Table of Contents
Role of Social Networking Sites in Internal Security Challenges
This article deals with the ‘Role of Media in Internal Security Challenges.’ This is part of our series on ‘Internal Security’, an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Social Media / Social Networking
Definition: IT IS A GROUP OF ONLINE APPLICATIONS THAT ALLOW FOR THE CREATION AND EXCHANGE OF USER-GENERATED CONTENT AND ARE BUILT ON THE IDEOLOGICAL AND TECHNOLOGICAL FOUNDATION OF WEB 2.0.
Social media is different from (ordinary) Media. Social Media allows people to raise voices who otherwise couldn’t speak or wouldn’t be heard. Hence
- Media= Source of information
- Social Media = Source of Information + Platform for Expression
Categories of Social Media
| Blogs and Microblogs | |
| Content and Communities | Youtube and Dailymotion |
| Social Networking Sites | Facebook, Instagram etc. |
| Wikis | Wikipedia |
| Blogs | There are blogs of many writers, poets, and celebrities where the entries are written in a personal, conversational style. |
| Virtual World Games | World of Warcraft |
| Virtual Social World | Second Life |
But there is no clear demarcation between them.
Characteristics of social media
1. User-generated Content
- Citizens are participants, authors and content creators.
2. Conversation
- Allow the users to start a conversation. E.g., Twitter gives 24*7 opportunities for two-way discussion.
3. Building Relationships
- Social Media helps build new relationships and find friends based on shared interests, along with helping to maintain older ones.
4. Communication
- Social Media can send mail, text message or voice message. Social Media has reduced communication barriers among people.
5. Information Sharing
- Social Media is an information-sharing tool and can be assessed and commented on in real-time.
6. Building the Public Narrative
- Social Media has become the most crucial instrument in today’s world to build the public narrative. E.g., In Indonesia, Instagram influencers were given 1st Corona vaccine, along with doctors, to dispel the religious fears among citizens that the vaccine is not ‘haram’ given that Pig gelatine was used as a stabilizer in the vaccine.
7. Marketing
- Many organizations use social media strategies to reach out to customers and peers. Even governments have been using social media to broadcast information about schemes and programs.
But there are some negative characteristics
1. Unregulated Nature
- Its content cannot be controlled, censored or shut down.
- It can harm national security and lead to riots.
- The servers of most of the social media channels are located outside India.
2. Algorithmic filtering / Echo Chambers
- Algorithms of Social Media sites are designed to create filter bubbles/echo chambers in which users only see viewpoints they agree with, which further hardens their prejudices.
3. Unequal Participation
- On social media, the fringe groups could appear mainstream and vulnerable populations with lower social media footprint could end up ignored.
4. Fake News
- It has allowed criminal actors to launch misinformation campaigns and incite violence.
5. Foreign interference
- Foreign countries and their agencies can use Social Media as an information weapon to influence public sentiment in elections. E.g., Alleged interference by Russians in the 2016 US Presidential elections.
6. Provide a wider audience to the extremists
- Extremists also use social media to live stream violent acts. E.g., White Supremacists livestreamed the killing of people in Christchurch, New Zealand (in 2020), showing how terrorists are using technology for their end.
Threats posed by Social Media
1. Use of Social Media by Terrorists
1.1 Spread Propaganda
- Internet & social media are used to spread ideological instructions & induct recruits by terrorist organizations. E.g., ISIS was able to attract Youth from European Nations and the US via their Social Media propaganda.
1.2 Financing
Terrorists use social media to gather funds to finance their activities. Methods used by them include
- Direct Solicitation: through websites, mass mail etc.
- E-commerce: Terrorists use online payment tools to collect funds
- Exploitation of Online Payment Tools: Younis Tasauli, a terrorist, was the mastermind of UK Credit Card Fraud. Money collected through fraud was used to fund terrorist activities.
1.3 Training
- Terrorist groups are using Social Media sites to instruct on making explosives and carrying out terrorist attacks, along with methods to join the terrorist organization.
