Last Updated: May 2023 (Telescopes)
Table of Contents
Telescopes
This article deals with ‘Telescopes‘. This is part of our series on ‘Science and Technology, which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Important Telescopes
Important Telescopes for the purpose of exam include
- 30 m Telescope ( Hawaii)
- National Large Solar Telescope ( Ladakh)
- Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA)
- MULTI-APPLICATION SOLAR TELESCOPE (MAST), Udaipur
- GROWTH India Telescope
It has to be noted that Light Pollution is a severe problem for Astronomers as artificial light from buildings, street lights, and malls makes it challenging to observe and study the stars in the sky. Hence, Telescopes are set up in remote regions (far away from the cities).
Terrestrial Telescopes
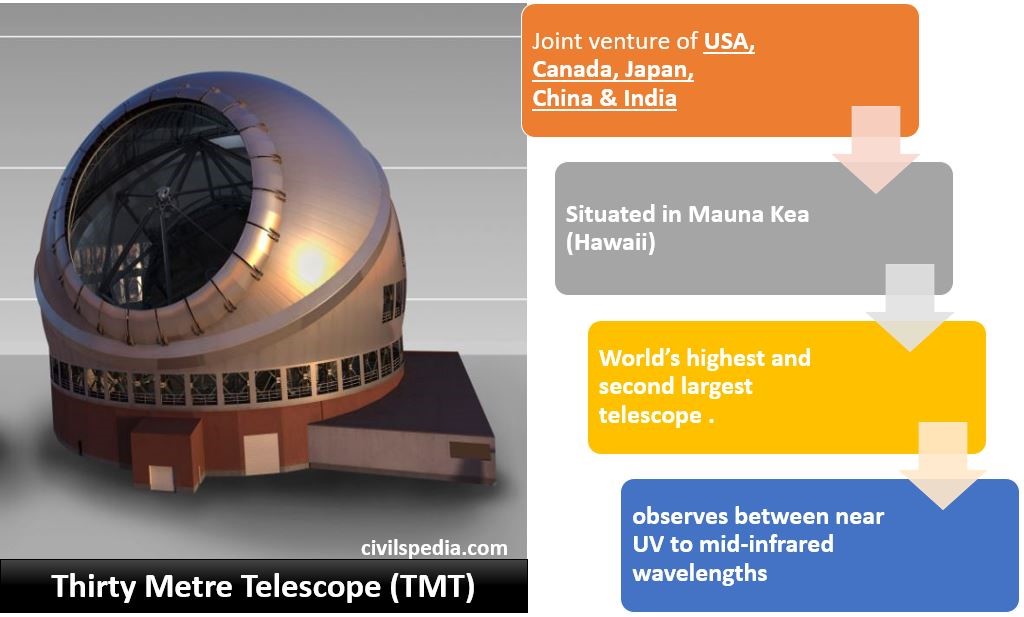
1. Thirty-Meter Telescope
- It is called Thirty Meter Telescope because its primary mirror is 30m wide.
- After the E-ELT (European Extremely Large Telescope), it is the world’s highest and second largest telescope.
- It is located at the Mauna Kea volcano summit in Hawaii (USA).
- It is the joint project of India, Japan, the US, China, and Canada with $1.5 billion.
- India has financed 10% of the cost and will get proportional time for use.
- It observes between near UV to mid-infrared wavelengths and corrects the blur caused by the atmosphere by its adaptive optics system.
Controversy associated with Thirty-Meter Telescope
Three controversies are related to this project:-
- Mauna Kea is considered sacred by the local Hawaiian people.
- It presents a danger to the habitat of the Rare Weiku Bug found there.
- The land was given for use essentially rent-free.
2. National Large Solar Telescope
- NLST is being built by the Dept. of Science of Technology in Ladakh.
- It will be the world’s largest solar telescope.
- It can work both day and night.
- It will fill the longitude gap between Japan and Europe. Currently, there is no telescope between these regions.
- It will help in understanding sunspots. Thus it will help protect satellite communication as sunspots pose a threat to their working.
Why is Ladakh chosen?
- Placement at a higher altitude will fundamentally enhance the NLST capacity.
- Prolong region of sunshine, clear sky (high visibility).
- Low concentration of aerosol and dust particles in the atmosphere.
- Lower wind speed.

3. Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA)
- ALMA is the joint venture of the USA, Japan, Canada, Taiwan, South Korea, and Chile.
- It is at 5000 meters. This place is most suitable as it is free from background noise, and the atmosphere is clean, dry and cool.
- It consists of 66 high-precision antennas.
- Aim: Explain very old and important astronomical anonymities and search for the origin of the Cosmos.
- ALMA is the most powerful telescope used for observing the cold universe in which scientists study molecular gases and dust.
- Using ALMA, astronomers have obtained high-resolution images of 20 nearby protoplanetary disks depicting the planet’s birth.

