Last Updated: May 2023 (Metallic Minerals)
Table of Contents
Metallic Minerals
This article deals with ‘ Metallic Minerals (UPSC Notes).’ This is part of our series on ‘Geography’, which is an important pillar of the GS-1 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Introduction

- Minerals containing one or more metallic elements are called metallic minerals.
- Metallic Minerals provide a strong base for the development of the metallurgical industry & hence the process of industrialization.
1. Iron Ore
- Iron ore is the most critical mineral on which a nation’s economy hinges.
- In 2018, India became the 2nd largest producer of Steel in the world, following China.
- India has the largest reserve of iron ore in Asia.
- Haematite and Magnetite are the two primary varieties of iron ore found in our nation.
- Due to its superior quality, Indian iron ore is in high demand in the global market.
- In the country’s north-eastern plateau region, the iron ore mines are located adjacent to the coal fields, adding to their advantage.
4 Main Ore Types
1. Magnetite
- It is also known as Black Ochre.
- It has a high iron content of up to 70%.
- As the name suggests, it has magnetic properties.
- The largest concentration of Magnetite is found in Sweden, Liberia & former USSR. It is found in India as well.
- It is used in Electronic industries.
2. Haematite
- It is the industrially most important ore.
- It contains 50-65 % iron content
- It is known as Red ochre.
- The largest concentration of Haematite is found in the Lake Superior Region, Labrador & Quebec in Canada, Guinea Highlands in Venezuela, Brazil etc. & the Dharwarian & Singhbhum rocks of India.
- In India, it is found in the Chotanagpur Plateau region, Dharawar & Cuddapah systems of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu (Salem, Tiruchi) & Goa.
- The main use of Haematite is in the iron & steel industries.
3. Limonite
- Limonite has less than 50% iron content.
- It is yellow in colour.
- It is used as pigment for paint manufacturing.
4. Siderite
- Siderite is the carbonate of iron. It is found interbedded in sedimentary rocks.
- Iron content is 20-30%. Hence, it is economically unviable to extract.
- It acts as a source of Manganese & Magnesium.
Distribution in World
| North America | Lake Superior Region, Labrador & Quebec |
| South America | Brazil |
| Africa | Liberia, South Africa & Algeria. |
| Europe | Sweden, France (Normandy & Lorraine), Former USSR, UK & Germany |