- Al Qaeda even had an online magazine called ‘INSPIRE‘.
1.4 Planning & Execution
- It involves remote communication between several parties, and social media help terrorist organizations in this regard.
- End-to-end encrypted messages provided by platforms such as WhatsApp also help these terrorist organizations as these can’t be intercepted by intelligence agencies.
1.5 Cyber Attack
- It is the deliberate exploitation of computer networks as a means to launch an attack. Terrorist organizations are frequently carrying out cyber attacks.

2. Use of Social Media in Riots
- In the past few years, several instances have come to focus where communal clashes are being planned or instigated through fake videos circulating on Social Media.
- Police acknowledged that WhatsApp groups were used to incite Muzaffarnagar riots in the run-up to the 2014 elections. Indian Mujahidin and Hindu fundamentalist groups incited these riots by circulating fake videos.
- Facebook and WhatsApp were used in the Delhi riots of 2000.
- Gau-rakshaks, Jat agitators, and protestors in Kashmir also took advantage of WhatsApp groups to organize themselves.
The Government has responded by banning the internet in such instances, making India the global leader in imposing internet blackouts. But that is only a tactical solution which prevents immediate violence.
- PARLER, a social network site similar to Twitter, was very popular among Trump supporters and was used by them to instigate Capitol building violence following the defeat of Donald Trump. The app was later banned from App Store.

3. Fake News
Fake news is news, stories or hoaxes created to misinform or deliberately deceive readers.
Agenda behind spreading Fake News
- Influence the view of people
- Push a political agenda or cause confusion: Governments of countries such as Venezuela, the Philippines and Turkey were found to employ an army of ‘opinion shapers’ to spread the view of the party in power, drive their agendas and distort online discussions.
- It can often be a profitable business for online publishers.
Fake news can be in the form of
- Satire
- Propaganda
- Out-of-context information
- Conspiracy theories
- Clickbait
Some incidents associated with Fake News
| 2012 | It led to a Mass-Exodus of North Easterners from Bangalore. |
| 2013 | Muzaffarpur Riots happened due to the spread of fake news (discussed above) |
| 2016 | Russia is alleged to have used fake news to manipulate the US Presidential elections, leading to the win of Donald Trump. |
| 2020 | Riots happened in Delhi after Anti-CAA protests due to the spread of fake news on social media. |
| 2021 | Capitol Hill violence happened in Washington DC due to the circulation of fake news that US elections were rigged and the real winner of the election was Donald Trump. |
Reasons for the spread of Fake News
- The rapid pace of information dissemination: The pace at which false information can spread, especially on Social Media, is unprecedented.
- Regulation problems: Social Media is difficult to regulate & censor due to its decentralized nature.
- Algorithmic filtering: Algorithms are designed in such a way that the content suggested conforms with what a person is watching based on his browsing history. It creates filter bubbles and echo chambers which harden a person’s prejudices.
- The fake news industry has developed as an organized industry, and companies have come up which provide the service of spreading fake news to anyone willing to pay the fees.
Threats posed by the Fake News
1. Political Threats
- Political parties try to gain political advantages by polarising the voters.
2. Economic Threats
- It can lead to loss of life and property, as fake news can lead to riots and lynchings.
- Fake news and subsequent breakdown of law and order machinery can also result in the shutting down of markets and disruption in the supply chains.
3. Societal Threats
- Fake news disturbs the social fabric of society as it can lead to tension and hostility between the communities.
4. International
- Other countries use it in psychological warfare.
- New technologies like Deep Fakes are used by the countries to target other countries.
5. Loss of faith in Media
- People have lost their faith in the media, and media houses are now seen as commercial entities
Ways to contain it
- Steps by various platforms
- Twitter: They tag those spreading Fake news as ‘Manipulated Media’.
- WhatsApp has introduced a feature to tell whether the message is forwarded. The veracity of forwarded messages is low.
- Facebook: Facebook has introduced features like tagging a page repeatedly flagged by their ‘fact checkers’.
