Table of Contents
Corporate Governance
This article deals with the topic titled ‘Corporate Governance.’ This is part of our series on ‘Ethics’. For more articles, you can click here.
Concept of Corporate Governance
What do we mean by Corporate?

Any Organization, whether public or private, which has a separate legal entity. For example
- Reliance Jio, BSNL etc. are corporations => If a person registers a case against them, it will be against this organization only (like Name of Person vs BSNL).
- But the Department of Communication or MEITY is not included in this because it has no separate legal entity. If a person registers a case against MEITY, the case will be against the Government of India.
What do we mean by Corporate Governance?
- Corporate Governance is the set of systems and processes to ensure that the company is governed in the best interests of all stakeholders (shareholders, employees, customers, society etc.)
- The concept of Corporate Governance is associated with gains that can accrue from following a moral path. It means Ethical Governance. Every Corporation should function in such a way that along with its own development and growth, it should ensure the development of its employees, shareholders, customers, society, nation and world.
What do we mean by Corporate Social Responsibility?
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is the moral responsibility of any organization (whether private or public) to positively impact the society in which it exists.
The world started to become aware of Corporate Social Responsibility and Corporate Governance with the start of LPG in the 1980s (because a large number of private entities came into sectors where earlier only the government was involved, and obviously, their main aim was maximization of profits).
Main thing through which Corporate Governance is ensured
- The main principle on which Corporate Governance works is the SEPARATION OF OWNERSHIP AND CONTROL. If such a separation exists, both will have checks and balances on each other. Hence, to ensure Corporate Governance, the company is owned by the Shareholders but controlled by Directors.
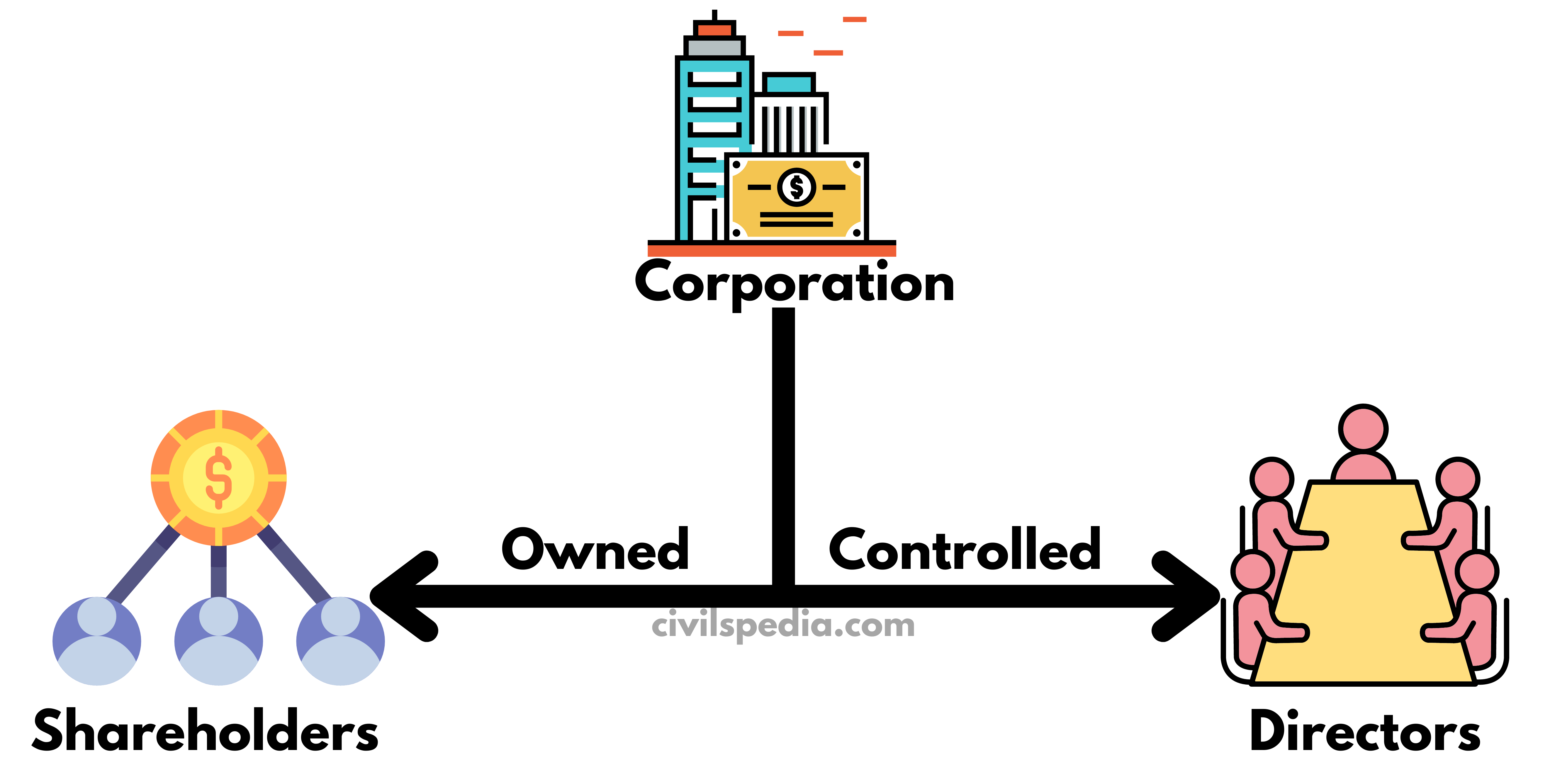
- If those who own the company and those who manage them are the same, all their actions and decisions will likely be governed by the motive of maximizing their profits, even at the cost of other stakeholders.
Types of Corporate Governance
There are two Models
Anglo Saxon Type
- It is found in those countries where the influence of the rule of law is strong.
- It only focuses on the interest of shareholders (only)
- Its impact is mainly seen in countries like Britain and USA
Continental Type
- It is found in those countries where the influence of administrative law is more.
- E.g., France and Germany
- In this, more emphasis is laid on the interests of shareholders, customers and employees.