| Asia | India & China (Manchuria & Wuhan) |
Distribution in India
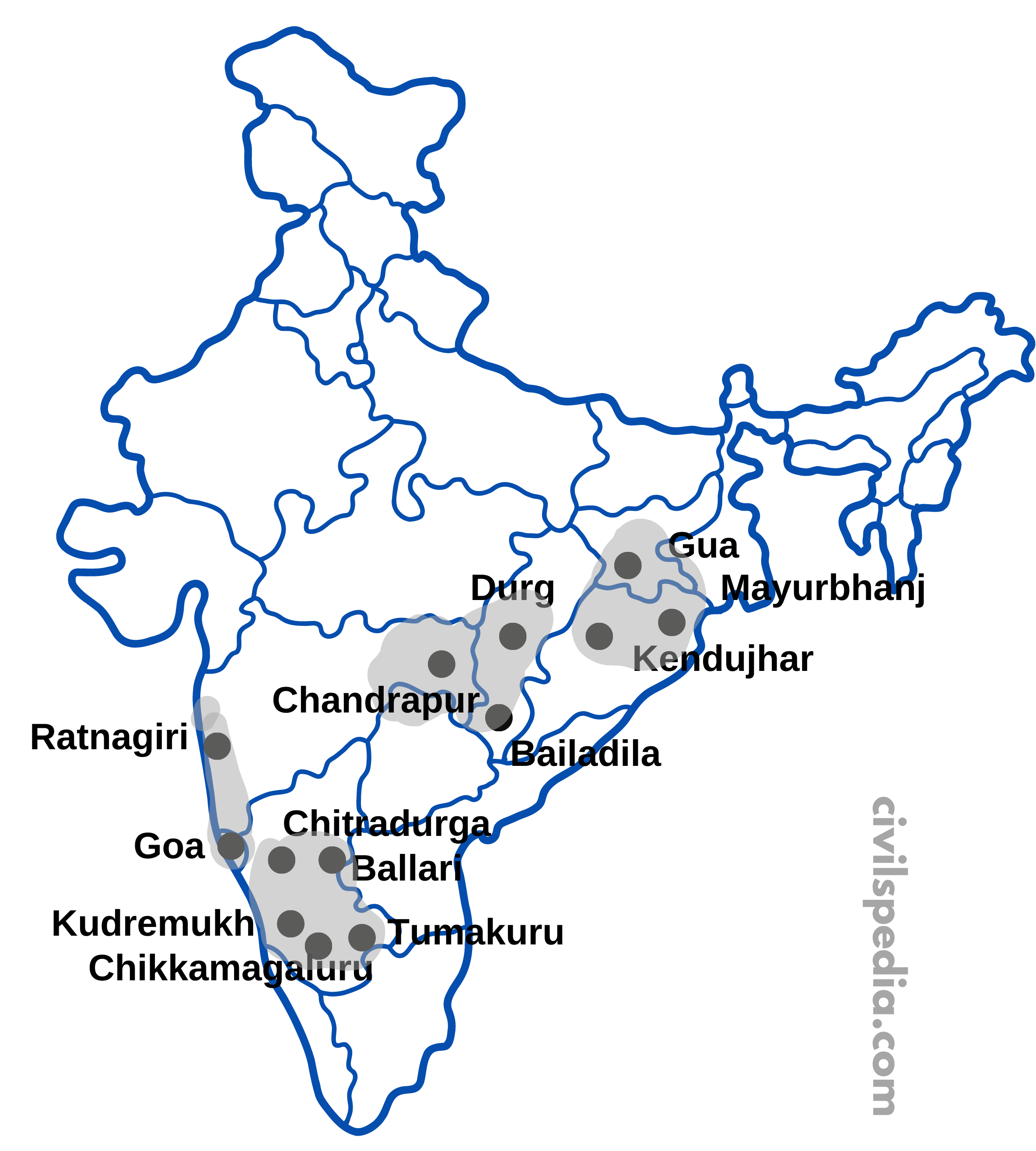
The country’s total reserves of iron ore were about 20 billion tonnes in 2004-05. Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Karnataka, Andhra, Telangana, and Tamil Nadu contain over 95% of the country’s iron ore deposits.
1. Odisha
- Iron ore occurs in a series of hill ranges in Sundergarh, Mayurbhanj and Jhar.
- Important mines are Gurumahisani, Sulaipet, Badampahar, Mayurbhanj, Kiruburu (Kendujhar) & Bonai (Sundergarh).
Details of Important Mines
| Badampahar | Iron ore is supplied to Bokaro, Jamshedpur, Rourkela & Durgapur steel plants. |
| Mayurbhanj | – Haematite with an iron content of more than 65% is found here (the highest quality found in India ) – Iron ore is supplied to Bokaro, Durgapur, Rourkela & Jamshedpur. |
2. Jharkhand
- There are some of the oldest iron ore mines & steel plants in this region.
- The most important mines are Noamundi and Gua in Poorbi and Pashchimi Singhbhum districts.
3. Chhattisgarh
Bailadila (Bastar) , Dalli Rajhara (Durg) & Dantewara are important mines in Chattisgarh
Details of Important Mines
| Bailadila | – It is located in the Bastar district & is the largest mechanized mine in India. – Haematite extracted from this mine is exported to Japan and supplied to the Vishakhapatnam plant. |
| Dalli Rajhara | – It is located in the Durg district. – Haematite extracted from these mines is supplied to the Hindustan Steel plant in Bhilai. |
4. Karnataka
In Karnataka, Iron ore is found in the following areas
- Sandur-Hospet area of Ballari/Bellary district.
- Baba Budan Hills and Kudremukh of Chikkamagaluru district.
- Parts of Shivamogga, Chitradurg & Tumakuru districts.
Details of Important Mines
| Baba Budan Hills | Mostly exported to Iran through Mangalore port. |
| Kudremukh Deposits | Exported to Iran. |
| Sandur Range | Supplied to Vijayanagar Steel plant. |
5. Maharashtra
- Found in districts of Chandrapur, Bhandara and Ratnagiri.
6. Telangana
- Found in Karimnagar and Warangal district.
7. Andhra Pradesh
- Found in Kurnool, Cuddapah and Anantapur districts.
8. Tamil Nadu
- Found in Salem and Nilgiri districts.
9. Goa
- Iron ore is found in North Goa.
- Mormugao port provides an additional advantage from where Iron ore is exported to Iran & Japan.
2. Manganese
- India is 5th largest producer of Manganese in the world.
- About 1/5 of Indian Manganese is exported mainly to Japan.