- Various Indian sites like altnews.in provide fact-checks about various fake news circulating on social as well as mainstream media.
- Fake news can also be checked using Blockchain technology and Artificial Intelligence.
- Using Legal Provisions
- Sections 153A and 295 of the Indian Penal Code (IPC) can be invoked against someone spreading fake news to create religious animosity.
- Defamation Suit: A person may pursue a civil or criminal defamation case if they perceive fake news as defamatory.
- Contempt of Court law can be evoked against those spreading fake news about Judicial proceedings.
- Fundamental Duty to develop scientific temper: Citizens of the country are also required to develop a scientific temper, humanism and spirit of inquiry and reform under Article 51A (b) (Fundamental Duties). It can help to contain the spread of fake news.
- International Examples / Case Studies
- WHO has established the Information Network for Epidemics (EPI-WIN) to track and respond to misinformation, myths and rumours regarding the spread of epidemics (like Covid 19).
- BBC America has started a new initiative called SLOW NEWS to contain the spread of fake news, as the main reason for the circulation of fake news is the speed at which fake news is circulated in the age of social media.
4. Negative impact of Social Media on Children
- Social Media sites like Facebook are difficult to regulate, and they expose children to inappropriate material for their age.
- In 2017, a game called Blue Whale on social media led to Children Suicides.
- Trolling on social media can lead to depression among children.
5. Use of Social Media by Organised Criminal Groups
- Criminal organizations use Social Media as support, communication and coordination tools to conduct their illicit activities.
- These kinds of illicit activities can be either purely information ones (i.e. spreading child pornography with fee, “virtual” identity thefts, phishing, the spread of viruses, Trojans, worms, etc.), or “traditional” ones (i.e. drug smuggling, human trafficking, money-laundering, transfer of documents from industrial espionage).