Principles of Corporate Governance in India
Corporate Governance includes the following principles:-
- Independence of the board of directors to take decisions in the best interest of Profits of the company, People of the society and the Planet (3Ps).
- Fairness in actions in the market
- The corporation shouldn’t indulge in excessive profit-seeking behaviour through fraud practices.
- Business should be carried out in a socially responsible manner. Companies should invest in building social and human capital.
Example of Corporations indulging in Fraudulent Activities

1. Bhopal Gas Tragedy
- The Bhopal Gas showed that India lacks a regulatory and legal framework even for dangerous industries.
2. Satyam Computer
- Satyam Computer owner Ramalingham Raju indulged in creative accounting to show higher profits. He transferred the company’s funds to an individual account.
3. Sahara Fraud
Sahara gathered funds from the sharemarket and transferred the funds to a private account.
4. Nirav Modi Scam and Punjab National Bank
- Nirav Modi gathered Rs 14,000 crore of money from Punjab National Bank using fraudulent means by colluding with the bank officials.
5. Volkswagen
- Volkswagen tweaked the vehicle software in such a way that they could dodge the Environmental Protection Agency about their emission standards.
Why do we need Corporate Governance in India?
- Liberalization and de-regulation the world over have given greater freedom to management. The greater freedom demands even greater responsibilities.
- Intense Competition: Players in the field are many. Competition brings in its wake weakness in standards of reporting and accountability.
- Inadequate monitoring and response failure by regulatory authorities: The enforcement machinery has not been strengthened with the same speed with which regulatory changes have been brought in. As a result, the oversight by regulators remains weak.
- Market conditions are increasingly becoming complex in light of global developments like WTO, the removal of barriers & reduction in duties.
- Failure of corporations due to lack of transparency & disclosures and instances of falsification of accounts (embezzlement). For example, it was witnessed in Satyam Computer, Franklin Templeton (India) and Sun Pharma Ltd. cases.
- The absence of Corporate Governance leads to fraud, mismanagement, embezzlement and harm to society & environment.
- Sustainable growth: Corporations following corporate governance witness sustainable growth. E.g. Tata Group of companies continues to be one of the biggest conglomerates even after 150 years of its existence as it followed the principles of corporate governance.

- To improve the functioning of the boards: Good corporate Governance curtails nepotism and favouritism and thereby helps fill the capability gap in the organizations.
