Last Updated: May 2023 (Indian Navy)
Table of Contents
Indian Navy
This article deals with the ‘Indian Navy.’ This is part of our series on ‘Science and Technology’ which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Structure of Indian Navy
- Indian Navy protects the territorial waters, coast and Indian geopolitical interests.
- It has 58,000 active personnel.
- It has 3 operational commands
- Eastern Command – Vishakhapatnam
- Western Command – Mumbai
- Southern Command – Kochi
Side Topic: Blue Water navy
- It is a mighty navy that can operate across the deep waters in open oceans. E.g. US Navy.
- Indian Navy also wants to be a Bluewater navy. The purchase/induction of Vikramaditya, nuclear submarines, fifth-generation air crafts etc., are part of that strategy.
Why Indian Navy needs to be modernized?
- India has a vast and long coastline of 7,500 km that needs to be defended by a strong and modernized navy.
- The majority of India’s international trade is carried through the Indian ocean. Hence, a strong and modernized navy is necessary to protect Indian interests.
- A modernized navy is the need of the hour to counter the Chinese String of Pearls strategy against India.
Naval Ships
How are Naval Ships named?
Different countries follow different conventions
Corvettes
- Corvette is the smallest class of ships that can be considered a proper warship.
- Their main use includes
- Coastal Patrol
- Fast Attack
- In India, Corvettes are named after personal arms. Eg : INS Khukri, INS Kirpan and INS Khanjar.
Frigates
- Frigates are warships with mixed armaments.
- In India, they are named after mountains or rivers or weapons. E.g., INS Sahaydri, INS Shivalik, INS Satpura, INS Talwar, INS Teg etc.
Cruise or Destroyer
- Destroyer is a fast, highly manoeuvrable ship with long -endurance. Generally, it escorts a fleet of vessels intending to protect them.
- In India, they are named after a state capital, a large city, or a great king or warrior from India’s history. E.g., INS Delhi, INS Kolkata, INS Mysore, INS Mumbai, INS Rana and INS Ranjit.
Submarines
- In India, Submarines are named after a predatory fish or an abstract name associated with the ocean.
- INS Arihant and INS Chakra are nuclear submarines; the conventional ones have had names from INS Sindhughosh and INS Sindhukirti to INS Shalki and INS Shankul.
Aircraft Carriers
- Aircraft Carrier is the highest class of warships whose presence can provide strategic advantage. They are used to carry aircraft to carry operations away from home shores.
- These are very expensive and generally escorted by destroyers, frigates, submarines etc.
- There is a special procedure to name such special ships. A committee is formed that invites the name and decides to name it. For Example,
- INS Vikramaditya: It is named after Vikramaditya meaning Sun of Prowess, a name taken after many Indian sovereigns.
- INS Vikrant: It is named after India’s first Aircraft Carrier, which India bought from the UK in 1957.
- Importance of Aircraft Carriers for India
- It enhances the Navy’s capabilities to carry operations away from its shores.
- It is essential to convert the Indian Navy to Blue Water Navy.
Side Topic: Nations and Number of their Aircraft Carriers
| USA | 11 Operational |
| China | 2 Operational (2 will be commissioned soon) |
| India | 1 Operational (1 will be commissioned soon) |
Indian Aircraft Carriers
1. INS Vikramaditya
It is an Indian Aircraft carrier. It is of Soviet origin and was known as Admiral Gorshkov. India bought this from Russia in 2004, and it was finally delivered to India in 2013.

