Table of Contents
Introduction to Mineral Resources of India
This article deals with ‘Introduction to Mineral Resources of India.’ This is part of our series on ‘Geography’, which is an important pillar of the GS-1 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Mineral Resources
- Minerals are aggregates of two or more than two elements having a definite chemical composition and atomic structure & formed by the inorganic process.
- The development of the entire secondary sector is based on minerals. India has vast deposits of minerals.
- In the earth’s crust, they are in the form of ore. They are extracted, processed & then utilised for the economic benefit of society.
Minerals have certain characteristics
- These are unevenly distributed over space.
- There is an inverse relationship between the quality and quantity of minerals, i.e., high-quality minerals are less in quantity than low-quality minerals.
- All minerals are exhaustible over time. These take a long to develop geologically, and they cannot be replenished immediately at the time of need. Thus, they have to be conserved & not misused as they do not have a second crop.
Classifications of Mineral Resources
Classification into Metallic and Non-Metallic Minerals
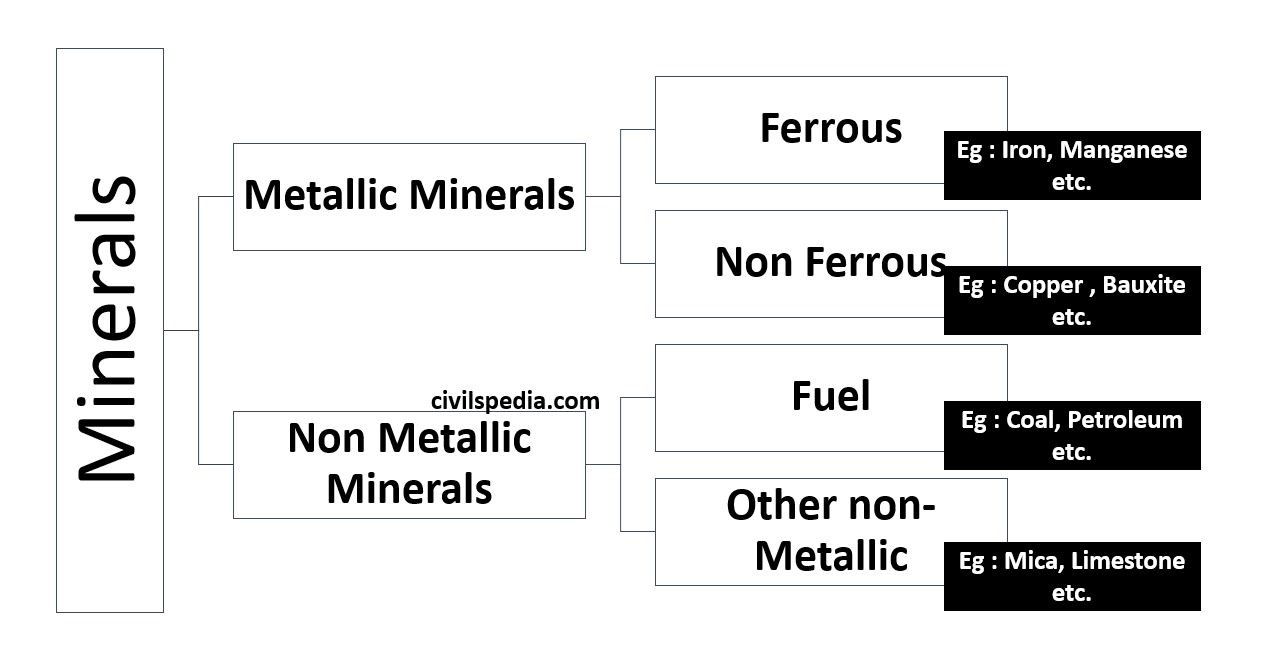
Classification into Renewable and Non-Renewable Minerals
1. Renewable Resources
- Resources which can be renewed or replenished fast
- They are always available & not affected by human activities.
- E.g., Solar Energy, Wind Energy etc.
2. Non-Renewable Resources
- These have been built over a large geological time.
- They need to be used judicially & in a planned way.
- Fossil fuels, iron, gold etc.
Distribution of Minerals in India
- Minerals are mainly associated with metamorphic & igneous rocks of Peninsular India. The vast alluvial plain tract of north India is devoid of minerals of economic use.
