Table of Contents
India Central Asia Relations
This article deals with ‘India Central Asia Relations.’ This is part of our series on ‘International Relations’, which is an important pillar of the GS-2 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
What is Central Asia?
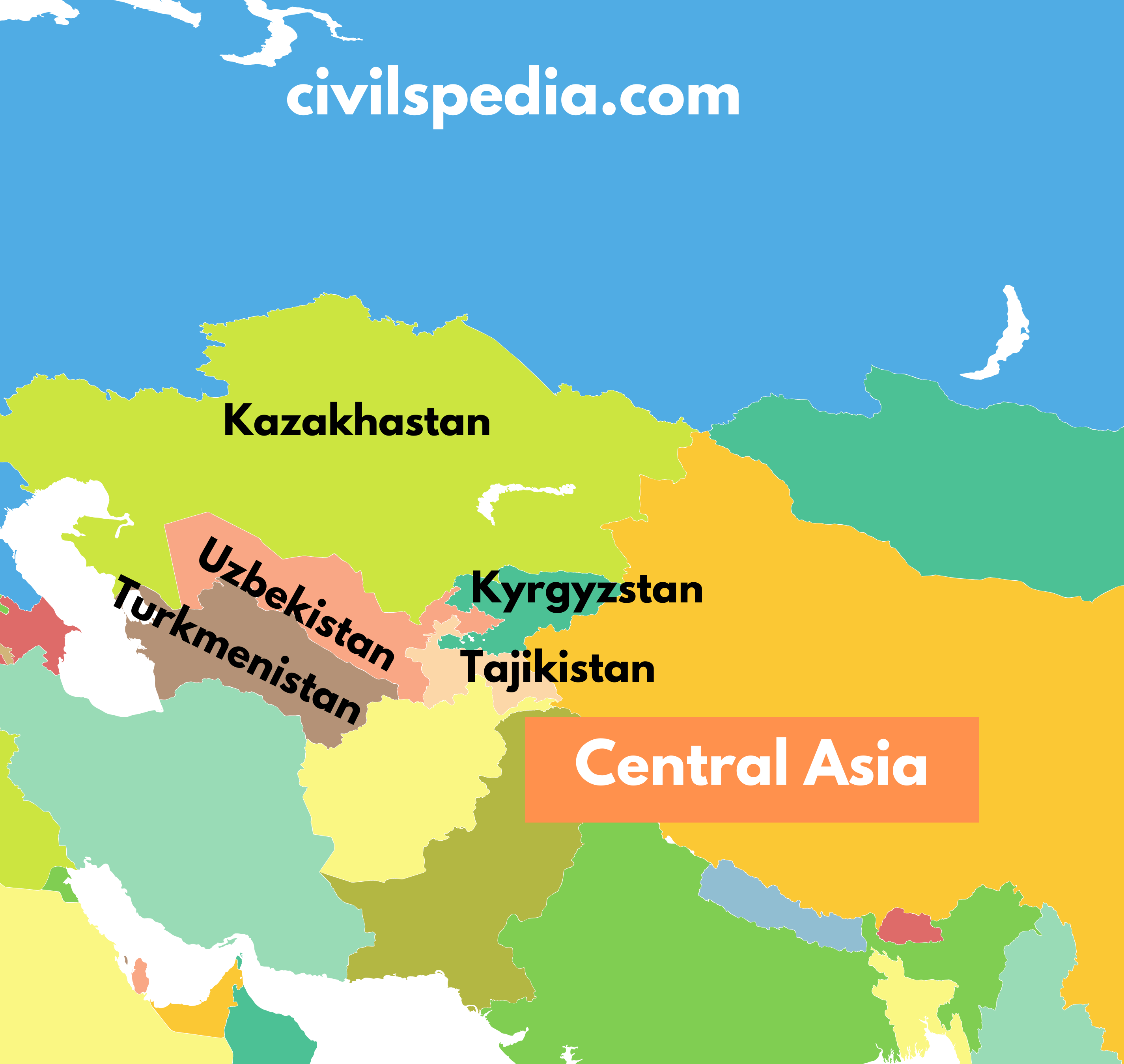
- Central Asia is a region made up of five nations forming the underbelly of Russia. These include
| Country | Capital |
| Kazakhstan | Astana |
| Kyrgyzstan | Bishkek |
| Tajikistan | Dushanbe |
| Turkmenistan | Ashgabat |
| Uzbekistan | Tashkent |
- These countries gained independence in 1991 after the disintegration of the Soviet Union.
