Last Updated: May 2023 (ISRO and Indian Space Program)
ISRO and Indian Space Program
This article deals with ‘ISRO and Indian Space Program.’ This is part of our series on ‘Science and Technology’ which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here
Evolution of World Space Journey

Space Program of India
- Indian Space Program is operated by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO).
- Vikram Sarabhai is known as the father of the Indian Space Program.
Objectives of Space Program
India has historically viewed space technology applications primarily for societal development. Hence, the objectives of the Indian Space Program are
- Using Space Technology for the socio-economic benefit of people.
- Make India self-reliant in space technology.
- Peaceful use of outer space.
Department of Space (DoS)
- Nodal Agency for Space-related activities in India is the Department of Space (DoS).
- ISRO is the primary R&D wing of DoS.
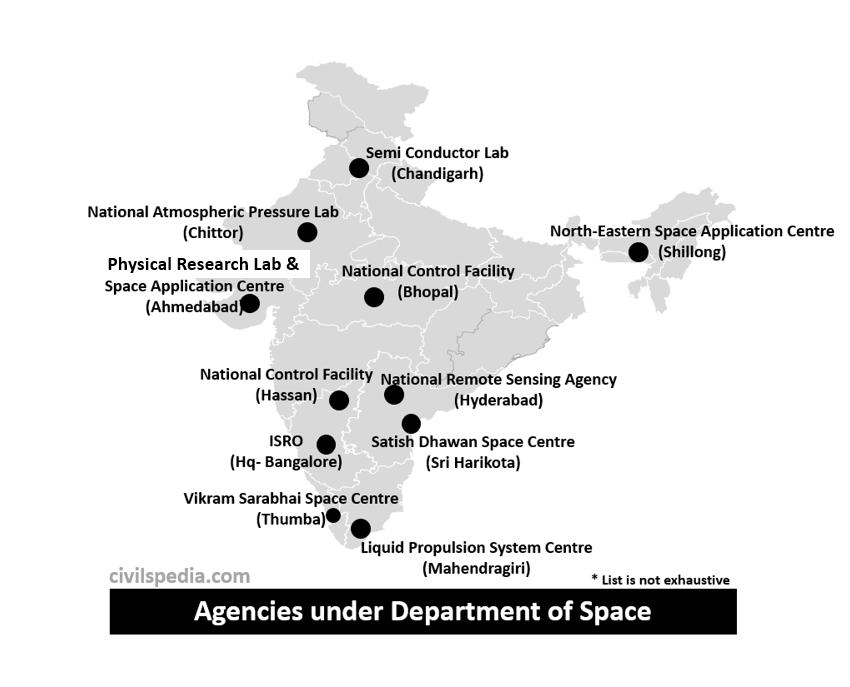
- Other Agencies of DoS include
| Physical Research Lab (PRL) | Ahmedabad |
| Semi Conductor Lab | Chandigarh |
| National Atmospheric Research Lab | Chittor |
| North Eastern Space Applications Centre | Shillong |
ISRO
- It is the primary body of Space Research under the Department of Space.
- Present Chairman = Dr K Sivan
- It is headquartered in Bangalore.
Timeline
| 1961 | Space Research started under the Department of Atomic Energy under Homi Bhabha. |
| 1962 | Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCSR) established & worked to establish TERLS (Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Centre) started. |
| 1969 | ISRO was formed. |
| 1972 | – Department of Space (independent department) formed. – ISRO was brought under the Department of Space. |
| 1975 | Aryabhatta – the first Indian satellite was launched (with Soviet Launch Vehicle). |
| 1980 | Rohini – the first satellite was launched using Indian Launch Vehicle. |
Regional Centres of ISRO
ISRO has its various regional centres like
- ISRO Satellite Application Centre, Bengaluru (ISAC): Design and fabricate satellites.
- Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre, Thiruvananthapuram (VSSC): Develop satellite launch vehicles (like PSLV and GSLV).
- Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota (SDSC): Satellite launching station of India.
- Space Application Centre, Ahmedabad (SAC): Conceptualize and carry out different space research projects.
- Liquid Propulsion System Centre, Mahendragiri, TN (LPSC): Development of satellite propulsion systems.
- ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network, Bengaluru (ISTRAC)
- Master Control Facility, Bhopal and Hassan (Karnataka): Observe and control all geostationary satellites.
- National Remote Sensing Agency, Hyderabad: Act as a key player in earth observation program and disaster management.
Side Topic: Equivalent of ISRO of other nations
| USA | NASA |
| Russia | RKA |
| China | CNSA |
| Europe | ESA |
| Japan | JAXA |
Antrix
- Antrix is the private arm of ISRO.
- It was incorporated in 1992 and awarded ‘Miniratna‘ status in 2008.
- Its main functions include
- Promotion and commercialization of space products.
- Providing technical consultancy services.
- Deals with the transfer of technologies developed by ISRO.
- It also offers various services and space products to international customers worldwide.
New Space India Limited (NSIL)
- NSIL is the commercial arm of ISRO.
- It was incorporated in 2019 as a Government-owned enterprise.
- The main functions of NSIL include
- NSIL will enable Indian industries to build the capacity of the domestic market for space manufacturing.
- NSIL will facilitate the transfer of ISRO technologies to the industry.
- The launch of a Brazilian satellite named ‘Amazonia-1’ in 2021 was the first commercial deal of NSIL.
Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACE)
- IN-SPACE works under the Department of Space.
- IN-SPACE functions autonomously and parallel to ISRO.
- IN-SPACE has its own directorates for technical, legal, safety and security, monitoring and activities promotion.
- The function of IN-SPACE includes regulation and promotion of the building of satellites, rockets and commercial launch services through Indian industry and StartUps.
