Last Update: May 2023 (Indian Satellite Launch Vehicles)
Table of Contents
Indian Satellite Launch Vehicles
This article deals with ‘Indian Satellite Launch Vehicles‘. This is part of our series on ‘Science and Technology’ which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Satellite Launch Vehicles
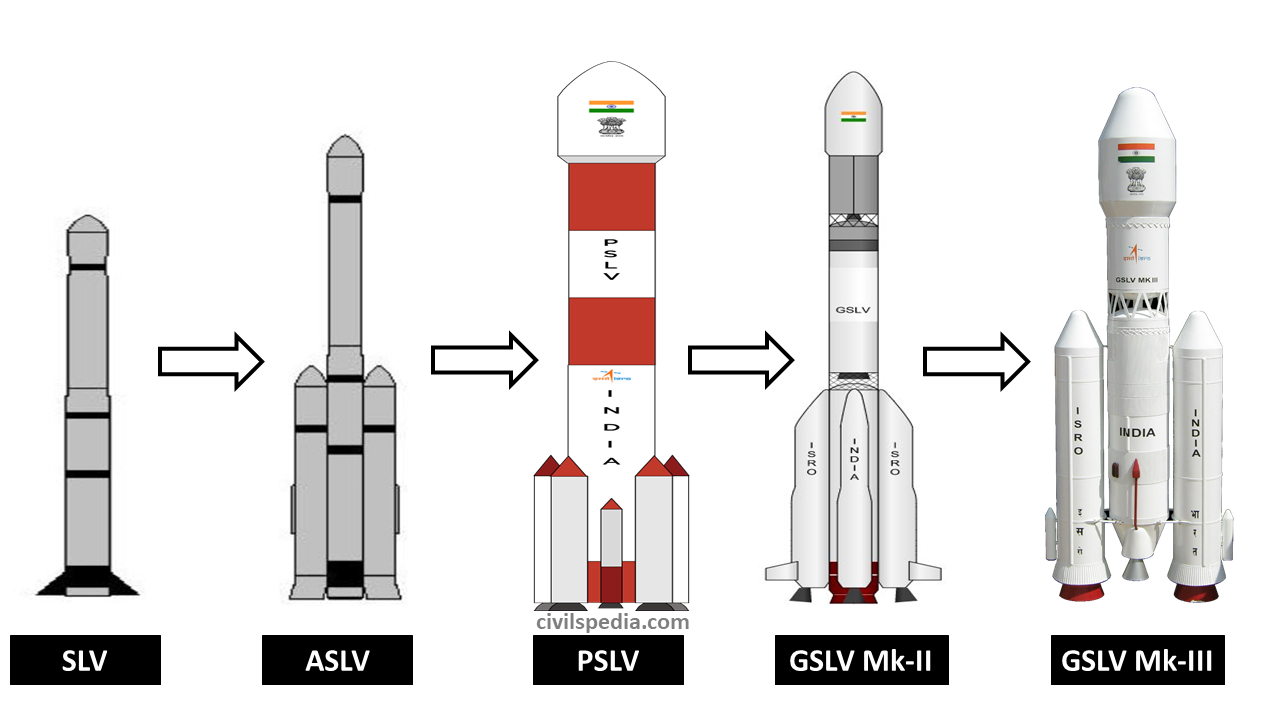
SLV
- SLV = Satellite Launch Vehicle.
- It was a four-stage launch vehicle (all stages used solid fuel).
- Payload that SLV could carry = 40 kg till 400 km.
- The first successful launch of SLV happened in 1980 in the project headed by Dr APJ Abdul Kalam.
- Later, India also used SLV to place the Rohini satellite in its orbit.