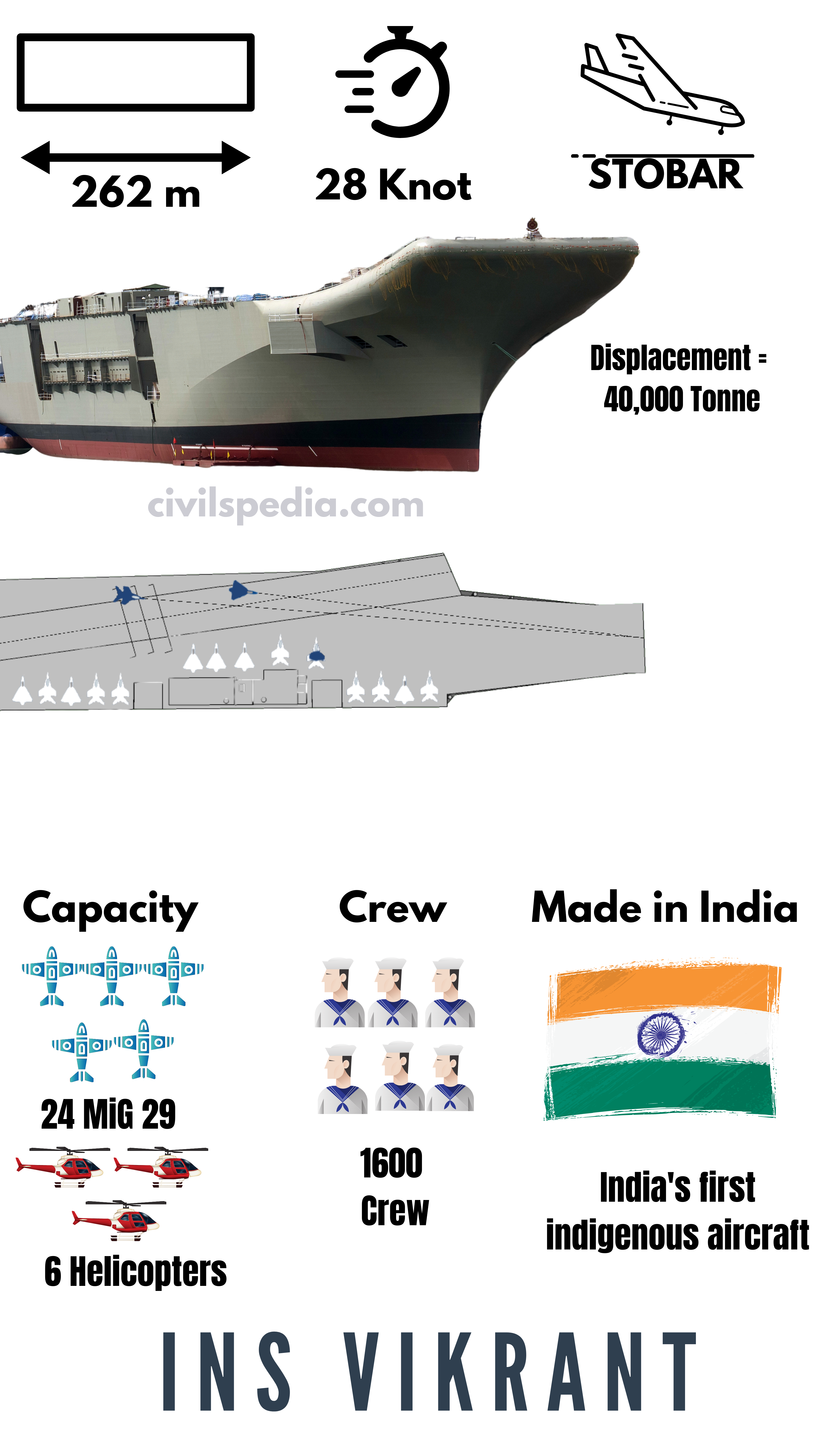
2. INS Vikrant or IAC-1
- INS Vikrant is the country’s first indigenous aircraft carrier. India has joined the elite club that can manufacture its aircraft carriers (others include the US, Russia, France, the UK and China). It was delivered to the Indian Navy and commissioned on 15 August 2022, marking 75 years of Indian independence.
- It is designed by the Indian Navy’s Directorate of Naval Design (DND) and built at Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL). Hence, it is a ‘Made in India’ ship. With this, India has joined the group of six nations which have this capability.
- Its features include
- Weight = 19,500 Kg
- Displacement of 40,000 tonnes.
- Speed of 28 knots
- It will carry 24 Russian MiG-29 aircraft and Kamov-31 helicopters, MH-60R Seahawk Helicopters and Advanced Light Helicopters (ALH).
- Two runways.
- It has STOBAR capability (i.e. Short Take-Off But Arrested Recovery)
- Long-range surface to air missiles.
- It has crew capacity of 1600
- Cost to built = Rs. 20,000 crore
Note: It is named after decommissioned INS Vikrant, India’s first Aircraft carrier, and was bought from Britain in 1961. It played an essential role in the Indian victory over Pakistan in 1971.
3. INS Vishal
- INS Vishal is the proposed name of India’s third aircraft carrier.
- It will be a 65,000-ton vessel, bigger than both INS Vikramaditya and Vikrant.
- It is not yet approved by the Government of India. However, it will be India’s second indigenous aircraft carrier when approved.
Other Warships
1. Kolkata Class (Project 15-A)
- Kolkata class is a group of destroyers made under Project 15A. These are a class of guided-missile destroyers constructed for the Indian Navy.
- There are three ships built under the Kolkata class.
- INS Kolkata
- INS Kochi
- INS Chennai
- These are built at Mazagaon Dock Limited (MDL) in India and are the largest destroyers to be operated by the Indian Navy.
2. Vishakhapatnam Class (Project 15-B)
- The destroyers of this class are more advanced than the Vishakhapatnam class and have stealth capabilities.