Uses
- Manganese is needed during iron forging. If Manganese is not added to iron, iron breaks. It makes steel anticorrosive, hard& tough.
- It is used to produce alloys by mixing with Copper, Bronze, Nickel etc.
- It is also used in manufacturing insecticides & pesticides, photography and dry battery.
Global Distribution
| Africa | South Africa and Gabon |
| South America | Brazil |
| Europe | Ukraine and Russia |
| Asia | India |
| Australia | Australia (Victoria & Queensland) |
Distribution in India
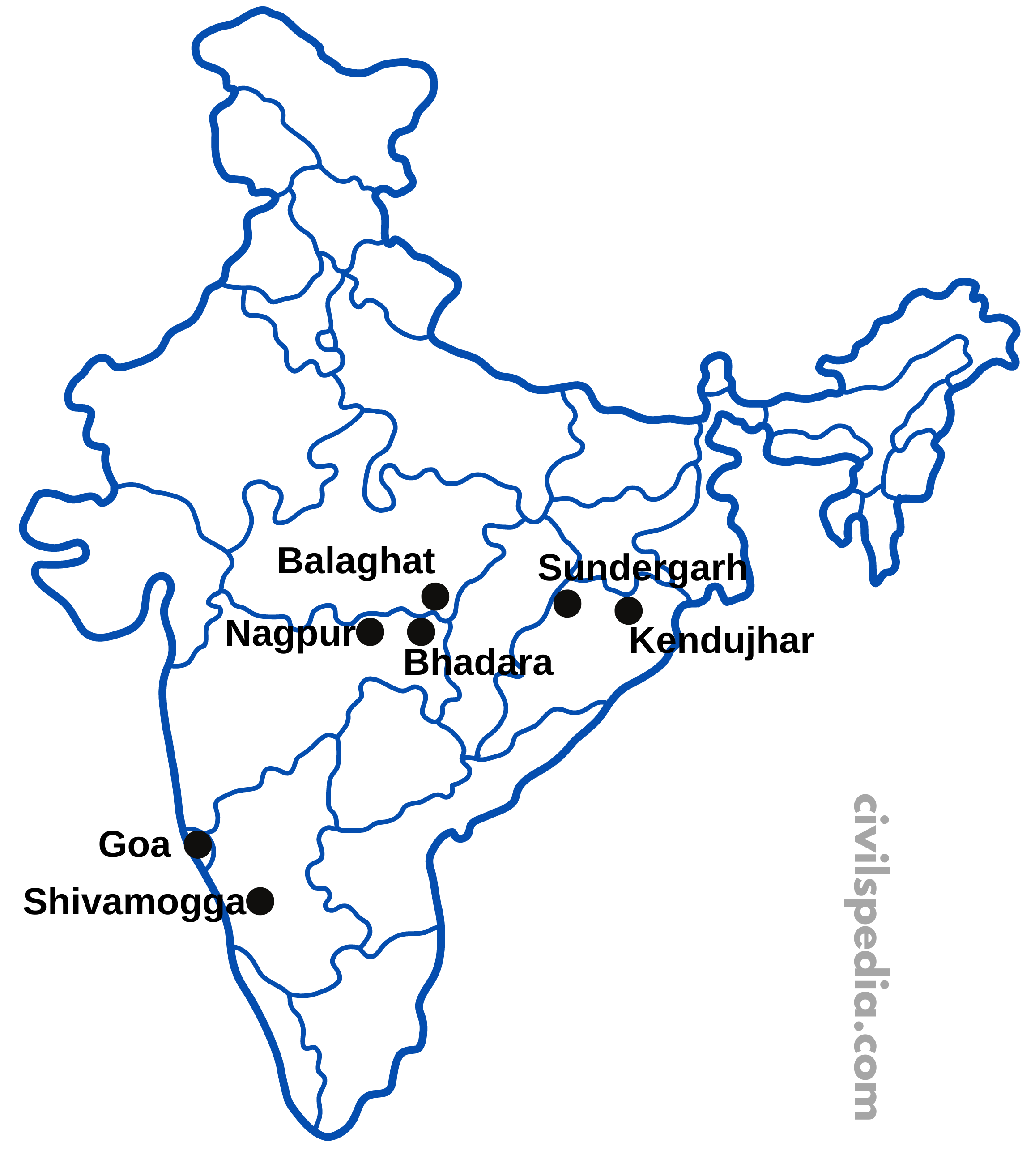
Almost all geological formations include deposits of Manganese. However, it is mainly associated with the Dharwar system.
| Odisha | – Odisha is the largest producer of Manganese. – Major mines are located in the Iron ore belt, i.e. Kendujhar, Sundergarh, and Koraput. |
| Karnataka | The Manganese mines are located in Dharwar, Belagavi, Ballari, Chikkmagaluru, North Canara, Chitradurg, Shivamogga and Tumkur. |
| Maharashtra | Nagpur, Bhandara and Ratnagiri districts. |
| Jharkhand | Manganese is found in all iron ore regions. Chaibasa is the biggest mine. |
| Madhya Pradesh | Manganese is found in the Balaghat region. |
Note: Manganese was mined for the first time in Srikakulam (1892) in Andhra Pradesh.