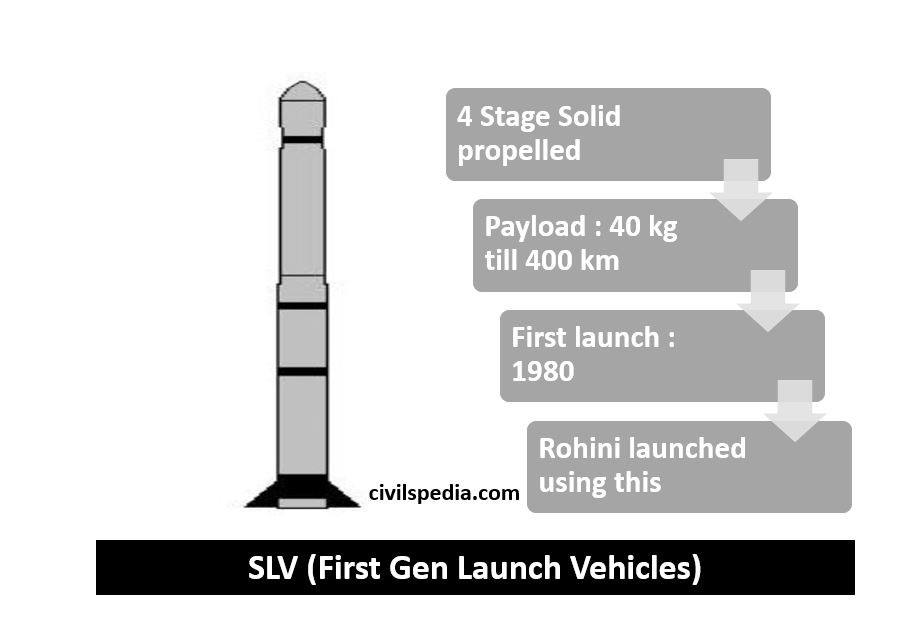
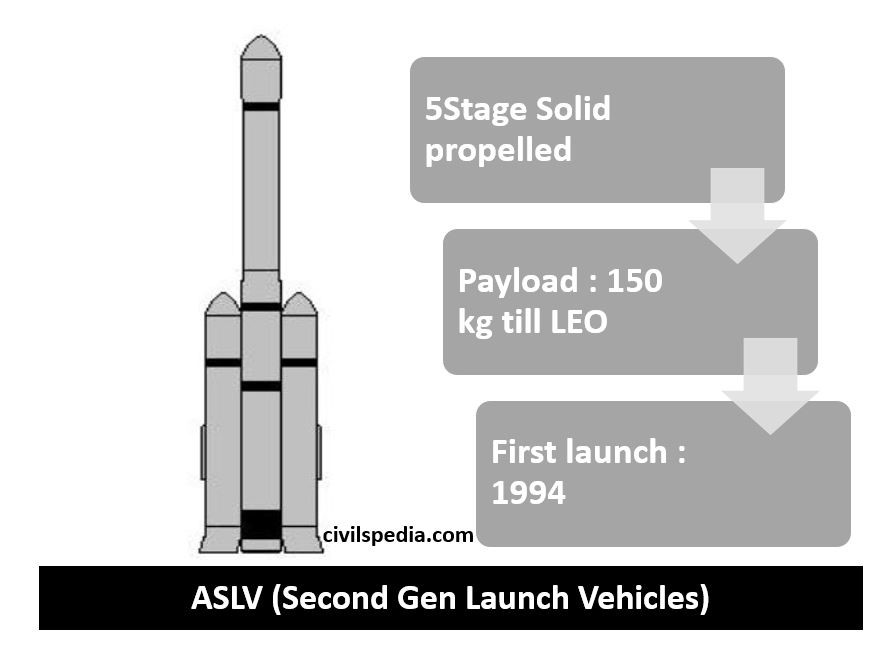
ASLV
- ASLV = Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle.
- ASLV was designed to augment the capacity of SLV.
- It was a five-stage launch vehicle (all stages used solid propellant).
- The payload that ASLV could carry = 150 kg till Low Earth Orbit.
- The first successful launch of SLV happened in 1994, and it is retired now.