- Mineral resources provide the country with the necessary base for industrial development.
- Each mineral region is associated with a prior geological activity.
Geological Events which led to the formation of Minerals
3 Geological events happened in India due to which minerals are found in those areas.
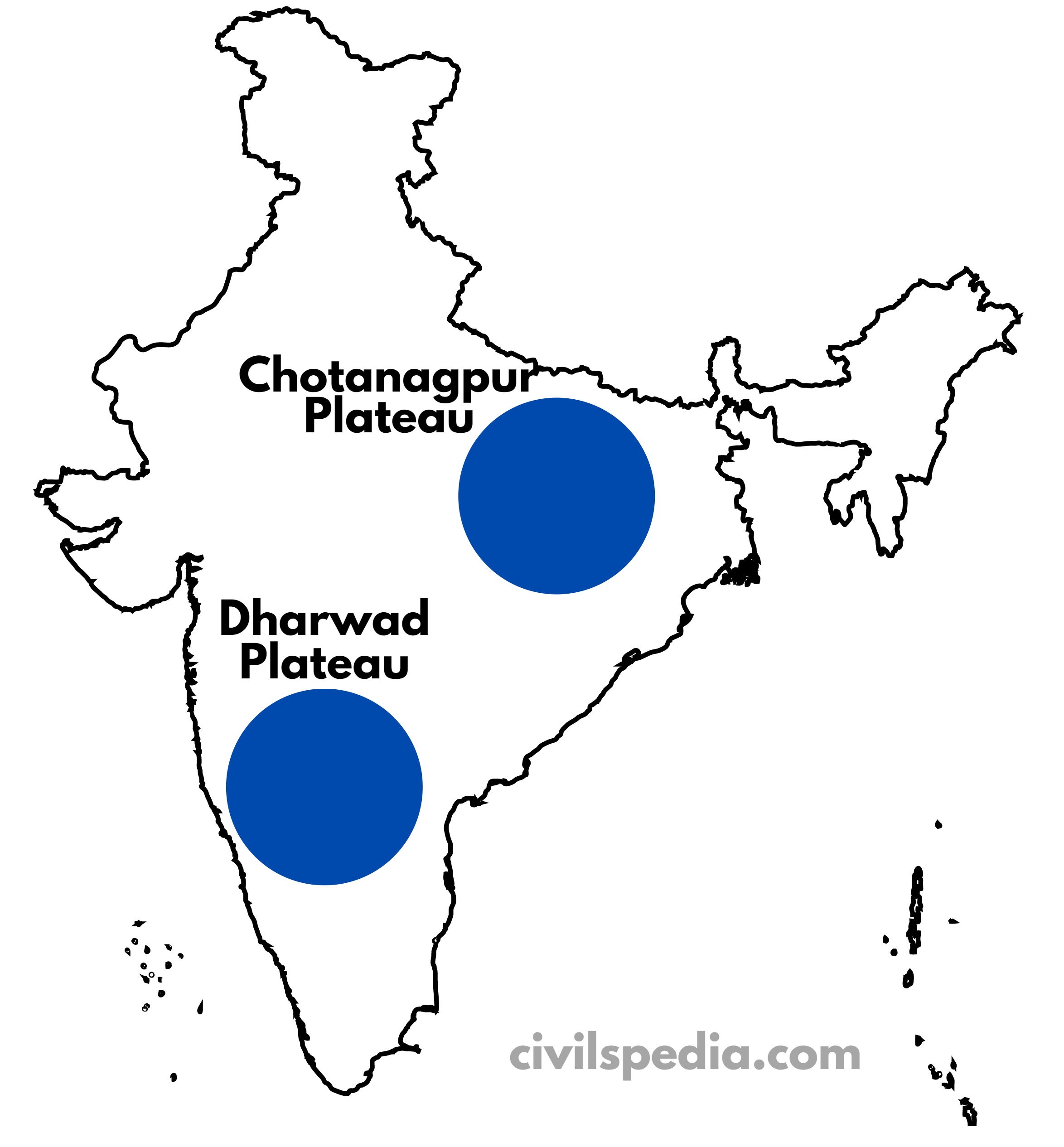
1. Shield Regions
- These were mountains millions of years ago but have now eroded to plateaus.
- Metallic Minerals are found in large quantities, particularly in Chotanagpur Plateau & Dharwad Plateau.