3. Bauxite
- 8% of the Earth’s crust is made up of Aluminium.
- Bauxite is mainly found in tropical & subtropical regions, but Aluminum is separated from the ore in an area with cheap electricity using the Hall Herault method.
- The first bauxite mine was in Les Baux village in France. Bauxite name derived from it.
Global Producers
| Bauxite reserves | Bauxite Producers | Alumina | Aluminium |
| Guinea | Australia | China | China |
| Australia | Brazil | Australia | Russia |
| Brazil | China | Brazil | Canada |
| India (Rank 6) | India (Rank 5) | India ( Rank 6) |
Global Distribution
| North America | USA (but significant import from Jamaica, Surinam etc.) |
| South America | Guinea, Jamaica, Surinam and Brazil |
| Europe | France, Yugoslavia, Hungry and Russia(Urals) |
| Asia | Vietnam, India and China |
| Australia | Australia (exported to Japan) |
Distribution in India
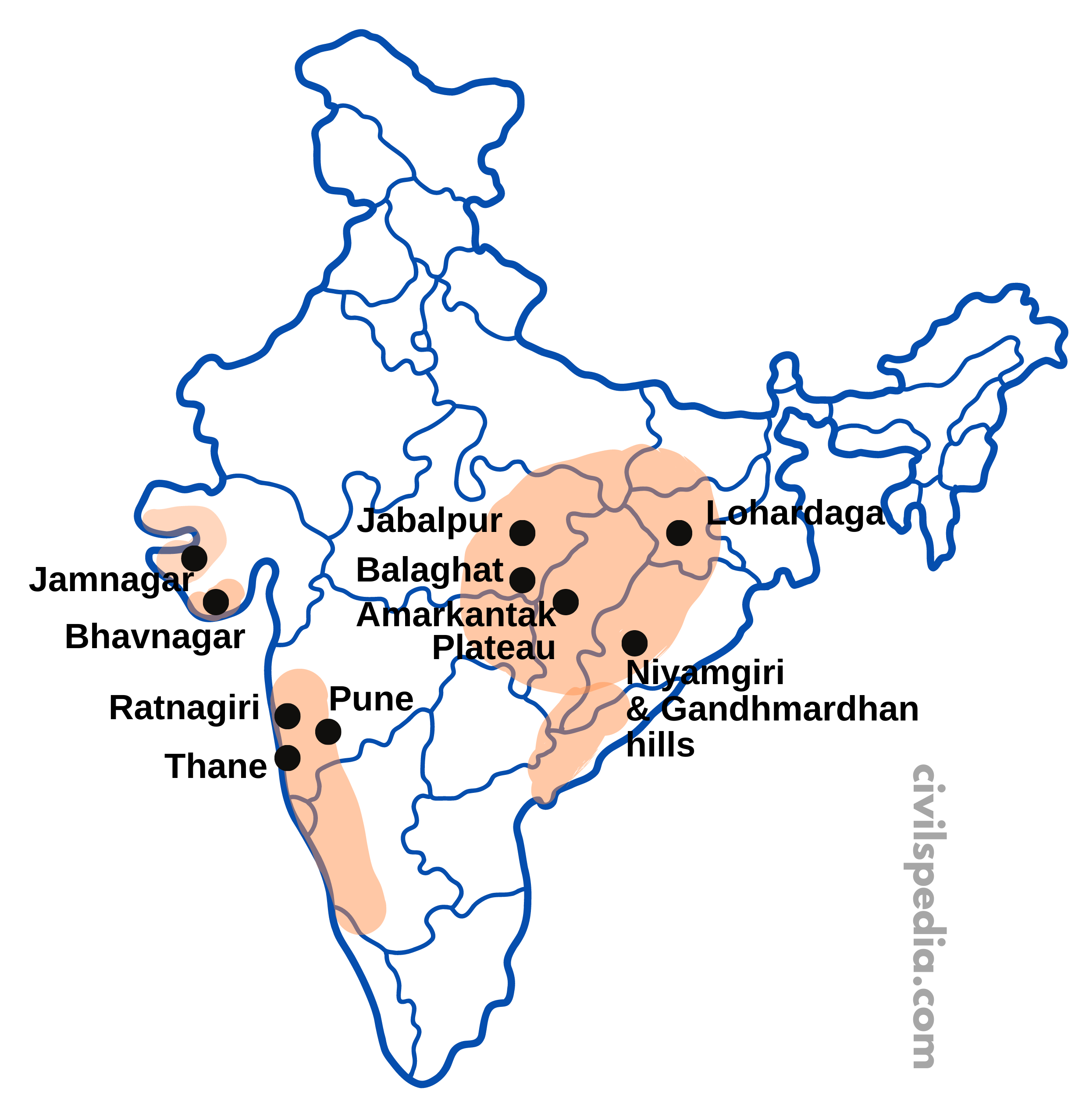
Bauxite is found mainly in tertiary deposits. It is associated with laterite rocks, commonly found in coastal areas and Peninsular India.