Issues with Corporate Governance in India
According to various committees such as Kotak Committee and Narayan Murthy Committee, Indian corporations face the following Corporate Governance issues.
- Creative Accounting: Indian corporations such as Satyam Computers indulged in Creative Accounting, leading to their eventual downfall.
- Insider trading: For example, Aptech India ltd
- Nepotism in board appointments: The board members are relatives or known ones.
- Independent directors have either played a passive role or can be removed easily if they don’t side with promoters. Hence, Independent Directors aren’t independent enough. Moreover, recent experiences like ILF&S and DHFL showed that independent directors are not fulfilling their roles and responsibilities.
- Executive Compensation policies are not transparent.
- Family-owned Indian companies have excessive controls and poor succession planning.
- Lack of serious efforts by the board toward Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) projects.
- Corporate Fraud: Corporate frauds are happening as the main motive of the corporations is profit maximization.
- Lack of Diversity: Corporate boards lack diversity. The representation of other genders on the boards is nominal.
- Lack of transparency and disclosure.
Areas of Importance within Corporate Governance include
- Independent Directors: Independent Directors are the directors who aren’t involved in day-to-day activities but primarily attend board meetings. They protect the interests of Minority Shareholders. The number of independent directors is set to a minimum of one-third of the board strength, and they are required to hold at least one separate meeting in a year without the participation of non-independent directors.
- Remuneration Committee: Established to avoid directors setting their own remuneration levels high (a check on directors)
- Audit Committee: Acts as an interface between the Board of Directors and the External Auditors. It is made up of Independent Directors.
- Public oversight: This gives the public an insight into the company (e.g. via Public open day). Since the public can be affected by the company’s decisions and are important stakeholders, hence they have the right to know what is happening inside the company.
- Other Areas of Importance
- Code of Conduct and Code of Ethics should be inculcated in employees.
- There should be a strong Whistleblowers Policy
- There should be a Corporate Social Responsibility Policy.
Steps taken till now to strengthen Corporate Governance
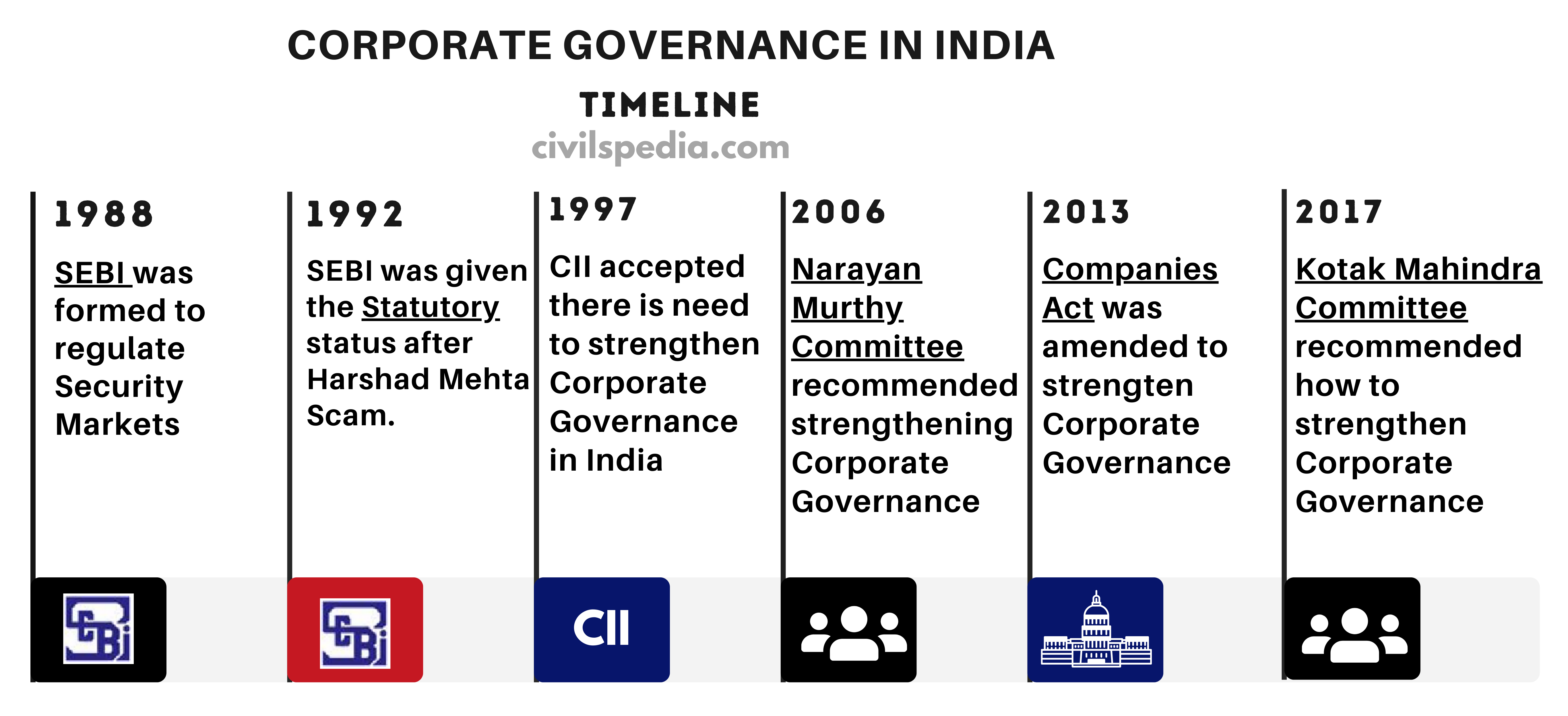
Narayan Murthy Committee Recommendations
- 1/3rd to 1/2rd of the Total Directors of the Company should be Independent Directors.
- Auditing the accounts of Big Corporations should be done under the vigil eye of CAG & Indian Auditing Services.
- Whistleblowers Protection Act should be applicable to both public and private sectors.
