Table of Contents
Gaganyaan
This article deals with ‘Gaganyaan‘. This is part of our series on ‘Science and Technology’ which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here
Gaganyaan Program or Indian Human Spaceflight Program (IHSP)
- Gaganyaan Program is India’s first manned Spacecraft. On 15 August (2018) Speech, PM Modi has set a target of 2022 for the Space Manned Mission.
- India will become 4th country after US, Russia and China to have this capability.
Spacecraft / Space Shuttle
- Satellite Launch Vehicles are used to send satellites in the Orbits. In the same way, Spacecraft is used to send astronauts into space.
- Examples include China’s Shenzhou, America’s Atlantis, Russia’s Soyuz, SpaceX’s Dragon Capsule and Boeing’s Dreamliner.
- India’s Gaganyaan is also a spacecraft.

Timeline
| 1984 | Rakesh Sharma travelled to space (becoming the first and only Indian citizen to do so). |
| 2007 | The first proposal for ISRO’s human-crewed space mission. |
| Dec 2014 | Experimental flight of manned mission launcher GSLV MK-III tested. |
| July 2018 | ISRO conducted Pad Abort Test (PAT). Pad Abort Test is part of the crew escape system, which assists in quickly pulling the astronaut cabin along with the crew out to a safer distance from the launch vehicle during a launch abort. |
| 15 August 2018 | PM Modi announced that Gaganyaan will be launched by 2022. |
| 2022 | First, Indian manned Spacecraft will be launched. |
Earlier Manned Missions
| Vostok 1 Mission (USSR,1961) | Took Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union into space, making him the world’s first human in space. |
| Mercury Mission (USA, 1961) | Alan Shepard was the first American sent to space. |
| Shenzou (China, 2003) | This mission put the first Chinese citizen in space. |
| Rakesh Kumar | Rakesh Kumar was the first Indian sent to space on a Russian Soyuz Space vehicle. |
What will Gaganyaan Project include?
- Gaganyaan is India’s manned mission to space.
- In the mission, GSLV MK-III will carry a 3-member crew to the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and safe return to the Earth after the duration of a few orbits to two days.
- An extendable version of the spaceship will allow flights up to 7 days & docking capability with the space station.
Key Components of Human Space Program
- Building up a Habitable Module
- Other life support systems like Space Suits
- Astronaut training
- Capabilities for recovering Astronauts safely
- Crew Escape System
Do you know?
Indian Astronauts will be called ‘Vyomanauts‘.

Objectives of Gaganyaan Programme
- The exponential growth of science and technology in the country.
- Improvement of industrial growth.
- Inspiring youth.
- Development of technology for social benefit.
- Improving international collaboration.
Benefits / Significance of Human Space Program
- It will help India in doing Research and Development in space. Indian scientists will get the opportunity to conduct experiments in space through Gaganyaan Mission.
- It will encourage our scientific community and will help in making India a knowledge-based economy. Significant advancement will happen in material processing, astrobiology, resources mining, planetary chemistry, planetary orbital calculus.
- The Manned Space Program is essential to control resources present outside the Earth. If we plan to set up colonies outside the Earth in the future, such programs will be of great help.
- It has the added advantage to achieve the status of great power.
- Indian industry will find significant opportunities as Gaganyaan Mission is expected to source ~60% of its equipment from the Indian private sector.
- According to the ISRO chief, the Gaganyaan mission would create 15,000 new employment opportunities.
- It will increase India’s soft power and give space to Indian Space diplomacy. India will be the fourth country to launch a human space mission, establishing India’s role as a key player in the space industry.
Challenges
- The human body is designed according to Earth’s gravity. There is a microgravity environment in space, which affects hand-eye and head-eye coordination. In the absence of gravity, blood and body fluids cannot distribute to the lower part of the body and accumulate in the upper part. Additionally, the size of the heart decreases, bones become weak, and the brain cannot interpret information correctly.
- Humans in space are subjected to a high degree of radiation, increasing cancer risk.
- Space is a hostile environment as there is a lack of gravity, danger of radiation and absence of atmosphere.
- Financial: These missions require exorbitantly huge investment as they are highly technology-intensive. It will cost ISRO Rs. 10,000 crores.
- Re-entry and Recovery: The biggest challenge in the case of human flight is the re-entry of the vehicle back into the Earth’s atmosphere and recovery of the module as it is subjected to extreme heat due to friction with the air. Even the slightest deviation can result in disaster.
