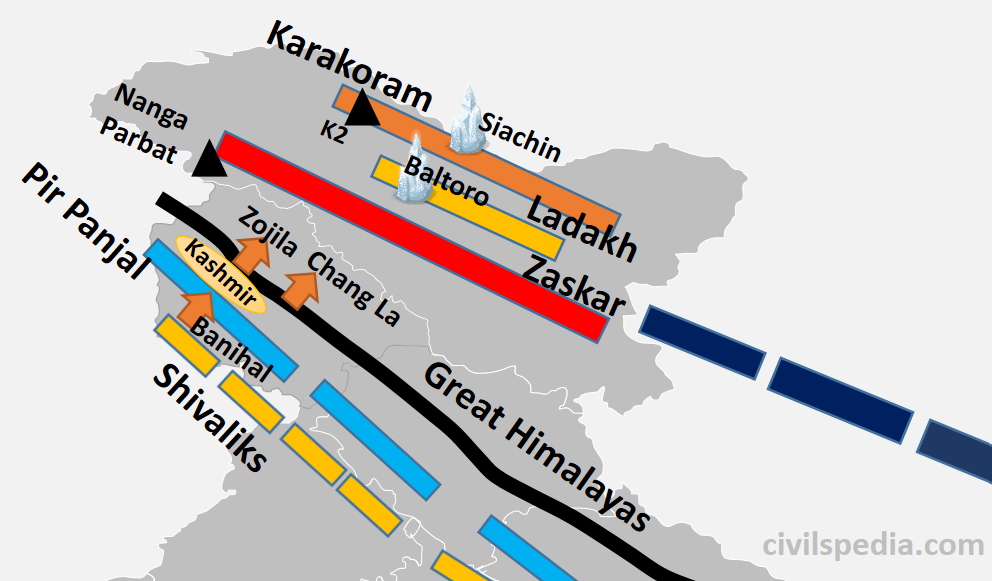
Parliamentary System
This article deals with ‘Parliamentary System– Indian Polity.’ This is part of our series on ‘Polity’ which is important pillar of GS-2 syllabus . For more articles , you can click here.
Introduction
In India, there is a Parliamentary form of government at the State and Centre levels.
| Centre | Article 74 and Article 75 speak about it. |
| State | Article 163 and Article 164 speak about it. |
Definition of Parliamentary System

Government in which the Executive is responsible to the Legislature for its policies is known as Parliamentary System of Government.
It is also known as
- Cabinet System
- Responsible Government
- Westminster Model of Government
Features of the Parliamentary System
- The President is the nominal (de jure) head, while the Prime Minister is the real (de facto) Executive.
- The Party, which secures a majority of seats in Lok Sabha, forms the government.
- Ministers are collectively responsible to Parliament (i.e. they swim and sink together).
- Usually, members of the Council of Ministers belong to the same Political party and hence share the same ideology.
- There is a double membership. Ministers are members of the Executive and legislature.
- The Prime Minister plays a leadership role, and he is the leader of the council.
- President can dissolve the lower House on the recommendation of the Prime Minister.
Merits of the Parliamentary System
- Harmony between the Legislature and Executive as members of Executive are members of the Legislature, too.
- Government is responsible as it is answerable to Parliament for acts of omission and commission.
- Prevents despotism as Executive is controlled by various tools like No Confidence Motion, Zero Hour Discussion etc.
- There is ready alternate government if no-confidence motion is passed against the ruling party.
- It provides broad representation as the Executive consists of a variety of members
Demerits of the Parliamentary System
- The government is unstable and stands at the mercy of Legislators.
- There is no continuity of policies. When government changes, policies also change, which is bad for the economy.
- The government can become autocratic if the ruling party enjoys an absolute majority.
- It is against the Principle of Separation of Power.
- It is not conducive to administrative efficiency as ministers are not experts in their fields.
Why did India Choose the Parliamentary System?
- Historical Continuity: Familiarity with the system due to its presence in British India.
- Emphasis on Responsibility: Preference was given to the system that prioritizes responsibility over stability.
- Recognition of the need to avoid the Legislative-Executive divide, which was necessary for an immature democracy like that of India
- Fear of an Overly Strong Executive: Constituent Assembly feared too strong Executive
- Representation in a Diverse Society: In a diverse society like India, this system provides representation to more diverse groups in the Executive
- Avoidance of Personality Cult: The alternative to the Parliamentary Executive was a Presidential form of government. However, the Presidential Executive puts much emphasis on the President. There is always danger of a personality cult.
Indian System is different from British System
| India Parliamentary System | British Parliamentary System |
| Republican system | Monarchial system |
| Parliament is not supreme and enjoys limited and restricted powers due to the written constitution, judicial review and fundamental rights | It is based on the Doctrine of Sovereignty of Parliament |
| PM can be a member of any of the two houses | PM should be a member of the Lower house |
| Non-MP can be appointed as a Minister, but he has to acquire membership within 6 months | MP alone can be appointed as Minister |
| There is no legal responsibility of the Minister | The legal responsibility of the Minister is present |
| There is no Shadow Cabinet | Shadow Cabinet is present |
Features of the (American) Presidential System
- The President in the American Presidential System holds a dual role as both the head of state and head of government.
- President is elected by the electoral college for 4 years and can be removed by impeachment.
- President governs with help of his secretaries who are not elected and are answerable to him only.
- Advice of secretaries not binding on the President
- The President and his secretaries are neither answerable to the Congress nor have any membership.
- The American Presidential System operates on the fundamental principle of the separation of powers in which the executive, legislature & judiciary are independent & separate.
Should India switch over to Presidential System?
Question of changing over to Presidential System has been raised various times
| 1956 | Nehru himself expressed his doubts about whether the Parliamentary System could meet the needs of the times and the complexities of modern administration. |
| 1960s | The desirability of a switch-over to the Presidential system was discussed & several eminent men, including a person like JRD Tata, advocated a Presidential system for India. |
| 1967 | After Nehru, Congress’s monopoly of power began to be eroded at the level of States. The Presidential model is described as a remedy for all of India’s ills. |
| Indira’s Reign | Demand became the most prominent |
Arguments against
- This issue was sufficiently discussed in the Constituent Assembly, and it made an informed choice after considering both the British and American models.
- It would violate the ‘basic structure‘ of the Constitution.
- Presidential system centralises power in one individual unlike the Parliamentary System, where Prime Minister is first among equals.
- A diverse country like India can only function with consensus-building. But the Presidential System works on a “winner takes it all” approach.
- ‘Outside’ talent can be brought into a parliamentary system, too. Examples: C.D. Deshmukh, T.A. Pai, Manmohan Singh etc.
Arguments in flavor
- There is no genuine separation of powers as the legislature cannot truly hold the executive accountable since the government wields the majority in the House.
- During the time of the coalition government, the government is unstable and stands at the mercy of MPs & MLAs
- Cabinet posts would not be limited to those who are electable rather than able. Experts can become ministers/secretaries.
- Fear that an elected President could become a Caesar/Authoritarian is ill-founded since the President’s power would be balanced by the legislature (including Rajya Sabha)
- It is good for diverse country like India because to get Bills passed, President instead of facing a monolithic opposition, would have the opportunity to build issue-based coalitions on different issues.
- The Parliamentary system was taken from Britain, but conditions similar to Britain do not exist in India. It requires the existence of clearly defined political parties, whereas, in India, a party is all too often a label of convenience.
The Present Parliamentary System has been tried and tested for nearly 70 years. As a famous saying goes – Why fix a thing which isn’t broken? Rather than changing the system, we should reform thoroughly and cleanse the electoral processes.