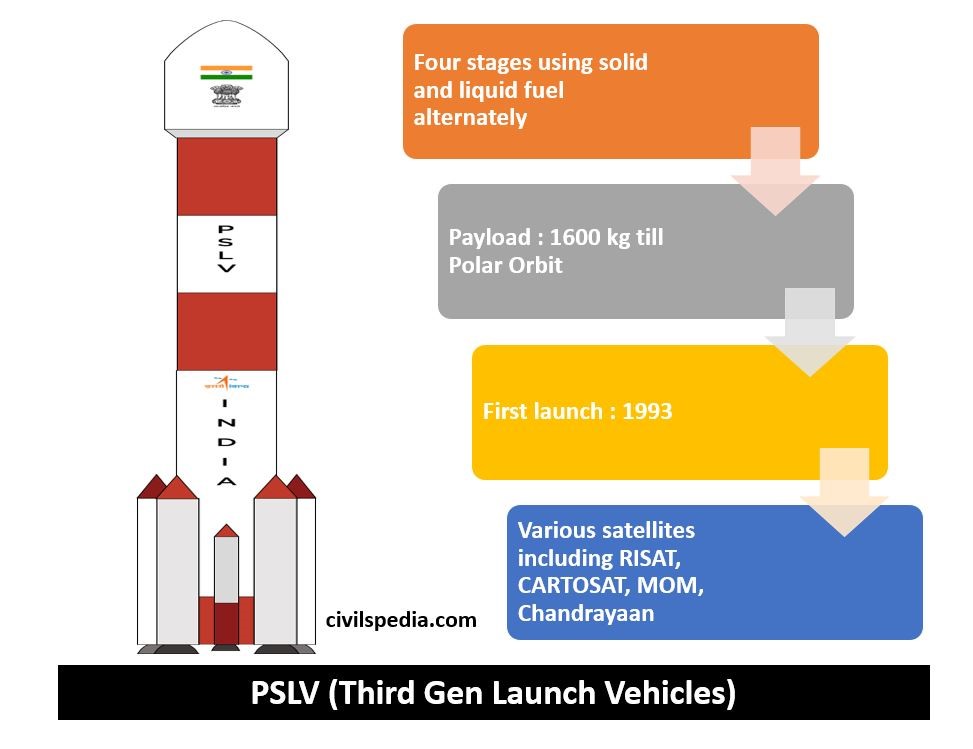
PSLV
- PSLV = Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle
- The first launch using PSLV happened in 1993.
- The payload that PSLV can carry = up to 1600 kg till Sun-Synchronous Polar Orbit.
- PSLV is very reliable, and 54 of its 57 launches were successful.
- ISRO used it to launch Indian Remote Sensing Satellites (IRS) such as Cartosat, Oceansat etc. and some other historic missions like Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), IRNSS/ NAVIC etc.
- It has three variants, i.e. PSLV–G, PSLV-CA and PSLV-XL. The latest version of PSLV, i.e. PSLV-XL, can carry up to 1750 kg. Chandrayaan & Mars missions were launched using this.
- Stages of PSLV: Four stages using solid and liquid fuel alternately.
| First | – It uses solid fuel, i.e. HTPB- Hydroxyl Terminated Poly-Butadiene. |
| Second | – It uses liquid propellant, i.e. UDMH-Unsymmetrical Di Methyl Hydrazine with Nitrogen Tetroxide as an oxidiser. – It employs a Vikas engine. |
| Third | – It uses solid fuel, i.e. HTPB- Hydroxyl Terminated Poly-Butadiene. |
| Fourth | – It uses liquid propellant, i.e. Mono Methyl Hydrazine. – It employs Vikas Engine. |
PSLV and importance to the Indian Space Program
- PSLV was the country’s first operational launch vehicle and is dubbed as the ‘workhorse of ISRO’.
- It is highly successful and reliable. It has a record of 97% successful launches, which is one of the most successful in the world.
- It is used to carry IRS satellites to Polar Sun Synchronous Orbits with utmost precision. Till now, India has launched 54 Indian satellites and 222 foreign satellites using PSLV.
- It poses potential competition to the west due to its lower launch price and is helping India to earn a lot of revenue.
- It has also helped India in launching spy satellites and boosting national security.