- Reason for minerals: Volcanic Activity when it passed over Reunion Island.
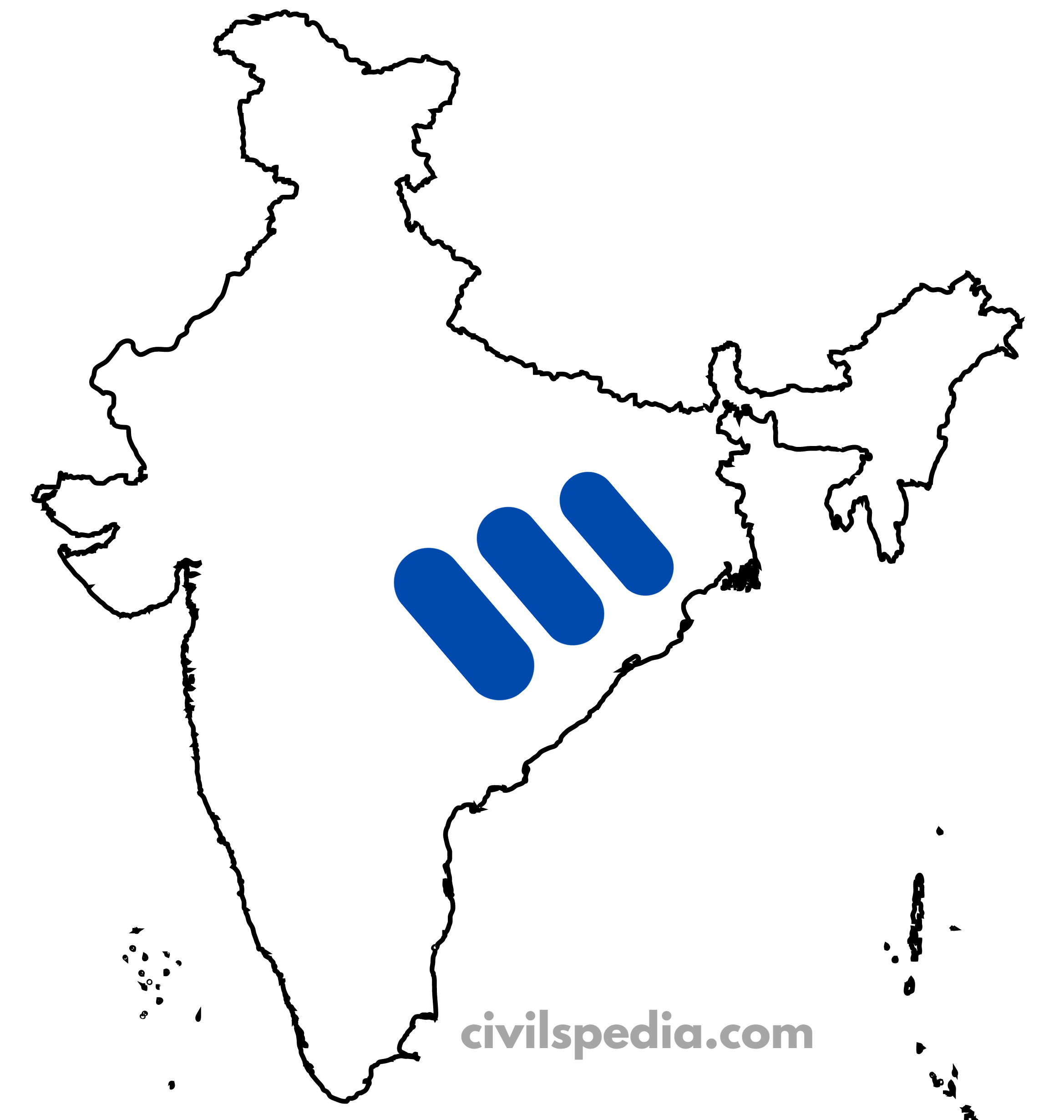
2. Rift Valley during Gondwana Time
- During Gondwana times, the rifting along Damodar & Mahanadi led to large-scale forest submergence. Over the years, this has resulted in the formation of Coal deposits.