- There are four ships built under this Vishakhapatnam Class
- INS Vishakhapatnam (undertrials)
- INS Mormugao (commissioned)
- INS Imphal (construction)
- INS Surat (construction)
3. Nilgiri Class (Project 17-A)
- Nilgiri Class is a group of frigates made under Project 17A.
- There are seven frigates made under Nilgiri Class (all named after hills)
- INS Nilgiri
- INS Himgiri
- INS Udaygiri
- INS Dunagiri
- INS Taragiri
- INS Vindhyagiri
- INS Mahendragiri
- These are built at Mazagon Dock Limited (MDL) in India.
4. Talwar or Krivak Class
- It is a class of Indian Stealth Frigates being built in Russia.
- Total four frigates are to be built under the project, two of which have already been built
- INS Tushil
- INS Tamala
- 2 more are under construction.
- Features of this class include
- Stealth features with low radar and underwater noise signatures
- Installed with Surface to Surface Missiles
- Equipped with Surface Surveillance Radar and Sonars
5. Kamorta Class (Project 28)
- Kamorta class is a group of Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) stealth corvettes built under Project 28 by Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata.
- There are four corvettes built under Kamorta Class.
- INS Kamorta
- INS Kadmatt
- INS Kiltan
- INS Kavaratti
6. INS Astradharini
- India’s first indigenously designed (95%) and built torpedo launch and recovery vessel (TLRV).
- It is an advanced replacement for Astravahini.
Side Topic: Decommissioned Ships
INS Vikrant
- The warship was decommissioned in 2014.
- Initially known as HMS Hercules, India purchased it from Britain in 1961. It played a strategic role in the 1971 war with Pakistan.
- Now Bajaj is using its steel in making motorcycles.
Submarines
Submarines are of three types & India need the correct mix of all three
1. Conventional Submarines (SSK)
- They use the diesel-electric engine as their source of power & have to surface daily to get oxygen for fuel combustion.
- India needs 20 SSKs but has only.
- 9 Sindhughosh Class (Russian Kilo Class)
- 4 Shishumar Class (German Type 209)
- 5 Scorpene Class submarines inducted from Project 75
India had plans under Project 75 & Project 75(I), under which the intention is to build two production lines in collaboration with two foreign submarine builders to build 6 submarines each. In the meantime, the Navy would come up with indigenous designs to produce 6 submarines immediately, each on these production lines producing a total of 24 subs by 2030. Although the project is behind schedule, we have made 5 subs under Project 75.

5 Subs (out of 6) under Project 75 has been made (Scorpene-Class Submarines made by French Maker DCNS )
1. INS Kalvari
- It was inducted in 2017 (5 years behind schedule).
- It is the first submarine constructed under Project 75.
- The literal meaning of “Kalvari” is ‘ Sea Tiger.’
2. INS Khanderi
- It was inducted in 2018.
- Khanderi is the name of Maratha Island Fort.
3. INS Karanj
- It was inducted in 2019.
- The name ‘Karanj’ is derived from Karanja island, a town in the Raigad district.
4. INS Vela
- It was inducted in 2021.
- The name ‘Vela’ is derived from the name of a predatory fish. It was also the name of one of India’s decommissioned submarines of Soviet origin.
5. INS Vagir
- It was inducted in 2023
- Vagir is the name of sandfish (a predatory variety of fish).
6. INS Vagsheer
- It is the sixth submarine developed under Project 75.
- It will be commissioned in late 2023.
2. Nuclear Submarines (SSN)
- These are powered by nuclear reactors (but they can’t launch Ballistic Missiles). As a result, they can remain submerged for months.
- Given the security needs of India, the Indian Navy needs 6 SSNs.
- MoU was signed with Russia to provide 2 Akula Class SSNs on lease for 10 years. India got one in 2012 (INS Chakra) & the other one has still not reached India.
3. Nuclear Submarines with Ballistic Missiles (SSBN)
- They are nuclear-powered submarines along with the capability to launch Ballistic Missiles with nuclear warheads.
- These Submarines act as the third leg of the nuclear triad.
- India needs 3 to 5 SSBN but don’t have any.
- India is building an SSBN class submarine known as INS Arihant indigenously. The submarine is almost ready.

- INS Aridhaman is the next in line after Arihant and is still in the development stage.
Side Topic: Nuclear Triad
Nuclear Triad means the 3-pronged capability to launch a nuclear strike
- Land-launched nuclear missiles (e.g., Agni Missiles of India).
- Nuclear-missile-armed submarines (INS Arihant is SSBN).
- Strategic aircraft with nuclear bombs and missiles (Su 30 MKI can be integrated with Brahmos).