- ISRO launched the maximum number of satellites in the world in a single operation, i.e. 104 satellites using PSLV.
Side Topic: POEM Platform
- The PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM) has been designed to use Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle’s final and otherwise abandoned stage for in-orbit research.
- In general operations, the PSLV is a four-stage rocket where the first three spent stages fall back into the ocean, and the final stage (PS4) — after launching the satellite into orbit — ends up as space junk.
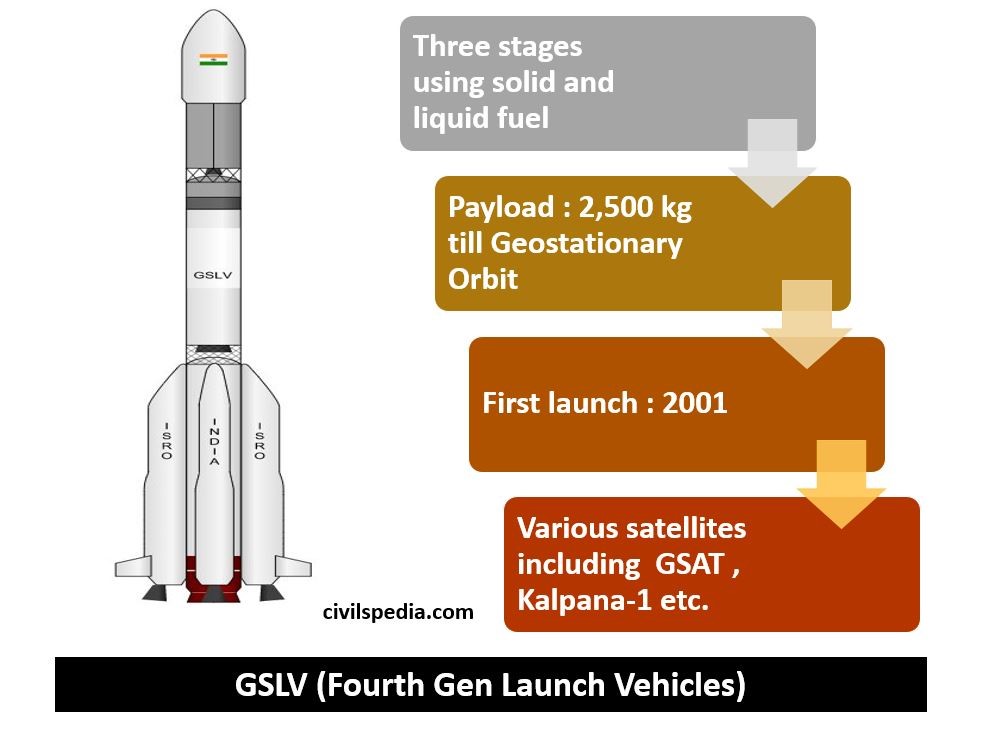
GSLV / GSLV MK-II
- GSLV = Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle
- The first launch using GSLV happened in 2001.
- ISRO made it to launch Geosynchronous and Geosynchronous Satellites.
- It can carry up to 2500 kg till Geostationary Orbit (and 5,000 kg till Low Earth Orbit (LEO)).
- It can be used to launch Indian National satellites (INSAT) & GSAT in Geostationary and Geosynchronous orbits. (but most of Geostationary Satellites are around 3000 kg to 4000 kg, which GSLV MK II can’t take till Geostationary Orbit & we used to be dependent on Ariane Aerospace for their launches)
- The next version of this launch vehicle is GSLV MK-3.
- Stages of GSLV: GSLV is a 3 stage vehicle
| First | Solid propelled |
| Second | Liquid propelled with hypergolic fuels |
| Third | Liquid propelled |
Stage 1 & 2 are directly taken over from PSLV.
GSLV MK-III
Earlier (before June 2017), ISRO was in the position to launch only satellites weighing between 2 & 2.5 tons into geostationary orbits. But most contemporary communications satellites usually are in the weight category of 3 to 5 tons & therefore require a more powerful launcher. Moreover, India’s future missions to the Moon, Mars and Venus also need a powerful launcher. Appreciating this need, ISRO has made GSLV-Mark III a vehicle capable of placing 4-ton satellites in geostationary orbit.