| Odisha | – Odisha is the largest producer of Bauxite. – Niyamgiri & Gandhmardhan hills are biggest fields . – Bauxite Mines are present in Kalahandi, Sambalpur, Bolangir and Koraput. |
| Jharkhand | Lohardaga |
| Gujarat | Bhavanagar and Jamnagar |
| Chattisgarh | Amarkantak plateau |
| Madhya Pradesh | Katni-Jabalpur area and Balaghat |
| Maharashtra | Kolaba, Thane, Ratnagiri, Satara, Pune and Kolhapur |
4. Copper
- Copper is a soft brown metal found in igneous & metamorphic rocks.
- The main ores of Copper are Cuprite, Malachite, Chalcocite & Bornite.
- In the electrical industry, Copper is a crucial metal for producing cables, electric motors, transformers, and generators.
- It is alloyable, malleable and ductile and a good conductor of heat and electricity. Since gold is a soft metal, Copper is mixed with it to strengthen jewellery.
- The most important alloys of Copper include
- Brass: Alloy of Copper and Zinc
- Bronze: Alloy of Copper and Tin
Global Distribution
| North America | USA (West coast), Canada (Ontario & Quebec) and Mexico |
| South America | Chile and Peru |
| Europe | Russia (Urals), Georgia and Armenia |
| Asia | Kazakhstan |
| Australia | Australia (Mt Esa & Mt Morgan) |
| Africa | Zaire (Katanga Plateau), Zimbabwe and Zambia. |
Distribution in India
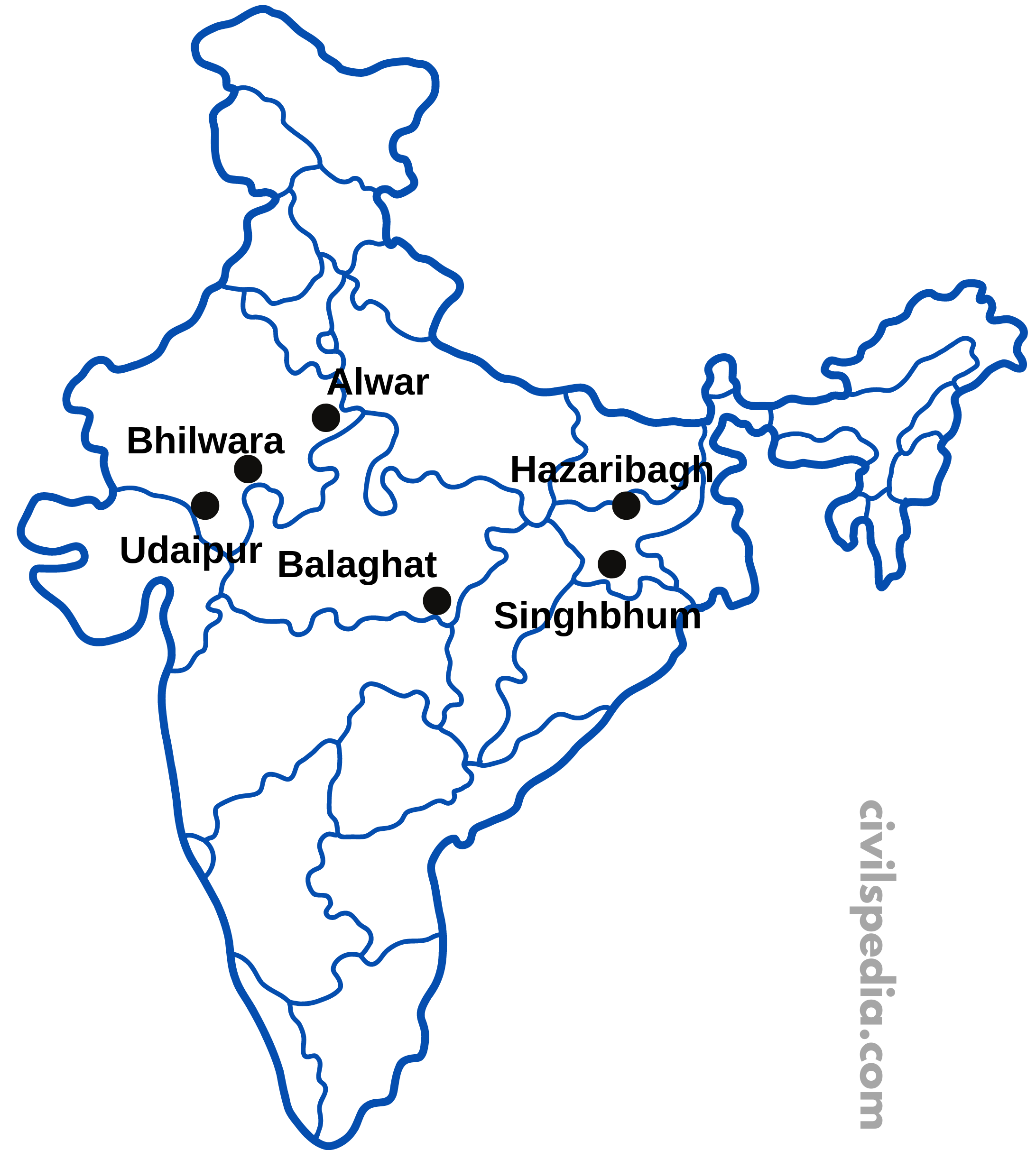
| Jharkhand | Singhbhum and Hazaribagh |
| Madhya Pradesh | Balaghat |
| Rajasthan | Udaipur, Bhilwara & Alwar |
Indian share in world production is 4%. India isn’t self-sufficient and imports Copper from Zimbabwe, Australia, USA & Mexico.
5. Gold
- Gold is known as the international currency.
- Properties: durable, doesn’t rust, luster, malleable & ductile.
- It is used as an ornament as well as to mint coins (historically).
Global Distribution
