Table of Contents
Mauryan Architecture
This article deals with topic titled ‘Mauryan Architecture .’ This is part of our series on ‘Culture’ . For more articles , you can click here
Introduction
- Major architectural input of Mauryan Art was wood. Hence,remains are very scant
- Reminiscent of Persian Achaemenid Architecture.
- Ananda Coomaraswamy has divided Mauryan Art in following way
Mauryan Palace
- Remains are scanty because timber was the main material
- Pillar fragment was discovered in Kumrahar (place in Patna) in 1903 . 72 pillars found in 1903 were arranged in neat chessboard pattern & 8 pillars were discovered later . Pillars were made of buff colored Chunar sandstone & smooth polished surface
- Although they were made of same stone as free standing Ashokan pillars but they were thinner & shorter. All have hole on the top clearly for metal dowels that connected shaft to capital which in turn supported roof.
- Some marks were found on their bases including crescent on hill (insignia of Mauryas) .
- Discovery of large quantity of ash & pieces of burnt wood indicated that floor & roof were made of wood & structure was subjected to fire
- There were no traces of walls & hall seems to be open on all sides
- Spooner was struck by similarity between pillared hall at Kumrahar & Darius’s hall of Public audience at Persepolis in Iran but Maurya structure is less elaborate than persian palace . Along with that, precise function of 80 pillared Mauryan hall is unknown

Stupas
- Stupas were known before the time of Ashoka too but Ashoka divided the existing body relics of Buddha & erected Stupas to enshrine them . Hence, Stupa became object of cult worship
- In Buddhist Tradition, originally 9 stupas were erected – 8 over relics of Buddha & 9th on vessel in which relics were originally kept at Rajagriha, Vaishali, Kapilvastu, Allakapa, Ramagrama, Vethadipa, Pava, Kushinagar and Pippalvina.
- Material used in initial Stupas
| Core of Stupa | Made up of Unburnt Bricks |
| Outer Face | Made of Burnt Bricks & covered with thick layer of plaster |
- In subsequent century, stupas were elaborately built with certain additions like the enclosing of the circumambulatory path with railings, gateways & sculptural decoration. Thus, with the elaborations in stupa architecture, there was ample space for the architects and sculptors to plan elaborations and to carve out images
- Three chhatra on the stupas represent triratnas of Buddhism i.e. Buddha (The enlightened), Dhamma (doctrine) and Sangh (order).
1 . Barhut Stupa
- Barhut is situated in eastern part of MP
- Stupa at Barhut was made by Ashoka around 300BC but improvised & beautified by Shungas
- Unlike Mauryan imperial art, inscription on railings were made by lay people&monks
- Earliest stupa railings (vedika) to have survived
- Sculpture mainly include Yaksha & Yakshinis
- Has nine feet railing (vedika) & gateway(torana) made in imitation with wooden architecture
- On railings are depicted stories of virtuous qualities of Budha & Jataka stories
- Sculpture done here is low in relief and narratives are few in words
- In one sculpture, story of Queen Mahamaya (mother of Buddha) is depicted where she is reclining on bed and elephant is shown on top heading towards womb

2. Sanchi Stupa
- Sanchi is in MP
- Monuments present in the complex : Two stupas+ some temples + Pillar edicts + monasteries
- Stupa is the Oldest stone structure
- It has long history
- It was commissioned by Ashoka
- Later , Pushymitra Shunga of Shunga Dynasty vandalised it
- Again it was rebuild by Agnimitra Shunga who also added Railings (Vedika) to it
- Later, it was repaired by Satavahanas who also added Toranas (Gateway) to it.
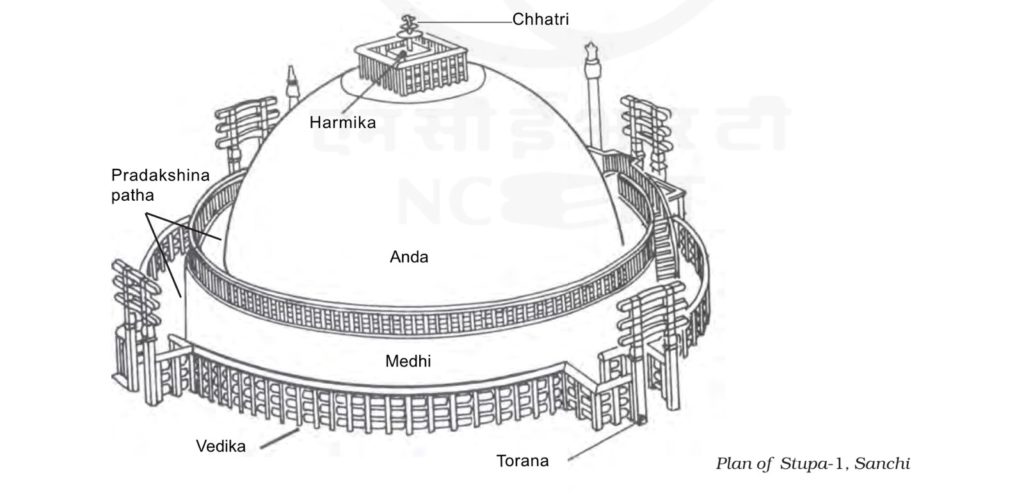
- Nucleus is hemispherical brick structure built over relics of Buddha
- Has upper & lower Paradakshinapatha or Pathways
- It also has Four beautifully decorated Toranas depicting various life events of Buddha & Jataka stories
- In contrast to Barhut, relief in it’s railings is high & more naturalistic . Carving technique is also more advanced than Barhut

3. Dharmarajika Stupa (Taxila)
- Several Stupa-Monastery sites are there in Taxila out of which Dharmarajika (locally called Chir Tope) is most important
- Belong to Maurya period


Please complete remaining topics
We are working towards that