Anti-Microbial Resistance
This article deals with ‘Anti-Microbial Resistance – for UPSC.’ This is part of our series on ‘Society’, which is an important pillar of the GS-1 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
What is Anti-Microbial Resistance?
Anti-Microbial Resistance (aka Antibiotic Resistance) happens when microorganisms (such as bacteria, parasites, viruses and fungi) evolve when they are exposed to the antibiotic and develop resistance mechanisms to it or acquire that resistance from another bacterium.
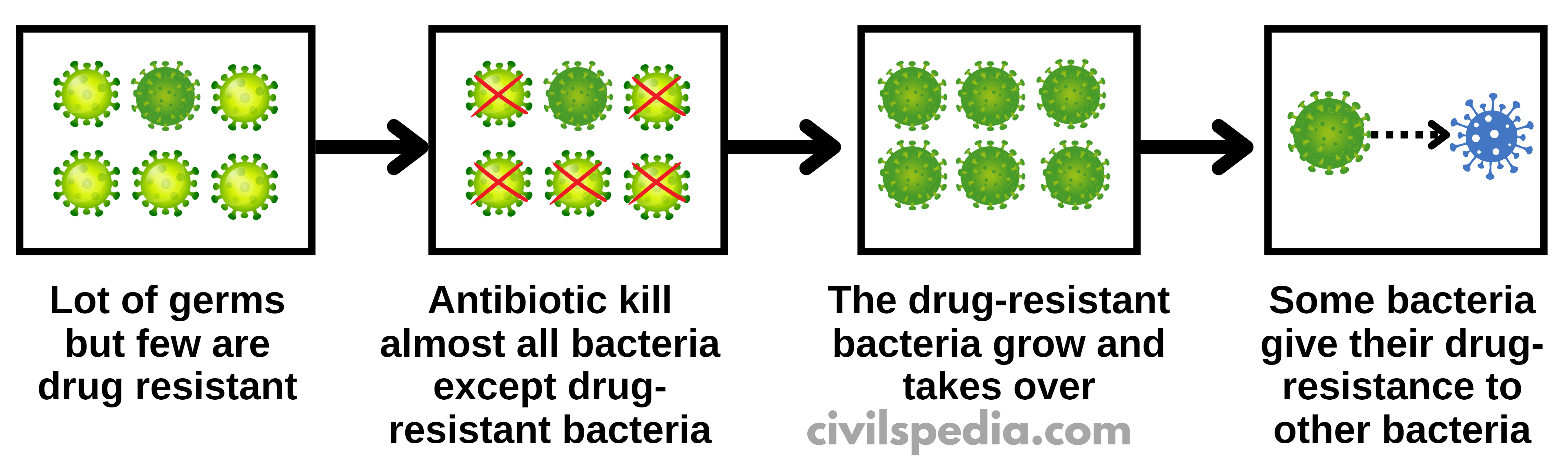
History
| 2010 | It became a topic of debate in India when the British journal Lancet named an enzyme as New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase-1 or NDM-1, which had antimicrobial resistance |
| 2016 | Resistance to Colistin was detected in China. Colistin is the last resort of antibiotics. |
| Sept 2016 | United Nations held a high-level meeting to tackle Antimicrobial Resistance. Note: It was only the fourth time the general assembly held a high-level meeting for a health issue (previously, it was for HIV non-communicable diseases such as heart disease and diabetes and Ebola). |
| 2017 | A US woman died from an infection that was resistant to all 26 available antibiotics. |
| 2023 | Muscat Conference on Antimicrobial Resistance held. Muscat Manifesto was released, calling for 1. Accelerating the political commitments in the implementation of One Health Action 2. Recognize the impact of AMR on humans as well as Animals. |
Causes of Anti-Microbial Resistance
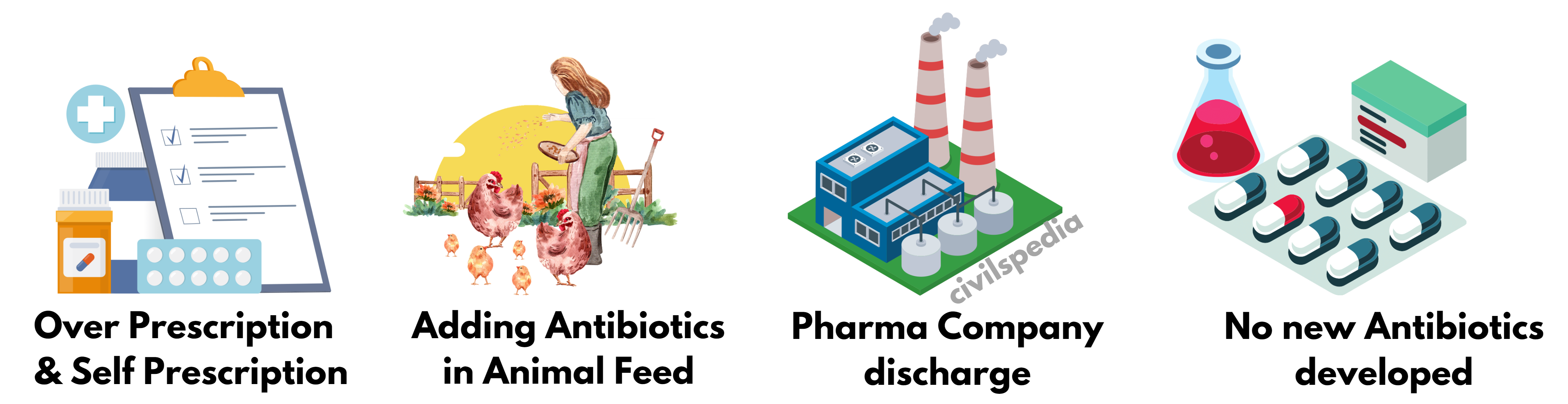
Significant sources of resistance:
- Overuse of antibiotics by human beings (over prescription)
- Self-medication
- Overuse of antibiotics in the veterinary sector
- Environmental antibiotic contamination due to pharmaceutical companies and hospital discharge.
- Lack of new antibiotics being developed
- Patients not finishing treatment
- Poor infection control in hospitals
Ways to control Anti-Microbial Resistance
Prescriber
Prescriber should
- Follow guidelines
- Perform Antimicrobial susceptibility tests
- Maintain hygiene, disinfection and sterilization in the hospital
Farmer