| Africa | South Africa, Zimbabwe and Ghana |
| North America | Canada and USA |
| South America | Columbia, Peru, Ecuador and Brazil. |
| Europe | Former USSR |
| Asia | China, Japan, Korea and India |
| Australia | Australia |
Distribution in India
About 90% of production is from Karnataka & rest is from Rajasthan, West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar & Andhra Pradesh. Three important gold fields in India.
1. Karnataka
1.1 Kolar Gold Mines, Mysore
- Mining started here in 1871.
- It still contributes 60 % of the total production of the country.
- The mine is more than 3000 m deep, and almost all gold has been extracted.
1.2 Hutti Goldfield, Raichur dist.
- It is the only gold-producing company in India.
2. Andhra Pradesh
- Ramgiri Goldfield and Anantapur.
3. Placer or Alluvial gold
- Gold is obtained from sand & sedimentary deposits of the river.
- It is found in the Subarnrekha river in Jharkhand & Lo in the Singhbhum district of the Chotanagpur plateau.
6. Silver
- Silver is white & valuable metal.
- It is used in making ornaments & mint coins (historically).
- Main ores include Argentine, Stephanite & Proustite.
- It is found in association with zinc & lead.
Global Distribution
| North America | Mexico, Canada and USA |
| South America | Bolivia and Chile |
| Europe | Spain, Germany, Sweden, Italy and France |
| Asia | Japan, Myanmar and India |
| Australia | Australia |
Distribution in India
- India is not very rich in silver.
- Rajasthan is the largest producer owing to following
- Zowar mines in Udaipur.
- In Hindustan Zinc Smelter in Udaipur, Silver is obtained as a by-product of Zinc & Lead.
- Other producers include
- Tudoo Lead Smelter: Dhanbad(Jharkhand)
- Kolar Gold Field & Hutti: Karnataka
- Vishakhapatnam Smelter: Andhra Pradesh