4. Multi-Application Solar Telescope (MAST), Udaipur Solar Observatory
Purpose and Significance
- For a detailed study of the Solar activity, including its magnetic field.
- The observatory is situated on an island in the middle of Fatehsagar lake.
- It is Asia’s biggest telescope.
Why is an observatory made in the middle of the lake?
- A large water body surrounding the telescopes decreases the amount of heating of the surface layers.
- It reduces the turbulence in the air mass and improves image quality.

5. Growth India Telescope
- It is part of a multi-country joint initiative termed the Global Relay of Observatories Watching Transients Happen (GROWTH).
- The US, UK, India, Japan, Germany, Taiwan and Israel are part of this initiative.
- Location: Hanle (Ladakh)
- It is a fully robotic telescope and can be controlled remotely.
- Aim: Study cosmic events happening over relatively small periods of the cosmological timescale.
Telescopes in the Space
1. Astrosat
- Astrosat is India’s first dedicated astronomy satellite (like Hubble of West).
- It was launched in September 2015.

Features
- It can scan multi-wavelengths from ultraviolet to optical and low- and high-energy x-ray bands for studying distant stars, galaxies and other cosmic objects.
- It is situated at the height of 650 Km.
- It has been of immense benefit to our scientists, who have depended on inputs from other agencies and sources like the Hubble [US-European space telescope].
- It has put India in an elite orbit with the US, Europe, Russia and Japan.
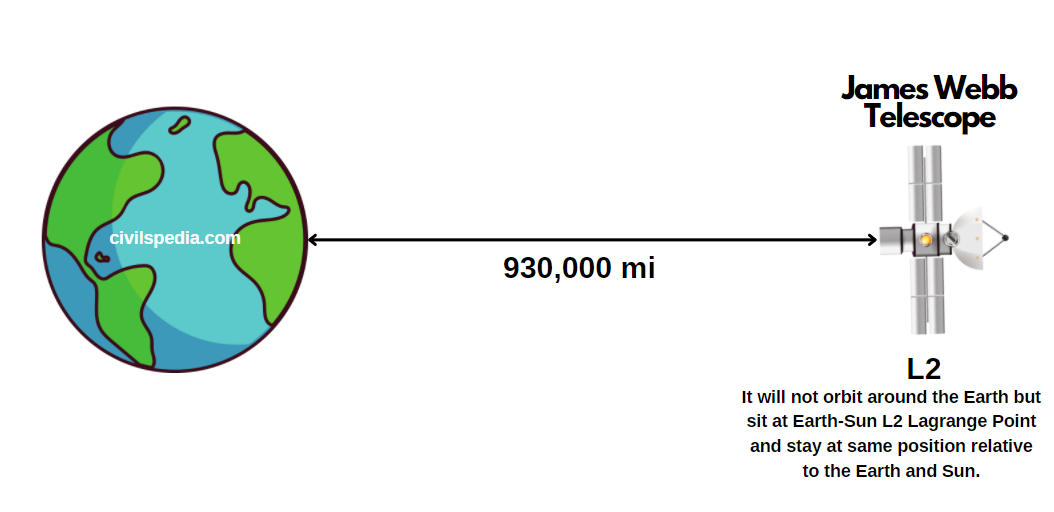
2. James Webb Space Telescope
- It is the Joint Venture of NASA, ESA & the Canadian Space Agency.
- It is the scientific successor of the Hubble and Spitzer telescopes.
- The primary mirror of JWST consists of 18 hexagonal mirrors of 1.32 m diameter each (compared to Hubble Telescope with one mirror of 2.4 m diameter). Further, these mirrors are made up of beryllium as it is light and strong and coated with gold to increase the mirror’s reflection.
- It will be placed at L2 (Lagrange Point), 930,000 miles from Earth’s surface.
- It has become NASA’s flagship infrared observatory. JWST carries four instruments
- Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam),
- Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec),
- Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI)
- Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph
- JWST will study the following
- Search for the very first galaxies that were formed after Big Bang.
- Evolution of the galaxies until now.
- Study formation of stars and their evolution in different phases.
- Potential to support life in these systems.
- Study solar systems, their planets, along with comets, asteroids and minor planets.
