Last Updated: May 2023 (Rare Earth Metals)
Table of Contents
Rare Earth Metals
This article deals with ‘Introduction to Mineral Resources of India.’ This is part of our series on ‘Geography’, which is an important pillar of the GS-1 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Introduction
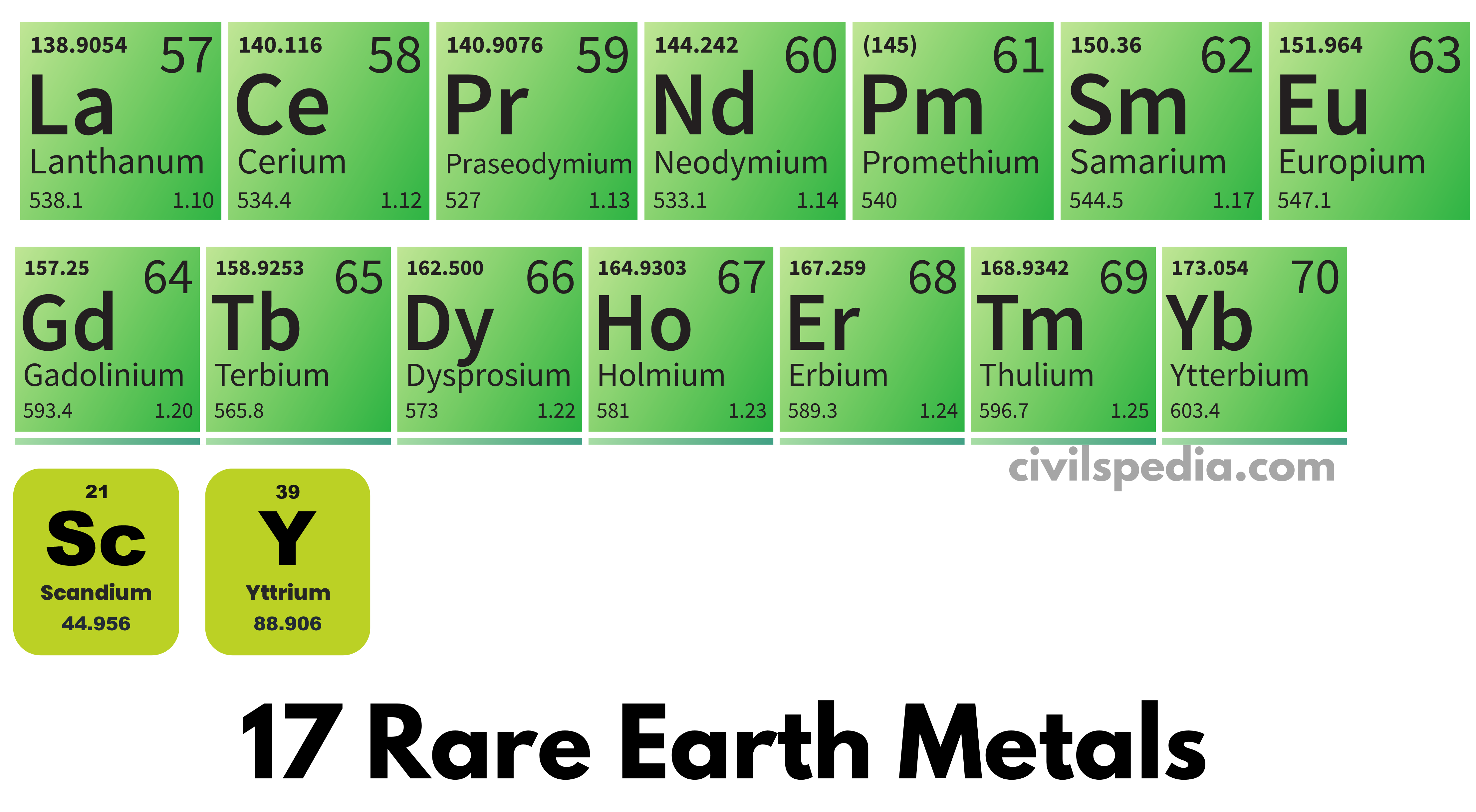
- Rare Earth Metals include 15 lanthanides with Atomic numbers 57 to 71 and two non-lanthanide metals, i.e. Scandium and Yttrium.
- As they frequently occur in the same ore deposits as the lanthanides and have comparable chemical characteristics, scandium and yttrium are also regarded as rare-earth elements. But they have different electronic and magnetic properties.
- Although they are termed Rare Earth elements, they are not so rare in occurrence. However,
- They tend to occur together and are difficult to separate from one another.
- Along with that, they do not occur in concentrated form and are dispersed throughout the world. It makes their extraction difficult and economically unviable.
- They are also hazardous to extract due to their radioactive nature.
- Two main ores from which Rare Earth Metals can be extracted are Monazite and Bastansite.
Uses of Rare Earth Metals
- They are used in various high-end electronic devices due to their useful magnetic, chemical and spectroscopic properties.
- They have the unique property to accept and discharge electrons, enabling them to be used in electronic devices, rechargeable batteries & fluorescent lighting.
- Due to their spectroscopic properties, they are used as fluorescent and as the main component in night vision glasses.
- Due to their magnetic properties, they are used in electromagnetic circuits and also to make powerful and stable magnets.
- Military uses
- They are used in night-vision glasses & precision-guided weapons.
- They are the critical component in making ultra-hard alloys used in making armoured vehicles.
- Some Rare Earth Metals and their uses
- Scandium: Television and fluorescent lamps
- Yttrium: Treat cancer and rheumatoid arthritis
- Lanthanum: Night vision glasses
- Neodymium: Guidance systems and wind turbine motors
- Europium: Fluorescent lamps
- Samarium: Powerful permanent magnets which are stable even at high temperature
- Cerium: Space program, especially space shuttles
Global Distribution
- There are two main sources
- Bastnasite deposits in China and the United States constitute the largest percentage
- Monazite deposits found in Australia, Brazil, China, India, Malaysia, South Africa, Sri Lanka and Thailand.
- China is the world leader, accounting for around 97% of world production. India, Brazil, Australia, the USA, Russia, Thailand and Malaysia comprise the rest.
- In 2023, large deposits of rare earth metals were found in Sweden. Until then, no rare earth deposits have been reported from the continent.
- Rare earth metals are also being recycled from e-waste.
Indian Distribution
- India has 3% of world reserves.
- The main source in India is monazite which is found in the form of sand on the beaches of Kerala.
- The Geological Survey of India recently found a high concentration of rare earth elements in western Rajasthan.