Main Features of GSLV MK-III
- It is the latest version of GSLV.
- GSLV MK-III made its maiden flight from Sri Harikota in 2017, placing GSAT-19 in Geostationary Orbit.
- Later, ISRO used the GLSV Mk-III to launch Chandrayaan-2 Mission (India’s second Lunar Mission).
- GSLV Mk-3 can carry
- Up to 4 tons till Geostationary Orbit
- Up to 10 tons till Low Earth Orbit (Polar Satellites)
- Hence, it has ended India’s reliance on the EU’s Arianespace launch vehicle to send GSAT satellites into Geosynchronous orbits.
GSLV MK-3 is a three-stage vehicle
| First | Solid propellant |
| Second | Liquid Propellant |
| Third | Cryogenic Engine uses the Liquid Oxygen & Liquid Hydrogen as oxidiser and fuel, respectively (this stage differs from GSLV Mk-2). |
Compared to solid and liquid propellants, a cryogenic propellant is more efficient. It provides more thrust by burning the same amount of propellant than Earth-based storable liquid and solid propellants.
Note: India had signed MoU with Russia to transfer Cryogenic Engines to India in starting 1990s, but the USA pressurised Russia not to supply these to India, arguing that it would violate MTCR Treaty (although Cryogenic engines are not used in Missiles). Due to this, India’s program suffered.
Significance
- GSLV Mark III has made India a competitive player in the multimillion-dollar commercial launch market. It will help in earning substantial foreign exchange.
- It will end India’s dependence on foreign launch vehicles to put its heavy satellites (GSAT series) in the geosynchronous orbit. (Earlier, India was dependent on France’s Ariane space ).
- India can also send its astronauts into space using this.
- It will boost India’s communication resources as the cost of launching Communication Satellites will reduce
- Cryogenic Technology used in it can be further used in making Inter Continental Ballistic Missile.
- It is a massive step in making India a ‘knowledge-based economy’. Till now, only USA (Saturn V), Russia (Proton M), China (Long March 5) & European Space Agency (Ariane), along with one private player (Space X), can launch geostationary and geosynchronous satellites.
Semi Cryogenic Engine
- MoU regarding this has been signed between the Russian Space Agency & ISRO.
- It would be India’s third Rocket Development Program.
- Project Cost – approx. ₹1,800 crores.
- It will be able to launch a 6 to 10-ton payload to the height of 36,000 km (more than GSLV-Mk-3).
- Currently, only Russia & US has this technology.
Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV)

- Due to the advancement in electronics, small satellites have started to be built on a large scale. Globally, more than 17,000 small satellites are expected to be launched till 2030. Earlier, these satellites were launched as piggybacks with big satellites. But ISRO has developed a small satellite launch vehicle (SSLV) to exploit this newly emerging market fully.
- India is also building its second launch station in the Thoothukudi district in Tamil Nadu, and it will house one launchpad exclusively for small satellite launch vehicles (SSLV).
- SSLV made its first successful flight in 2022 and its second in 2023.
- India’s SSLV has the following features.
- Weight = 110 ton
- Payload = Can launch satellites weighing up to 500 kg.
- Time to integrate for launch = 72 hours (in contrast to 70 days with present launch vehicles)
- Cost = Rs. 30 crores per launch
- Stage: Three solid stages followed by a liquid-fuel-based Velocity Trimming Module (VTM)
- New Space India Limited (NSIL) is the nodal agency (not ISRO)
- The new vehicle has been developed to capture the emerging small and microsatellite commercial market, with launches offered on demand.
- JAXA (of Japan) was one of the first space agencies to make this type of launch vehicle. A private company named bluShift is also focused on manufacturing Small Satellite Launch Vehicles. In January 2021, their Satellite Vehicle named Stardust1.0 came into operation with a mass of 250 kg and a carrying capacity of 8 kg.