6. Others
- Honey Trapping
- Cyberbullying: People can misuse social media platforms to spread rumours and share videos that destroy reputations.
- Trolling: Women, leaders from non-ruling parties and people from disadvantaged communities face a disproportionately high number of trolls.
- Jurisdictional challenge: There are complications in the jurisdiction as servers of social media sites like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram etc. are situated outside India.
Social Media and Police
The Police departments, globally and in India, are using social media in the following ways.
- To gather information.
- To create awareness by disseminating information and forewarning citizens.
- To maintain a public interface and reduce the communication gap.
- To increase citizen participation to identify crime.
- To get feedback from citizens and understand their grievances.
- Social Media provide anonymity. Hence, it helps citizens overcome their fear of complaining about law and order issues.
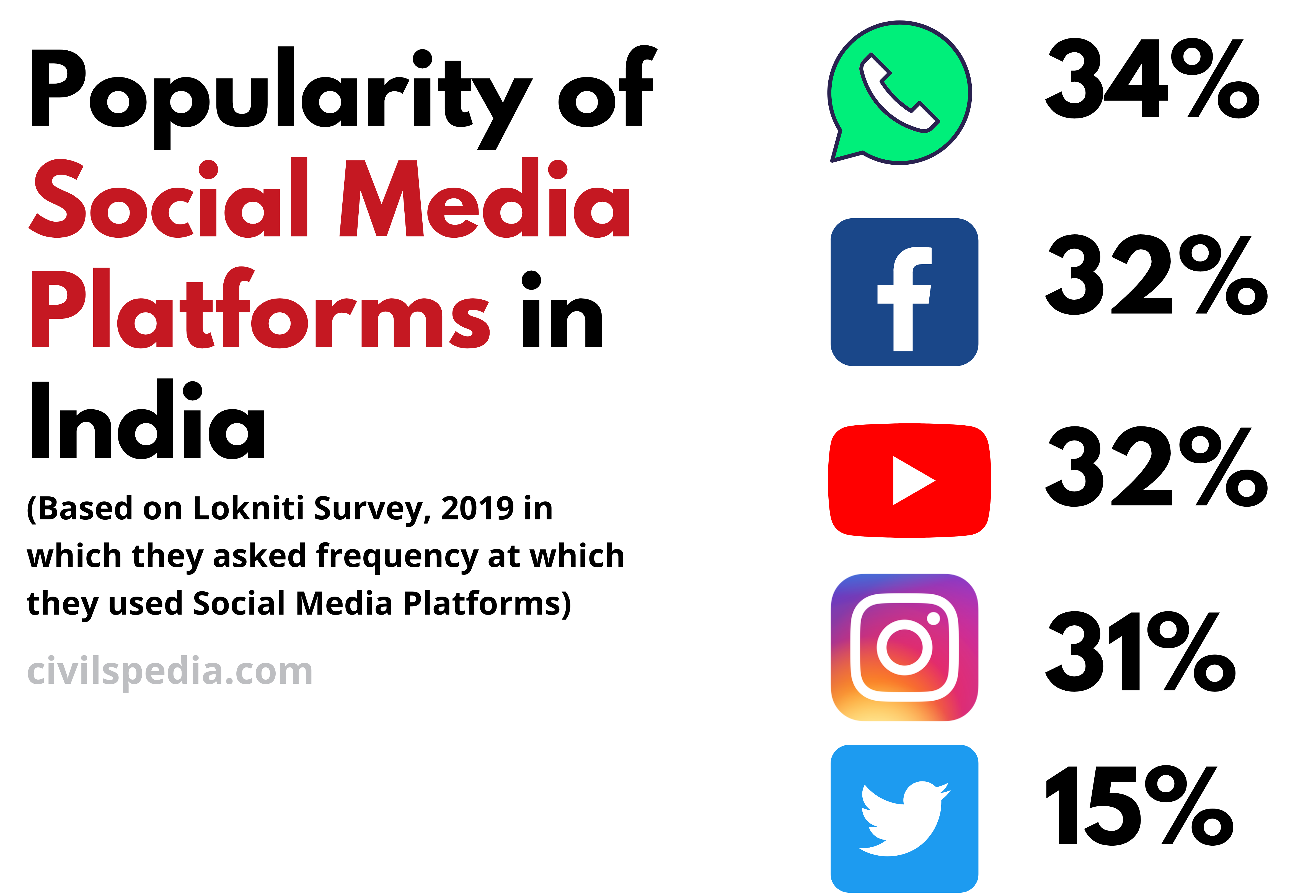
In India, the potential to use social media provides vast potential for policing in India, as millions of Indians are active users of Facebook, Twitter, WhatsApp and other platforms.
Police and other law agencies use it in many ways. Some examples are
- All the state police forces have their official Twitter, Facebook, Instagram etc., accounts for disseminating information and communicating directly with people.
- Social Media Labs Project by Maharashtra Police tracks activity on social media to anticipate and handle sudden flares up.
- Delhi Traffic Police is using platforms like Facebook and Twitter to ease the handling of traffic-related issues.
- Intelligence Bureau’s OPERATION CHAKRAVYUH uses Big Data Analysis of Social Media posts and other things to find trails of youth that are getting radicalized.