- The main regions where these are found are
- Damodar Valley
- Mahanadi Valley
- Godavari and Wardha Valley
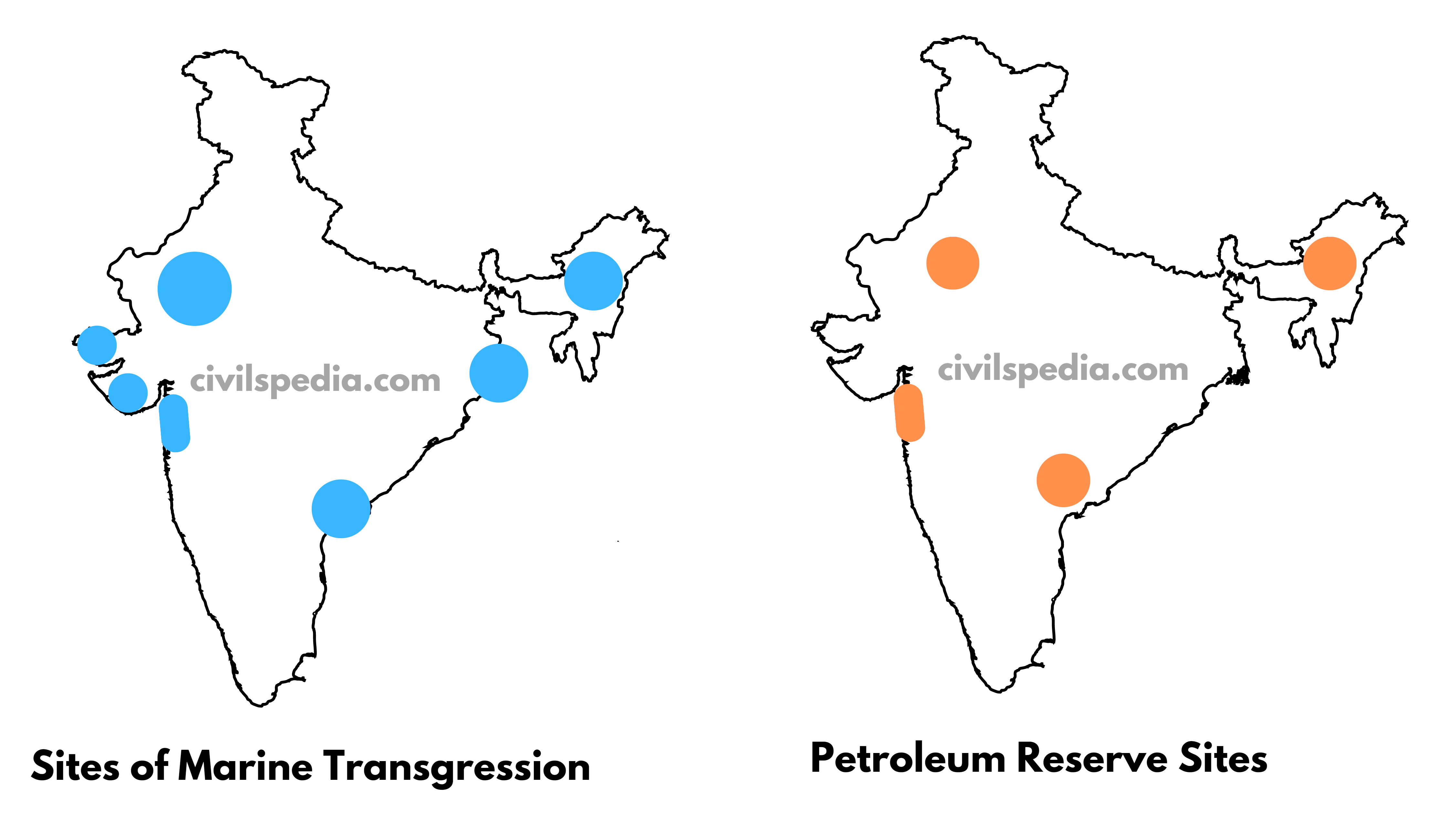
3. Marine transgression during Tertiary time
- Petroleum reserves are found at sites of marine transgression.
- These regions Include
- Gulf of Khambat and Gulf of Kutch.
- Brahmaputra-Shillong Shelf
- Bengal-Bangladesh Shelf
- KG Basin
5 Mineral rich Regions of India
There are 5 mineral-rich regions in India where most minerals are concentrated.
1. Northern-Eastern Belt
- It is the richest mineral region of India.