Private Sector Launch Vehicle: Vikram-S
- Skyroot is a Hyderabad-based company that has made a Vikram-S launch vehicle to enter the launch market.
- Properties of Vikram-S Launch Vehicle
- It is a single-stage sub-orbital launch vehicle.
- It is 3D printed.
- The core structure is built using carbon composites.
- It can carry between 290 kg and 560 kg payloads into sun-synchronous polar orbits.
- The engine used in the launch vehicle is named ‘Kalam-80’
- It made its first successful flight in November 2022. It was launched with support from ISRO and IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre).
- It is part of Mission Prarambh, which involves the Indian private sector’s entry into the space launch market.
Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV)
- In 2016, ISRO successfully launched the first technology demonstrator of the indigenously made RLV. However, many more such successful launches have to be undertaken before ISRO readies a reusable launch vehicle for commercial use.
- In simple words, it is a winged vehicle that will take off vertically like a rocket and glide back to land horizontally like a plane.
- It will have a two-stage-to-orbit configuration.
Advantages
- It will cut down the cost of launching satellites to 1/10th. The main launch cost currently comes from building the rocket, which can be used just once, as the rockets get burnt on re-entry into the atmosphere.
- A more developed version of the vehicle could be used for human-crewed missions in the future.
- It will also help in reducing space debris.
Note – No sovereign space agency has RLV for satellite launches. SpaceX is also working on this project.
Scramjet Engine
- ISRO successfully conducted the Scramjet (or Supersonic Combusting ramjet) engine test. India has become the fourth nation to successfully flight-test a scramjet engine after the United States, Russia and China.
- The scramjet engine uses natural oxygen present in the atmosphere to burn the fuel stored in the rocket. Hence, it reduces the amount of oxidiser carried along with the fuel, bringing down launch costs.
Benefits
- It increases lift-off mass as there will be no need to carry liquified oxygen on board. (Note: propellant accounts for nearly 85% of the weight of a rocket, and in that oxygen accounts for almost 60% .)
- Scramjet does not have rotating parts, so the chances of failure are also measurably reduced.
Mains Question: India & Satellite Launch Market
- Satellite Launch is a multi-billion dollar industry, and Antrix (commercial wing of ISRO) is emerging as a significant player in this sector.
- Among 10 countries that have launch capability to launch satellites, only US, Russia, EU, Japan, China and India (6) make their services available commercially.
- Satellite launch business has two basic categories:
- Launching satellites into Low Earth Orbit (LEO): India provides services here using PSLV.
- Launching 3-5 tonne satellites in Geostationary Orbit: After making GSLV MK III, hopefully, India will enter this market in the future. But presently, no commercial deal in this category has been made.
- India launched SAARC/ South Asian Satellite in 2017, indicating that it is now using satellite technology as a foreign policy tool.
- ISRO has made a world record with the launch of 104 Satellites in one launch. With this, India has shown its technological prowess to the world. Out of 104, 101 were foreign satellites.
- With the entry of private players like SpaceX, Boeing and Blue Origin, the satellite launch market is becoming more competitive.
- For becoming more competitive, India needs to take the following immediate steps.
- PSLV’s design should be shared with the Indian private industry.
- India should develop more launching sites to perform more annual launches.
- Small satellites below 100 kg are becoming popular nowadays, but they are launched as piggyback with large satellites. Countries like the US, Japan, Russia & China and private players like SpaceX are making LV launch these satellites. ISRO should make a conscious decision to develop a new rocket for launching the small satellites.
Challenges
- The entry of private giants like SpaceX, Blue Origin, Boeing etc., in this field increased the competition.
- ISRO is a minor player in the global space industry. Although ISRO is launching a large number of satellites on commercial terms, these are nano and microsatellites, while the main revenue comes from launching heavier satellites.
- Indian share is just 2%
- According to the Economic Survey, Antrix is marketing only medium and coarse resolution data products, but Commercial potential for the medium and coarse resolution data segment is facing a threat due to Free and Open Access to such data from Landsat-8 of US and Sentinel from the European Space Agency (ESA).