Social Media and Politics
Social Media has changed the ways of doing politics in India. Some of the examples to corroborate this fact includes
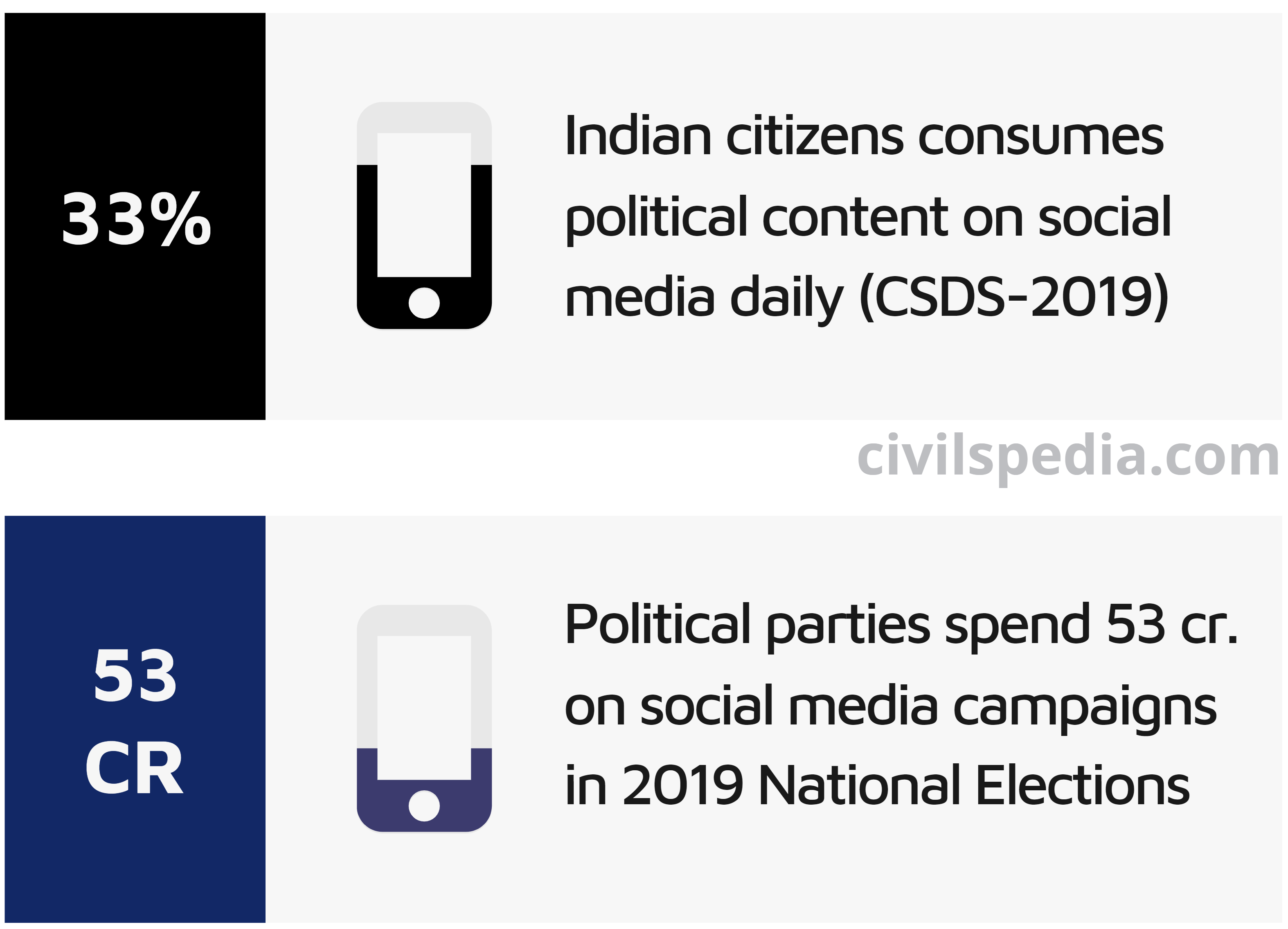
Benefits of Social Media in Politics
- Help the parties to disseminate their campaign, messages and ideas more effectively to the public.
- Facilitate two-way communication between the public and political parties.
- Cost-effective compared to print and digital media.
- Facilitate targeted delivery of the message.
- Levels the playing field
Issues
- Post-truth politics: “Post-truth” describes situations in which appeals to emotion and personal belief have a greater influence on public opinion than objective facts.
- Proliferation of fake news: Through social media, unverified information can circulate freely on the internet, increasing instances of fake news.
- Troll the dissenting opinion: Online abuse in the form of trolling, verbal threats etc., of people with dissenting opinions.
- Misuse of data: For example, 2018 Cambridge Analytica case where personal data of millions of Facebook profiles was harvested without their consent and reportedly used for targeted messaging.
- Propensity to fuel social instability: Allowing hate speech and extreme speech to thrive in unregulated online spaces, particularly in regional languages, has widened societal fault lines.