Farmers should
- Follow guidelines.
- Use only animal-specific antibiotics
- Maintain hygiene
Public
Public should
- Follow the prescription and don’t self-medicate himself
- Public awareness and education should be carried out
Politician
Politician should
- Establish Antibiotic Resistance related laws
- Make National Plans and Guidelines
- Invigorate the antibiotic development of pharmaceutical companies
Researcher
Researcher should
- Develop a new generation of antibiotics
- Develop Molecular Techniques for identifying resistance genes.
Initiatives taken by Government
1. Red Line Campaign

2. National Surveillance System for Anti-Microbial Resistance
- The program keeps a close watch on such cases.
3. National Action Plan on Anti-Microbial Resistance
- The program was started April 2017
- It focused on
- Hand Hygiene and Sanitation programs
- One Health Strategy
4. National Health Policy, 2017
- It had specific guidelines for the use of antibiotics and limiting the use of antibiotics.
5. Schedule H1 of Drugs and Cosmetic Rule, 1945
Schedule H1 was added to the Drugs and Cosmetic Rule 1945. Drugs in Schedule H1 are required to be sold in the country with the following conditions:-
- Their sale has to be registered in the register with the name of the prescriber and patient
- Drugs shall be labelled with the symbol Rx & drug warning.
International Steps
1. By WHO
- WHO is providing technical assistance to countries to develop national action plans to combat Antimicrobial Resistance and strengthen their surveillance systems.
- One Health Approach: The One Health approach recognizes the interconnectedness between human, animal, and their shared environment. It emphasizes the importance of addressing health issues comprehensively by considering the interdependencies and interactions between humans, animals, and their shared environments. The ‘One Health’ approach calls for optimal antibiotic use in both humans and animals.
2. UNO
- A high-level meeting on antimicrobial resistance was held at the United Nations General Assembly.
3. New Antibiotics
- For example, ODLs are a new class of antibiotics discovered by the University of Illinois and Nosopharm, a French company.