Table of Contents
Karst Topography
This article deals with ‘Karst Topography.’ This is part of our series on ‘Geography’ which is an important pillar of the GS-1 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Introduction
- Limestone is a sedimentary rock of organic origin. Chemically it is Calcium Carbonate (but where Magnesium is also present, it is known as Dolomite).
- Limestone is soluble in rainwater with Carbon dioxide (weak acid.)
- A region with a large stretch of limestone, therefore, posses a very distinct topography termed Karst (name derived from Karst District of Yugoslavia where such topography is particularly well developed)
There is the absence of surface drainage as most of the surface water goes underground and form underground channels. When this water meets non-porous rocks, it re-emerges onto the surface as a spring or resurgence.
Location
- Karst region is in Dinarik Alps in Yugoslavia.
- Such topography is also found in regions of the Himalayas, Rockies, Andes, Atlas, Shan Plateau, Belo Horizonte etc.
- In India, this is found in Chirapoonji, Jammu-Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Panch Marhi (M.P.), Bastar (Chattisgarh and Coastal areas near Vishakhapatnam.
Landforms
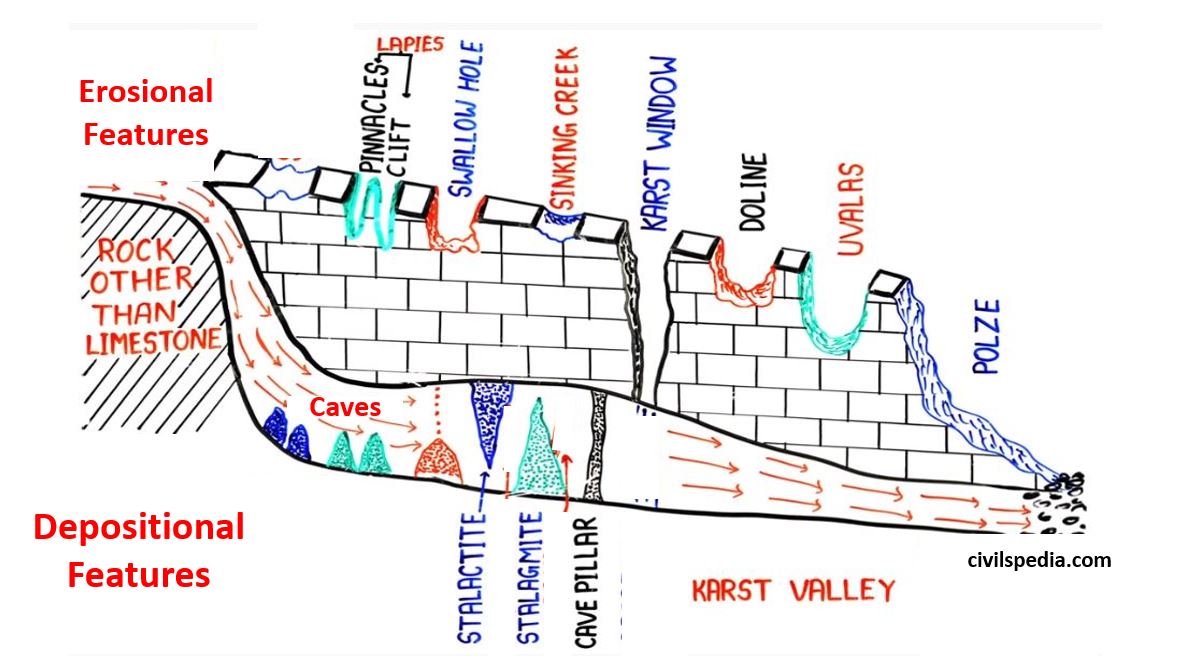
Erosional Landforms
1 . Lapies
- Lapies are the irregular grooves and ridges formed when most of the surfaces of limestone are removed by the solution process.
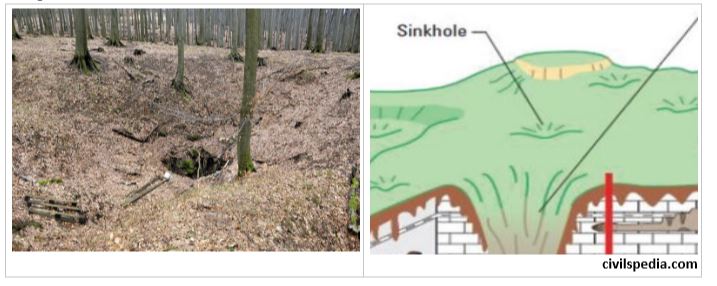
2. Swallow Hole /Sink Holes
- A sinkhole is an opening more or less circular at the top and funnel-shaped towards the bottom.
- On the surface of limestone, there are numerous small depressions carved out by solution at a point of weakness. Holes size grow through continuous solvent action to form Sink Hole.
3. Limestone Gorge
- When the roof of an underground tunnel collapses, a limestone gorge is formed.