- It consists of following
- Chotanagpur Plateau
- Kyanite (100% of India’s reserves)
- Iron (90% of India’s reserves)
- Chromium (90% of India’s reserves)
- Mica (75% of India’s reserves)
- Coal (70% of India’s reserves)
- Others: Manganese, Copper and Limestone
- Assam
- Petroleum Reserve
- Lignite Coal
- Chotanagpur Plateau
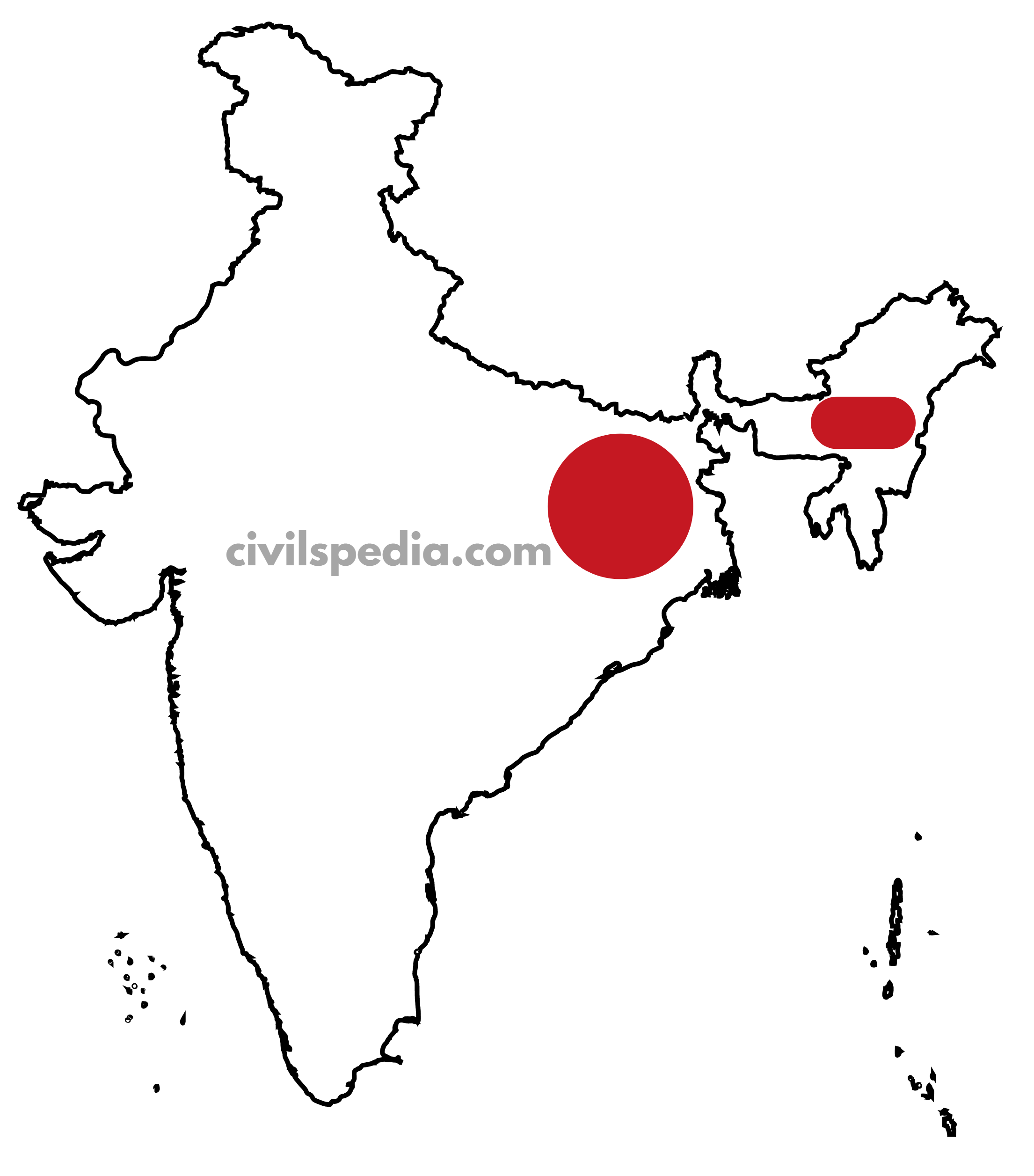
2. Central Belt
It is found in the Chhattisgarh region
- It is an extension of the Chotanagpur Plateau.