The above recommendations have not been implemented in the true sense. Although Whistleblower’s Act has been formed, it has many lacunae.
Kotak Committee Recommendations
- There should be at least 6 Independent Directors in the top 500 companies (earlier 3).
- At least 50% of Directors should be Independent Directors.
- No board meeting can be conducted without the presence of an independent director.
- At least 1 Independent Director should be a woman.
- Board of Directors Meeting should be held 5 times (earlier 4) in which one meeting should be exclusively dedicated to Corporate Governance.
- All the Independent Directors in the Board of Directors should be compulsorily present in the meetings.
- For government companies, it is recommended that the board have the final say on the appointment of independent directors and not the nodal ministry.
- Reporting System should be of ‘Matrix Type‘.
- Permission of Minority shareholders should be necessary in case payments to related parties exceed 2% of revenue.
- Disclosures of Auditor Credentials and Audit Fees should be mandatory.
- Market Regulator (SEBI) should be strengthened to improve corporate governance. SEBI should have the power to act against auditors if the need arises.
Benefits of Corporate Governance
- Reduced risks of corporate scandals and frauds
- Ensures adequate disclosure & transparency in business transactions
- Leads to statutory & legal compliance
- Protection of shareholder interests
- Improves strategic thinking at the top by inducting independent directors who bring a wealth of experience, and a host of new ideas
Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate Social Responsibility can be explained as
- Corporate: Meaning ‘Organized Business
- Social: Meaning ‘Dealing with People’
- Responsibility: Meaning ‘accountability between the two’
Corporate Social Responsibility is the moral responsibility of any corporation(whether public or private) to positively impact the society in which it exists.
Corporate Social Responsibility vs Corporate Governance
| Corporate Governance | Corporate Social Responsibility |
| Apart from Society, it also focuses on Customers, Employees and Shareholders. Hence, it has a relatively larger scope | It focuses on Social Interests only. Hence, it has a relatively narrow scope |
| It is expected from all Corporations, whether small or large (size doesn’t matter) | It is expected mainly from comparatively larger Corporations. (Although any company can do it, but it is expected from larger companies only). |
| More regulatory and legal efforts are required to implement it. | Comparatively, fewer regulatory and legal efforts are required. It can also be implemented on a moral basis. |
Basis /Reason /Rationale for CSR
- Corporations utilize the resources of society – both human & natural. So they have the responsibility to pay back to the community.