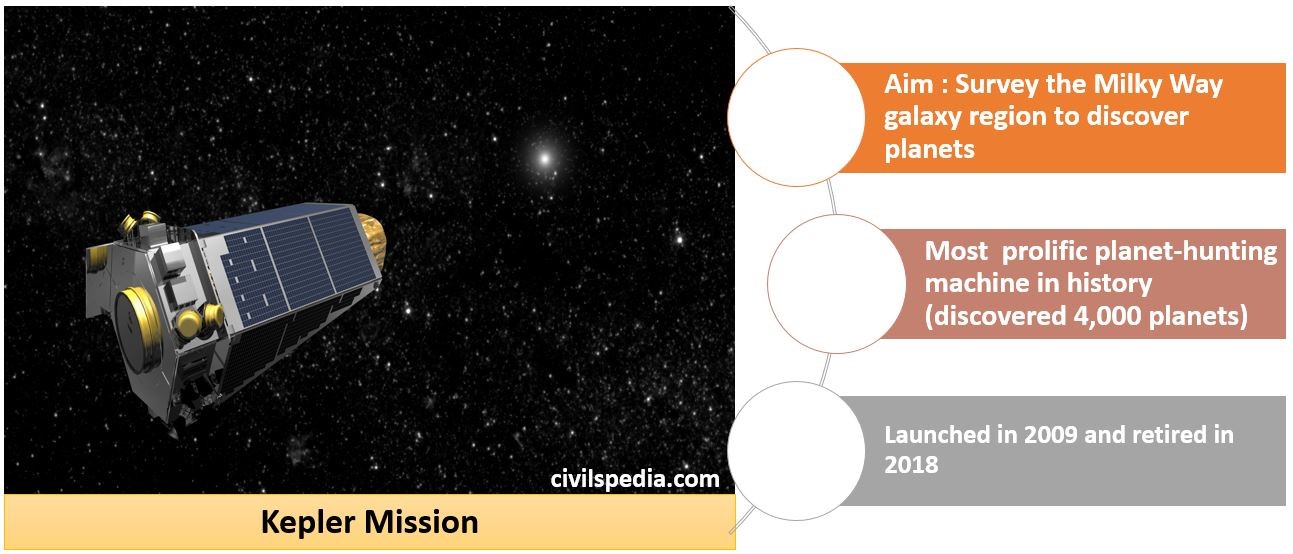
3. Kepler
- It was launched in 2009.
- Aim: Survey the Milky Way galaxy region to discover planets in or around the habitable zone (Goldilocks Zone).
- It was orbiting the Sun, nearly 156 million km from the Earth.
- Kepler is described as the most prolific planet-hunting machine in history. By June 2017, it had discovered more than 4,000 planet candidates and 2,300 confirmed planets.
- Nov 2018: NASA’s Kepler space telescope has been retired after running out of fuel.
Side Topic: Goldilocks Zone
- Goldilocks region denotes the area at the proper distance from its home star that it is neither at too high temperature nor too cold.
- Habitable exoplanets must have such a temperature in which water can exist in its liquid form.
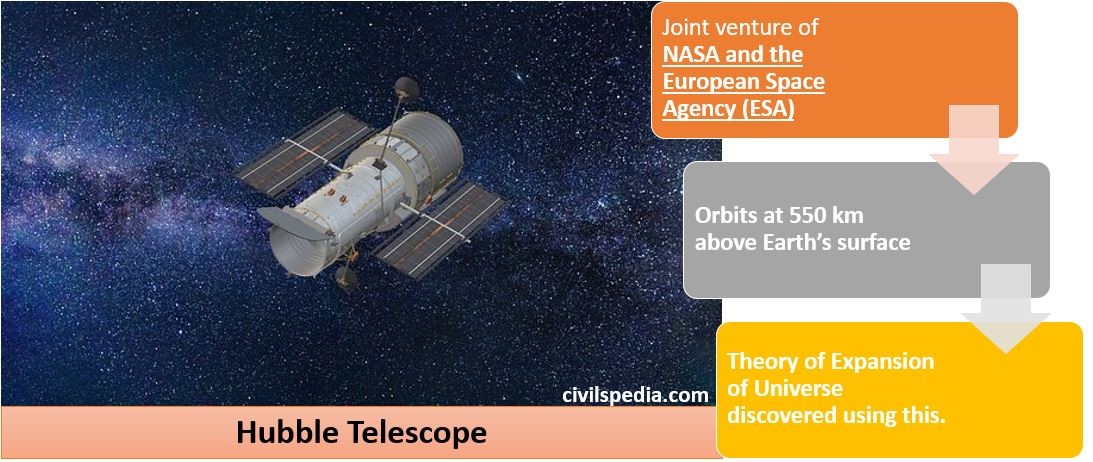
4. Hubble Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope was launched in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) in 1990 as a joint venture between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA).
- It used to orbit 550 km above Earth.
- Its main payloads include
- Wide Field and Planetary Camera (WF/PC),
- Goddard High-Resolution Spectrograph (GHRS)
- High-Speed Photometer (HSP)
- Faint Object Camera (FOC)
- Faint Object Spectrograph (FOS).
- These scientific payloads have helped uncover many secrets of the universe, including the theory of its expansion.
5. Spitzer Space Telescope
- NASA launched it in 2003.
- Aim: To study the universe in the infrared.
- It was retired in January 2020.