- Iron and limestone are found here.
- Coal is found here due to the Godavari-Wardha valley rifting.
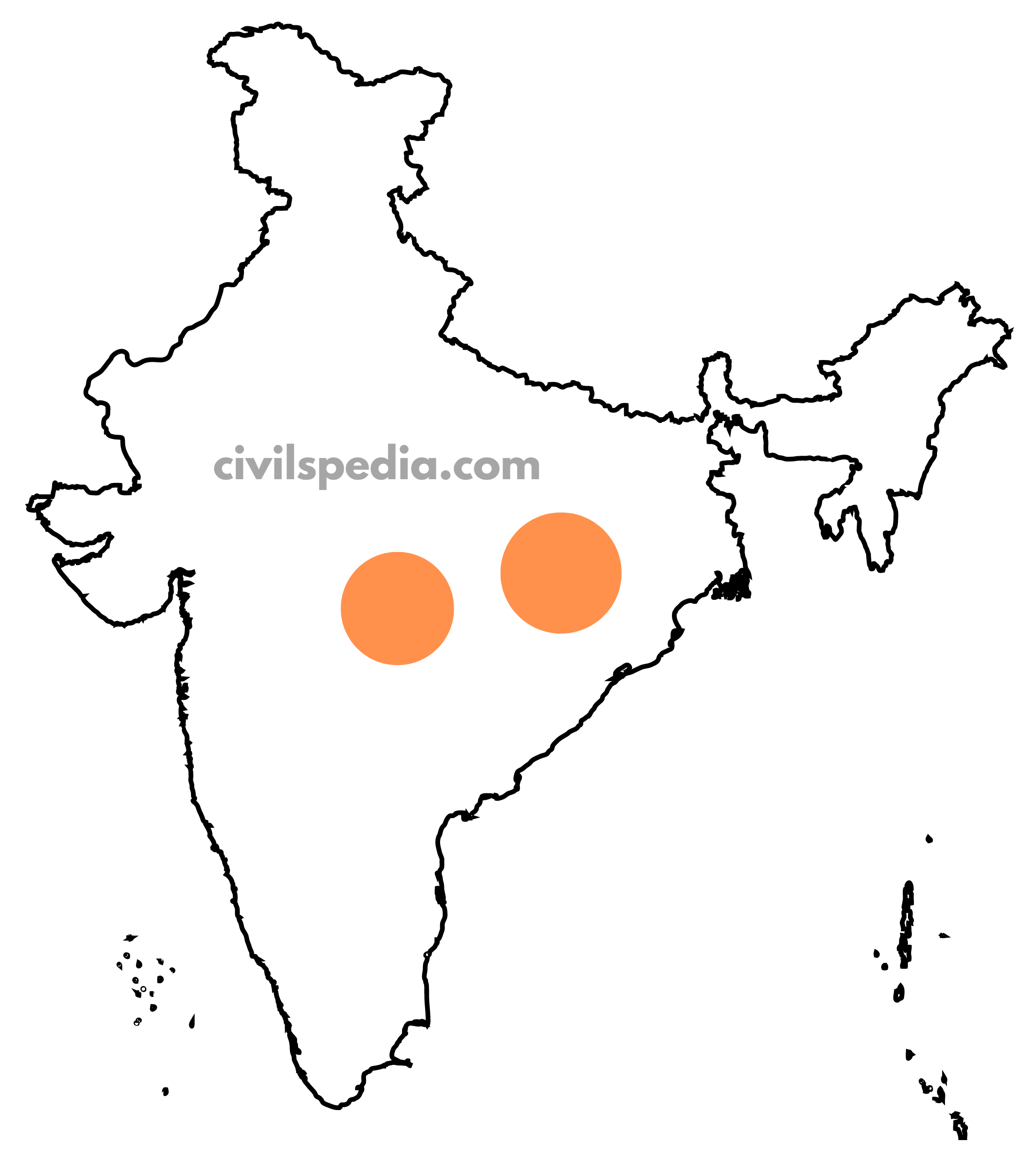
3. South-East Region
In this region, the following minerals are found
- East Karnataka (Hospet Bellary Region): Iron
- Andhra (Cuddapah & Kurnool): Iron
- Andhra (Nellore): Mica, Manganese and Coal
- Telangana: Bauxite