International Space Station
ISS
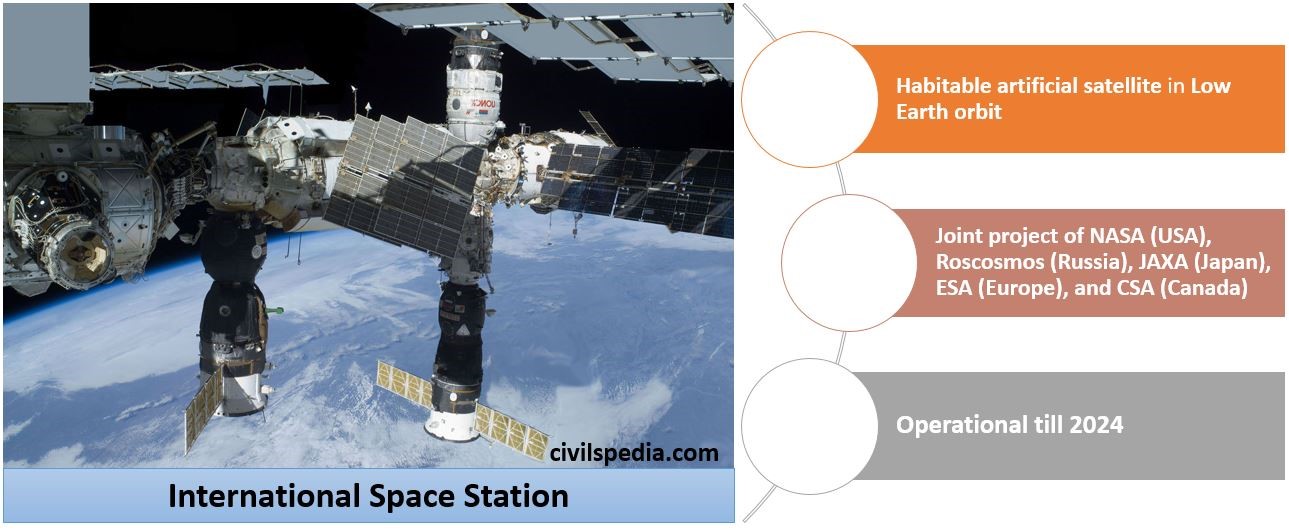
- ISS or International Space Station is a man-made or artificial habitable satellite in Low Earth orbit (between 278 km and 460 km) and travels at 15.7 orbits per day.
- The space station also acts as a laboratory in space where astronauts stay for an extended period to carry out experiments in microgravity.
- It is a joint venture of NASA (USA), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada).
- It has been operating since 1998 and will continue to operate till 2024.
- Building a Space Station is an expensive affair, and ISS is the most expensive object ever constructed by man, with a cost amounting to $150 billion.
- It will be operational till 2031.
- ISS is the ninth space station. Earlier, Mir, Salyut and Almaz were the Space Stations of the USSR, and Skylab was the Space Station of the USA.
Future Space Stations
- Tianhe: Chinese Space Station, which is under construction phase.
- Russian Plans: Russia will withdraw from ISS in 2025 and will launch its space station in 2030.
Uses of Space Stations
- It acts as a Microgravity Lab. It is used to conduct experiments in biology, physics etc., in a micro-gravity environment.
- Observe the long-term effects of space exposure on the human body.
- Study of cosmic rays, cosmic dust, antimatter and dark matter in the universe.
- It serves as a Space Terminal.
- It can also be used in Space Tourism.
Artemis Accords
- Artemis is the moon mission of NASA which aims to land the next man and the first woman on the moon by 2025.
- Artemis Accords are agreements between NASA and its international partners that want to cooperate on the Artemis program.
- It has been established to create a common set of principles to govern the exploration and use of outer space when numerous countries and private sector players conduct missions and operations in cislunar space (space between Earth and Moon). The agreement includes various norms such as transparency, peaceful exploration, Interoperability of systems, Registration of Space Objects, Orbital Debris & Spacecraft Disposal etc. Accord is primarily based on the 1967s Outer Space Treaty.
- Main provisions of the Artemis Accord include
- Interoperability
- Emergency assistance
- Safe disposal of space debris
- Preventing harmful interference
- Preserving outer space heritage
- Release of scientific data
- Registration of objects
- Peaceful exploration
- Transparency
- Signatories include the US, New Zealand, Australia, Canada, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, the Republic of Korea, the United Kingdom, the United Arab Emirates, and Ukraine. Major space players like India, Russia, China, France, and Germany are not signatories.
Indian Astronauts
Rakesh Sharma
- He was the first Indian to travel to space.
- He was born in Patiala in 1949 and later joined Indian Airforce as a pilot, from where he joined ISRO.
- As a cosmonaut, he went to space in a Soviet Spacecraft (Soyuz T-11).
Kalpana Chawla
- She was the first woman of Indian origin to go into space.
- She did his B. Tech from Punjab Engineering College (Chandigarh) and PhD in Aerospace Engineering from the USA.
- Her first space flight was on Space Shuttle Columbia in 1997. Unfortunately, in 2003, Kalpana Chawla was part of the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster and lost her life.
Sunita Williams
- Sunita Williams is American of Indian (Gujarati) descent.
- She has done 7 spacewalks and stayed in space for the longest time in a single flight (195 days).
Raja Chari
- NASA has selected Raja Chari to fly to ISS in SpaceX Crew-3 Mission (with 3 other astronauts).
- It is part of NASA’s Artemis program that aims to expand humanity’s horizons in space.
Anil Menon
- Anil Menon is a doctor of Indian origin who has worked in SpaceX as a surgeon during its project to launch humans into space.
- He has been chosen by NASA as a future astronaut.