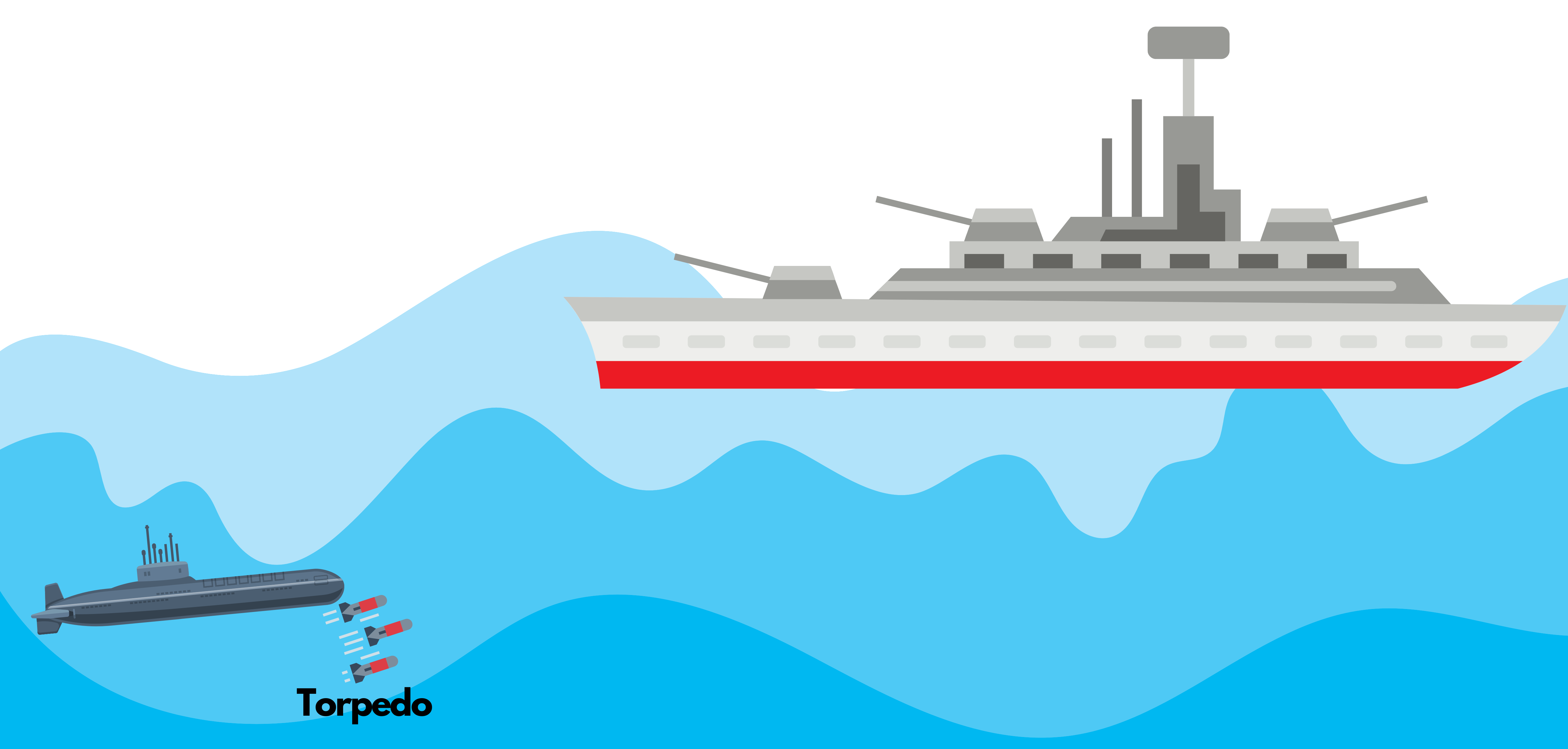
Torpedo
Torpedoes are underwater weapons fitted in warships and submarines with the aim to destroy enemy ships.
List of Indian Torpedoes
| Varunastra | Anti-Submarine Torpedo (India’s first indigenous torpedo) |
| Shyena | Anti-Submarine Torpedo |
| SMART | Long Range Torpedo |
Navy Aircrafts
Indian Navy has aircraft for reconnaissance and attack purposes.
List of Naval Aircrafts
1. Reconnaissance Naval Aircrafts
| P-8I | US Aircraft manufactured by Boeing |
| Dornier 228 | German origin reconnaissance aircraft |
| IL 38 | Russian origin reconnaissance aircraft |
2. Attack Naval Aircrafts
MiG 29: Russian origin attack planes posted on INS Vikramaditya
Side Topic: P-8I
- P-8I is the maritime surveillance, coastline defence, search and rescue and anti-submarine aircraft.
- Manufacturer: Boeing
- India has been using these since the delivery of the first aircraft in 2013. Presently, India has two squadrons of P-8I.