- These countries are landlocked but are ultra-rich in resources and have sparse populations.
- India considers the Central Asian countries part of its ‘extended and strategic neighbourhood’.
Historical Connection with India
- Al -Beruni came to India in the 11th century from Central Asia. He authored a famous book named Tahkik ul Hind.
- Babur, who founded Mughal Empire in India, was a native of Uzbekistan (Ferghana province).
Politics of the region
- Although these countries achieved their independence in 1991, authoritarian regimes have remained in power (except Kyrgyzstan.)
- They have not opened up their economies and always feared that western countries, especially the US supported by NATO, might try to change the regime like what happened in Tulip Revolution in Kyrgyzstan in 2005.
Economy of these States
- States which have a strong economies are
- Kazakhstan with high per capita income
- Turkmenistan, which is a major supplier of gas
- But this is not the case with other states. E.g. Kyrgyzstan & Tajikistan are economically weak because they don’t have hydrocarbon resources. These states are still dependent on Russia (For example, Tajikistan’s primary source of revenue is remittances from Russia).
Importance for India
1. Natural resources
The Central Asian region is endowed with rich natural resources
- Turkmenistan: It has the 4th largest gas reserves. India is part of the TAPI Pipeline starting in Turkmenistan
- Uzbekistan: Uzbekistan is rich in gas resources.
- Kazakhstan: Kazakhstan is rich in oil and Uranium (KazAtomPro)
- Tajikistan: Tajikistan has vast hydropower potential
Since India is an energy-hungry nation, these nations are natural allies in this respect.
2. Strategic Location
- It is located at the bridge between Europe and Asia.
- The central lynchpin in this is the International North-South Corridor.
3. Security