4. Karst Window/ Karst fenster
- It is a spring that emerges from underground, discharge its water and then abruptly disappears underground through a nearby sinkhole.
5. Doline
- Due to high chemical activity on swallow holes, their size and depth increases. Its diameter may extend up to some kilometres and its depth may run up to 100 meters.
- It can be cylindrical, conical, bowl or dish-shaped.
- The name doline comes from Dolina, the Slovenian word meaning valley.
6. Uvala
- Series of smaller sinkholes coalesce into a compound sinkhole is called uvala.
7. Polze
- Polje is an elongated basin having a flat floor and steep walls.
- It is formed by the coalescence of several sinkholes. The basins often cover 250 square km and may expose “disappearing streams.”
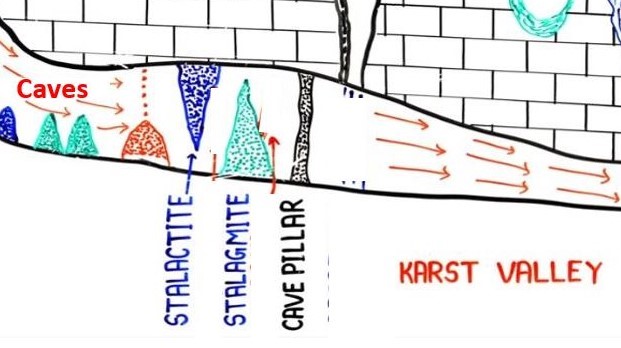
8. Cave
- In areas where there are alternating beds of rocks (shales, sandstones, quartzites) with limestones or dolomites in between or in areas where limestones are dense, massive and occurring as thick beds, cave formation is prominent.
- Water percolates down through the cracks and joints and moves horizontally along bedding planes. It is along these bedding planes that the limestone dissolves to form wide gaps called caves.
9. Tunnel
- Caves having openings at both ends are called tunnels.
Depositional landforms
- Where subterranean streams descend to underground passages, the region may be honeycombed with caves
- The most important features in limestone caves are Stalactites, Stalagmites and Pillars.
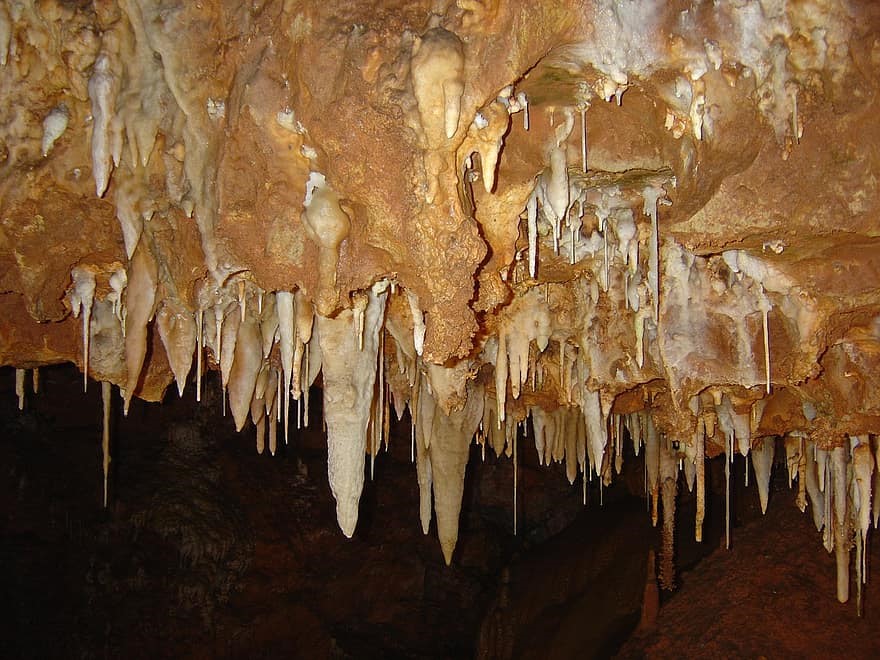
1 . Stalactites
- Formed on roof of caves .
- As rainwater seeps through the limestone, the water dissolves Calcium Carbonate in it. When from roof, water drips down, it leaves behind Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) forming Stalactite .
- They are thinner, long and pointed.

2. Stalagmite
- They are formed on the floor.
- All the dripping water has to land somewhere . When a drop finally hits cave floor , it deposits even more Calcite there in unassumed mound .
- They are shorter, fatter and more round.
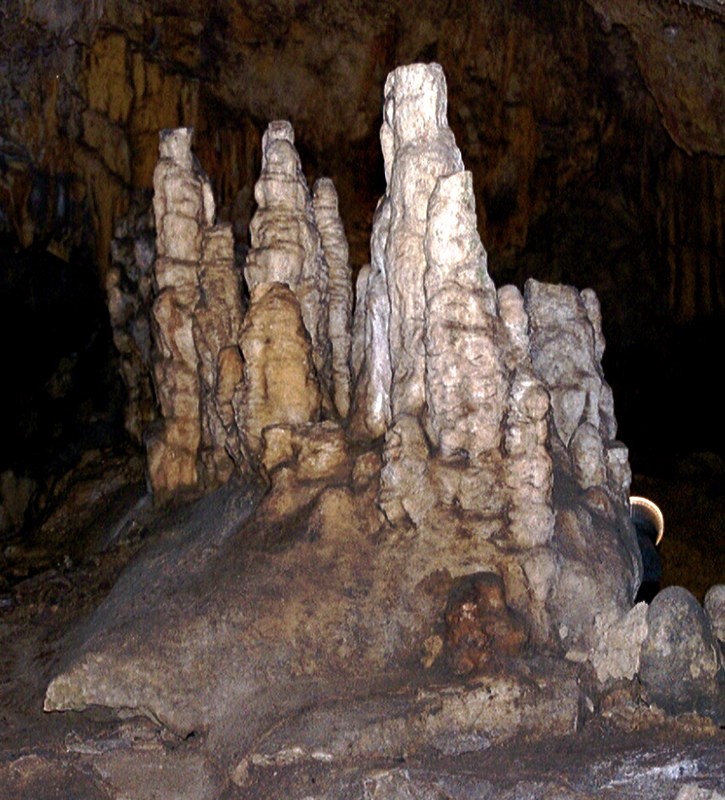

3. Cave Pillars
- Over a long time, stalactites hanging from roof is eventually joined to Stalagmite growing from floor to form pillar.