- Tamil Nadu (Neyveli): Lignite coal
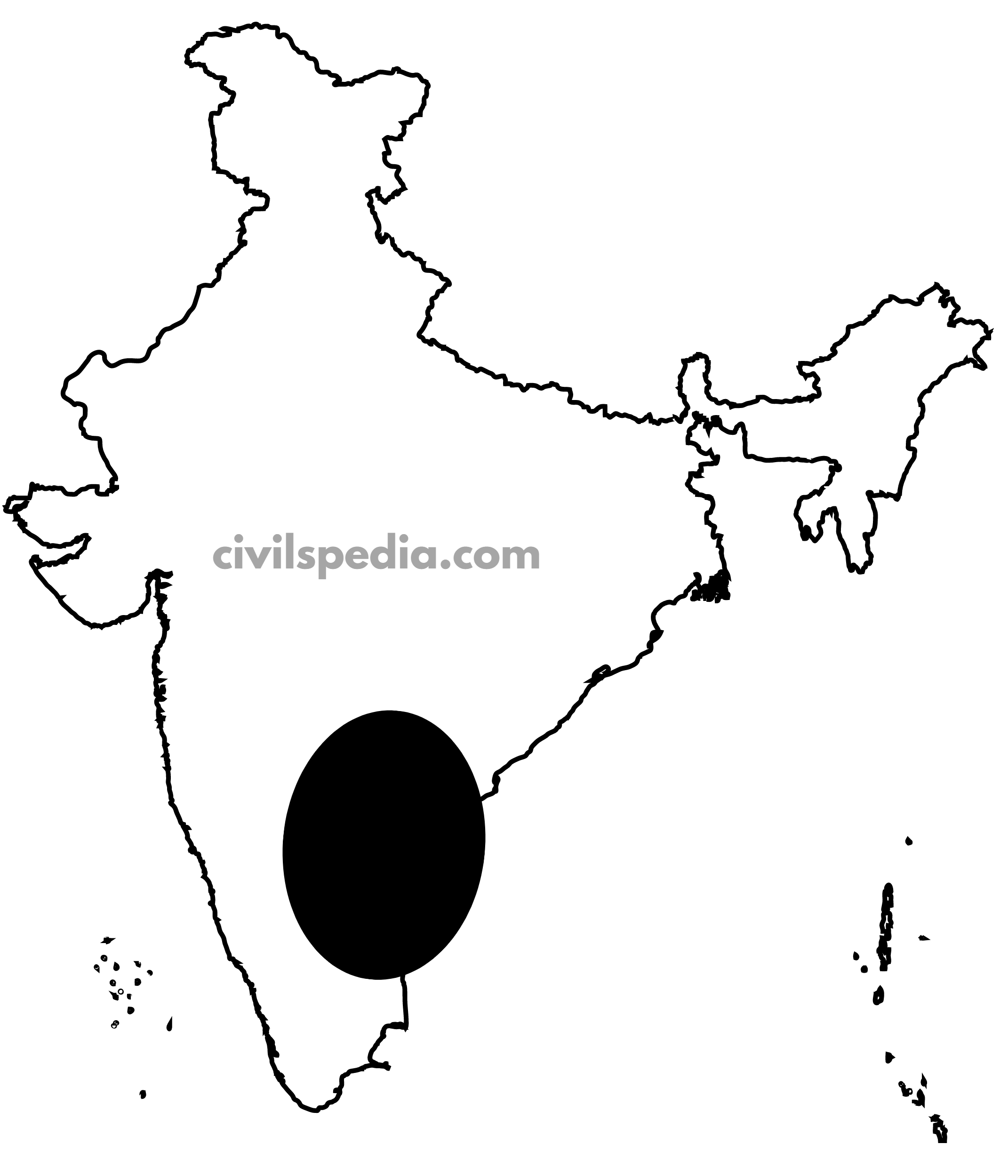
4. South-West Region
In this region, the following minerals are found
- Karnataka Dharwar: Iron, manganese, and limestone are found here
- Goa: Iron is found here
- Maharashtra (Ratnagiri): Iron is found here.
- Kerala has deposits of Monazite and Thorium and Bauxite clay.
