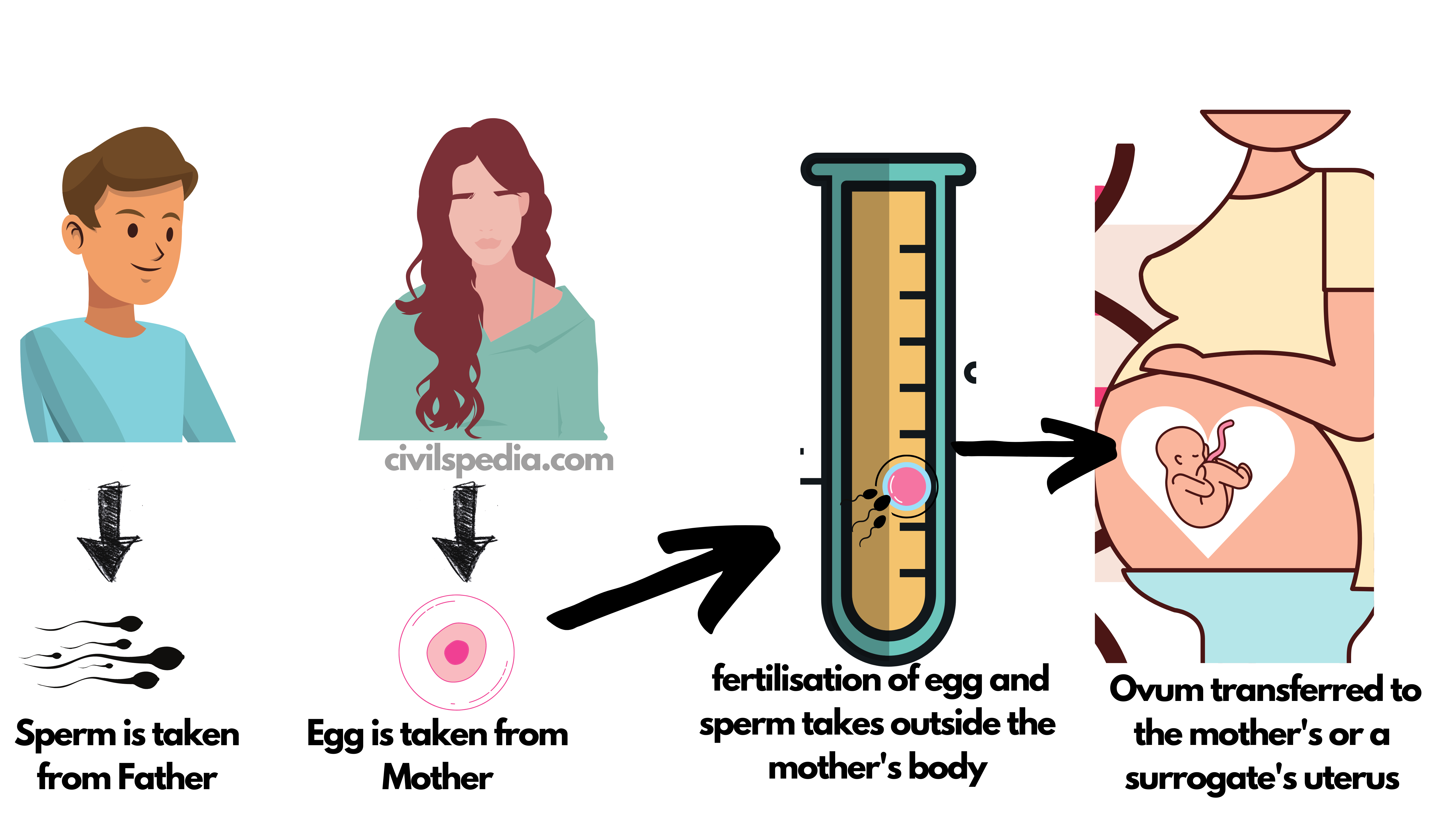
- This technique was discovered by Dr Edwards and Dr Steptoe in the UK. They successfully carried out the birth of the world’s first test-tube baby “Louis Joy Brown” whose mother had a blockage in the Fallopian tube. The second successful test-tube baby occurred in India, named Durga after 67 days of Louis’s birth,
- IVF is used in the following cases:-
- Defect in Fallopian Tube of women.
- A low number of sperms in men.
- Infrequent or absent ovulation.
- Endometriosis
- Age-related infertility.
- Hence, it helps infertile couples to have a baby of their own (with their eggs and sperm). Without using a donor egg or donor sperm, the DNA of the zygote will be of the intended parents only.
Issues with IVF / Test Tube Babies
- Multiple Births: During the process, drugs are induced to the patient’s ovaries to grow several mature eggs rather than a single one that develops each month. If more than one egg is fertilized and transferred to a uterus, chances of success increase. But this also increases the chance of twin births.
- Ovaries Hyper Stimulation Syndrome: Stimulations done to produce more than one egg cell can cause side effects like swollen and painful ovaries.
- Birth Defects: Test Tube Bodies have relatively higher risks of birth defects than naturally conceived babies.
- There is a danger of a mix-up of the baby in the laboratory processes leading to future legal suits.
2. Embryo Transfer
- In this technique, the fertilized egg or young embryo is transferred from donor mother to recipient mother or from test tube to the recipient mother. The best transfer stage is the 2 – 4 cell stage.
3. Artificial Wombs
- This technique is used in the final stages of multiple pregnancies as the foetus becomes cramped by transferring the foetus to the artificial womb. The artificial womb is a tank filled with amniotic fluid and a machine that pumps nutrients and oxygen into the baby’s blood.
4. Artificial Insemination
- It is the introduction of semen into a female’s reproductive tract.
- Semen collected from a male with desirable hereditary features can be frozen & transported long distances to fertilize females.
- It is used for those females who wish to conceive when normal conception is not possible.
5. Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT )
- In GIFT, egg and sperms are mixed and injected into Fallopian tubes, where the Fertilization takes place as it does naturally.
- In contrast to in-vitro, this is an in-vivo technique.
Application of Reproductive Technologies
- It helps in achieving enhanced fertility.
- It helps maintain future fertility (Eg: before undergoing chemo or radiotherapy).
- It can be used to restore fertility by the involvement of the couple.
- It helps restore fertility by the involvement of a third party in premature loss of ovarian function.
- Minimize severe maternal and foetal risks.
Assisted Reproductive Technology (Regulation) Act, 2021
The act to regulate ART or Assisted Reproductive Technologies was introduced in the Parliament in 2020 to standardise protocols of the growing fertility industry and provide for the regulation of ART services in the country.
Key provisions in the Act
1. Definition of ART: The Bill defines ART as all the techniques to obtain pregnancy using sperm and oocyte outside the human body and transferring the resulting embryo into a woman’s reproductive system.
2. Regulation of ART clinics and banks: Every ART clinic and bank must be registered under the National Registry of Banks and Clinics of India.
3. Rights of a child born through ART: Child born using ART will be considered biological child of commissioning parents and donor will have no rights over the child.
4. Written Consent: Clinic will have to take written consent from all the parties involved.
5. Offences and penalties: Offences mentioned under ART are
- Abandoning and exploitation children.
- Selling or buying gametes.
- Exploiting commissioning parents or donors.
- Transferring human embryos into animals.
Issues
- The act discriminates against the LGBTQ, same-sex couples and single parents. The act is entirely against Supreme Court’s Navtej Johal judgement.
- ART Act and Surrogacy Act doesn’t work in tandem with each other. Both the acts have set up multiple registration bodies while left some of the lacunae unaddressed.