- Corporate plants create negative externalities in the form of pollution. To compensate for negative externalities, the government can force them to work in the interest of society.
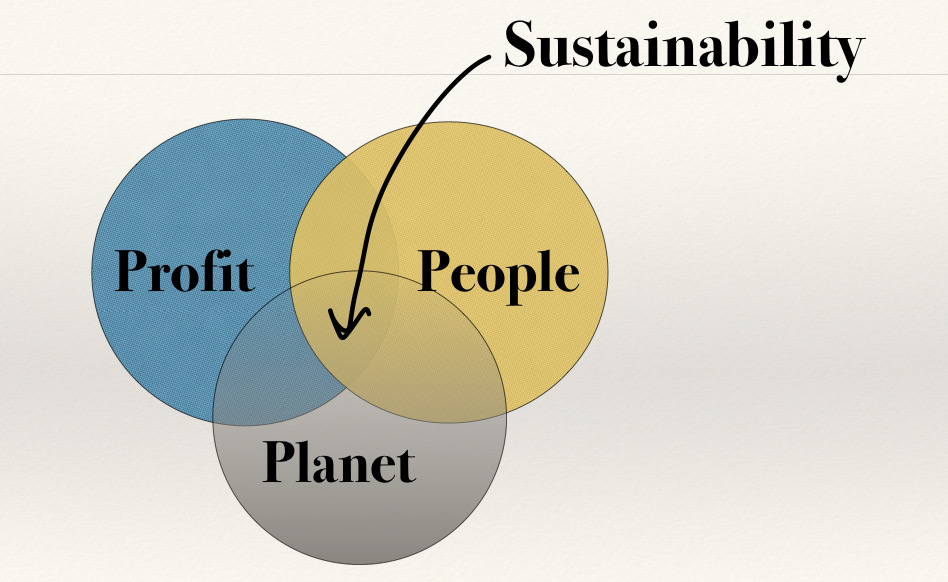
- Triple Bottom Line Principle of CSR: ‘Triple Bottom Line’ (TBL, or 3BL) means that Corporations should work for the ‘people, planet and profit’.
- Planet: The actions of corporations shouldn’t impact the planet negatively.
- People: Corporations should work to improve the lives of local communities.
- Profit: The corporations have the full right to increase their profit.
- Creates a favourable image of the company, which attracts customers. The reputation & brand equity of companies demonstrating their social responsibilities is very high. E.g.: Tata Corporation.
Case Study: Patagonia
- Patagonia is a garment company based in California.
- The company follows the triple Bottom Line Principle in letter and spirit.
- Planet: The company uses environment-friendly materials like organic cotton and recycled polyester.
- People: The company do a large charity and persuades its customers to donate their used products.
- Profit: The company is least interested in greater profits, and the owner donated his whole wealth to charity (around $ 3 billion) to fund the research to combat climate change.
The provision in the Companies Act regarding CSR
- Companies will have to spend 2% of their last three years’ average profit on social development-related activities like education, health, slum development etc.
- CSR rule applies only to companies having annual turnover above Rs 1000 crore and net profit of Rs 5 crore
- Companies have to set up a CSR Committee of 3 Board Directors.
Issues with CSR in India
- Less Importance to CSR: Most companies have not looked at their CSR strategies through the same lens as their core business functions.
- Lack of clarity about regulations as government changes the provision each passing month.
- Imbalance in CSR spending: Most of the CSR funds are spent on a handful of activities like education and health
- Geographic equity: Five states, i.e. Maharashtra, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Tamil Nadu, accounting for well over one-quarter of all CSR funding. Towards the bottom of the list are Nagaland, Mizoram, Tripura, Sikkim and Meghalaya-all from North-East.
- A large number of shell NGOs have come up which take up money from companies but don’t spend on targeted projects.
- Since there is no standardised way to measure the impact of CSR spending, companies can’t make informed choices.
Administrative Reform Commission’s (ARC) Recommendation on CORPORATE PHILANTHROPY
- When a corporate entity takes up a community benefit project, there should be some mutual consultation between the company and the local government so that there is no unnecessary overlap with other similar development programs in the area.
- The government should act as a facilitator and create an environment that encourages businesses and industry to take up projects and activities that are likely to impact the quality of life of the local community.