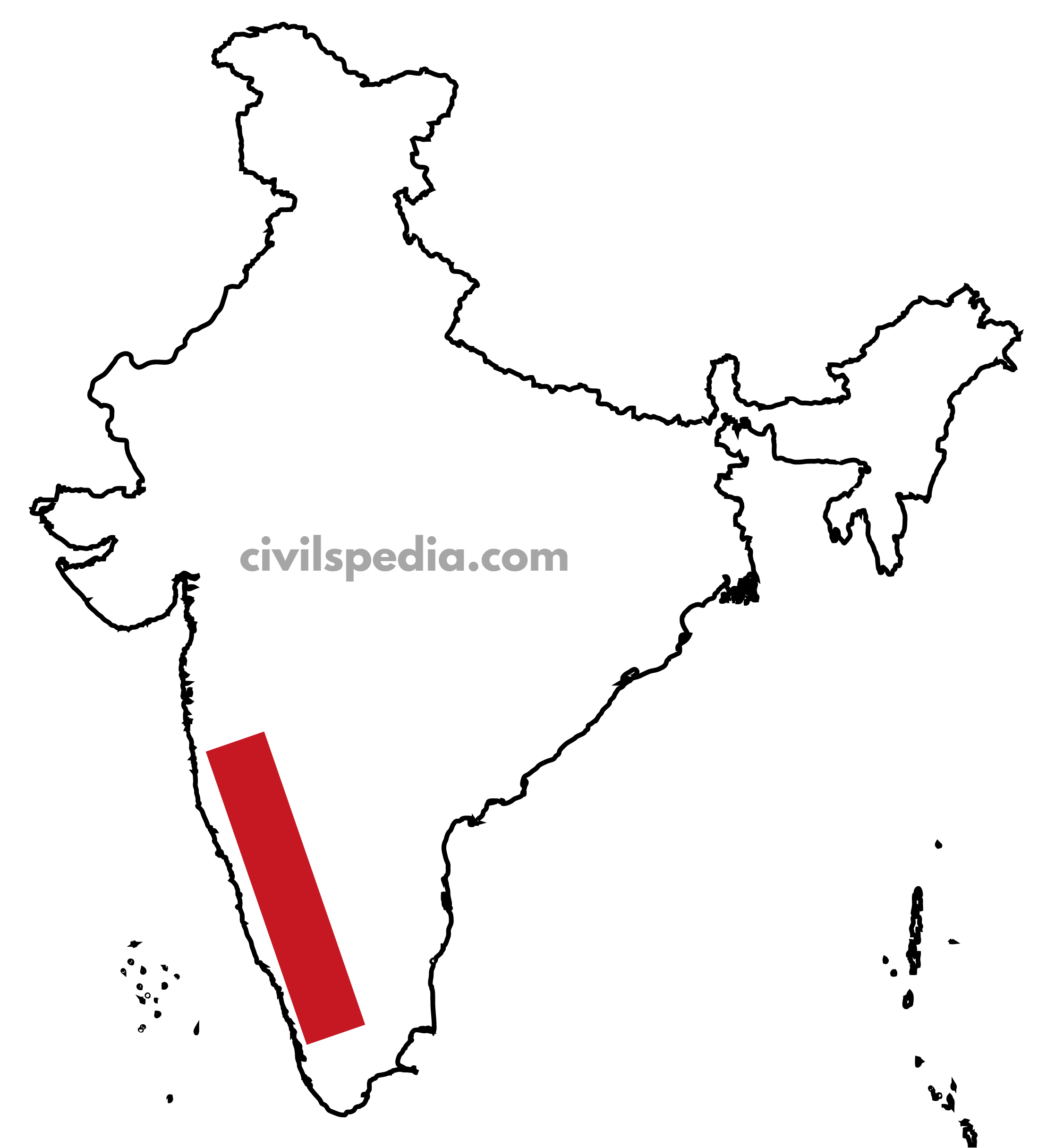
5. North-West region
In this region, the following minerals are found
- Petroleum
- Rajasthan: Barmer
- Gujarat: Gulf of Kutch
- Building material
- Rajasthan is rich in building stones, i.e. sandstone, granite, and marble. Gypsum and Fuller’s earth deposits are also extensive. Dolomite and limestone provide raw materials for the cement industry.
- From Lakes
- Salt from Playa lakes of Rajasthan.
- Lake Sambhar and Lake Didwana of Rajasthan – contain gypsum & borax deposits.