Satellite Launching Stations / Launch Pads
- Presently, India has only one launch station at Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh with two launch pads.
- India is building its second rocket launch station in the Thoothukudi district in Tamil Nadu.
- Note: Satellite launching stations (including that of India) is located on the east coast and as close to the equator as possible due to the following reasons:-
- The Earth’s rotation provides an additional boost, and the strength of the boost is higher closer to the equator.
- In case of failure, debris would fall into the Bay of Bengal, potentially saving property and lives.
Side Topic: Satellite Launch Stations of other countries
| USA | Cape Canaveral (Florida) |
| France | French Guyana (in South America) |
| Iran | Emamshahr |
| China | Jiquan |
| Japan | Uchinoura |
| Russia | Kapustin Yar |
Achievements of Indian Space Program
- India has emerged as one of the 6 most important countries in the field of space research.
- India is self-reliant in launching remote sensing and communication platforms.
- With GSLV MK-III, India is now in the elite club which can launch heavy Geo-Stationary Communication Satellites.
- World Record was created by ISRO by launching 104 Satellites in a single launch.
- ISRO is launching satellites for other countries as well and earning foreign exchange (Eg: Amazonia-1 (Brazil).
- Space program contributes to national security in the form of improving surveillance capability.
- The space program is helping India emerge as technological power and knowledge-based economy.
Challenges to Indian Space Program
- Indian Space Program needs to move from research and development to a commercial level.
- India should boost the frequency of launches. This will reduce the cost & make it cost-competitive.
- There is a need to develop capabilities to build a much larger number of satellites than the current 3-4 per year.
- Most of the space launches are for socio-economic development. ISRO needs to move ahead and work for the country’s military and defence needs as well.
Side Topic: Cases in news
Nambi Narayanan Case
In 1994, Nambi Narayanan, who was working on Cryogenic Engine and was on the verge of making it, was arrested for selling secrets. CBI later found that the charges were false, and he was discharged in 1996. The case was fabricated by IB Officials in connivance with the CIA because the US didn’t want India to develop a Cryogenic Engine as it would have challenged the monopoly of the US, Russia, and France.
Devas Antrix Case
In 2005, Antrix Corporation signed an agreement with Devas Multimedia to lease S-band transponders on two ISRO satellites (GSAT 6 and GSAT 6A) for a price of ₹1,400 crore, which is significantly lower than the market price. In 2009, the Devas – Antrix deal was exposed. This was named Antrix – Devas S-band spectrum scam. After a CBI investigation, the deal was annulled. Subsequently, Devas made an appeal in the International Court, which has declared that the annulling of the agreement by the Government of India was “unfair” and inequitable”.
Glance at ISRO’s flagship missions
1 . Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS)
- IRNSS or NAVIC is India’s indigenous GPS.
- It is already operational.
2. Reusable Satellite Launch Vehicle
- This mission will reduce the cost of delivering satellites into orbit to 1/10th of the present cost.
3. Cryogenic Engine (GSLV MK III)
- GSLV MK III with Cryogenic Stage has been developed successfully.
- It can be used to launch payloads of up to 4 tonnes into the geostationary orbit.
4. Chandrayaan 2
- After the unprecedented success of Chandrayaan-1, ISRO decided to launch Chandrayaan-2 in July 2019.
- It had Rover and Lander.
- Mission achieved a partial success.
ISRO-CHANDRAYAAN 2 (3D Animation)

5. Aditya Space Satellite
- Aditya Mission will study the Corona of Sun.
- ISRO will launch it shortly.
6. Venus Exploration program/ Shukrayaan
- To study the atmosphere of Venus for a period of 4 years.
- ISRO will launch it shortly.
- France is also collaborating with India on its mission to Venus.
7. Gaganyaan
- Gaganyaan is a 3-ton ISRO spaceship to carry a 2-member crew to the Low Earth Orbit and safe return to the Earth after a few orbits to two days.
- The extendable version of the spaceship will allow flights up to 7 days and have docking capability with space stations.
8. Second Launch Station
- India is building its second rocket launch station in the Thoothukudi district in Tamil Nadu.
- The project will house one launchpad exclusively for Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLV).
- Presently, India has only one launch station at Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh with two launch pads.
9. Space Parks
- The government is making a 100-acre Space Park in Bangalore.
- Private industry players would be allowed to set up facilities to make subsystems and components for satellites.
10. Village Resource Centre
- 473 Village Resource Centres (VRCs) have been established by ISRO.
- It uses Satellite Communication (SATCOM) network and Earth Observation (EO) satellites.
- VRCs provide services like telemedicine (by connecting sick people in villages through VSAT network to the doctors), Tele-education (providing a virtual classroom facility to far-flung villages), and providing advisories related to agriculture.
- There is a need to upscale VRCs and link all village Panchayats.
Outreach Programs of ISRO
- YUVIKA Program: Program aims to inculcate and nurture space research enthusiasm in young minds. Under this 1-month program, 3 students from each of state and UT is selected provided that the student has just finished 9th standard and is waiting to join 10th standard.
- Young Scientist Program: It is an ISRO program for school students aiming to teach and nurture space research fervour in young minds.
- Samvad with Students: Under the ISRO program called Samvad with Students, the ISRO chairman meets the students during his outstation visits, addresses their queries, and quenches the scientific thrust.
- ISRO-Student Collaborations: ANUSAT (Anna University Satellite), Student Satellite (STUDSAT), SRMSAT (SRM University), Jugnu (IIT Kanpur) etc.
This marks the end of the article titled ‘ISRO and Indian Space Program.’ For the rest of the articles, CLICK HERE.