- Tajikistan, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan border Afghanistan. After the US withdrawal from Afghanistan, Central Asian nations and India can cooperate to control terrorism and extremism in Afghanistan.
- Central Asia is known for its moderate practice of Islam. It can act as a counter to the radical Wahabist ideology of Islam.
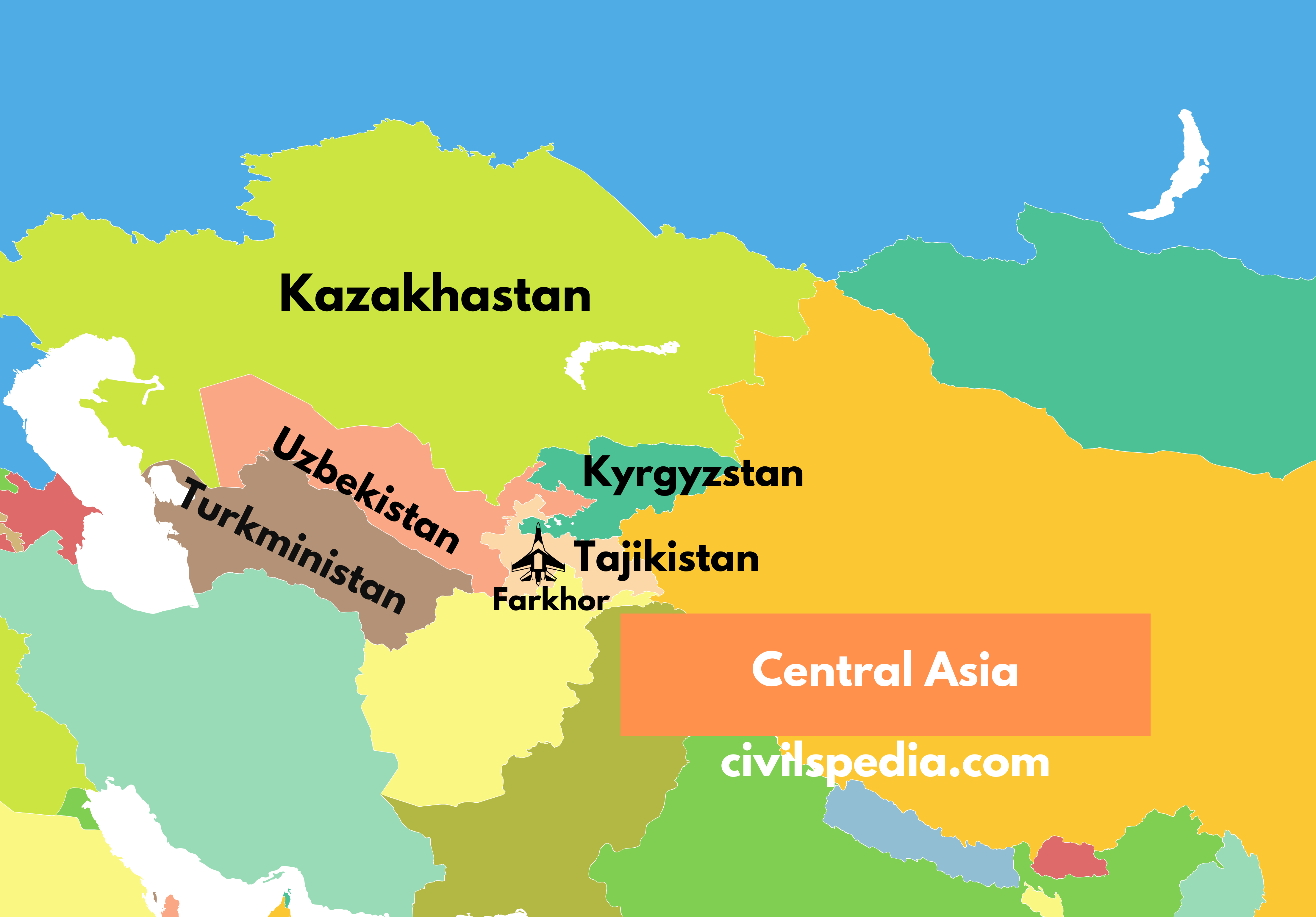
- India’s only foreign military airbase, i.e. Air Base in Farkhor (Tajikistan), operated by IAF.
4. Trade
- Trade between India & Central Asia is roughly $2 billion compared to their $50 billion trade with China. Hence, there is enormous untapped potential.
- Indian pharma and drugs, tea and coffee, are in huge demand in Central Asia.
- Various Indian Companies are involved in Energy Projects in Central Asia. These include
- NPCIL (Nuclear Power Corporation of India) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Kazakhstan (KazAtomPro)
- ONGC, Mittal Energy & KazMe2unaiGaz (KMG) have signed a deal regarding the offshore Satpayev Oil Block in the Caspian Sea.
- BHEL & NHPC are working on hydro projects in Tajikistan
5. The demand for Indian Products
- Indian Pharma and Drugs, Tea and Coffee have a huge demand in Central Asian countries.
- Bollywood is popular in Central Asian countries.
6. Drug Trafficking
- Tajikistan is a gateway for Afghan Drugs to Central Asia. This money is used for funding terror activities against India too.
Steps taken by India
- Connect Central Asia Policy: Dealt below.
- India has stepped up its multilateral engagements with Central Asian Countries through forums such as Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), Eurasian Community etc.
- India has renewed its efforts toward the completion of the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
- India has signed the Ashgabat Agreement.
- Indian government invited the leaders of the Central Asian nations as the Chief Guest for 2022 Republic Day.
TAPI Pipeline
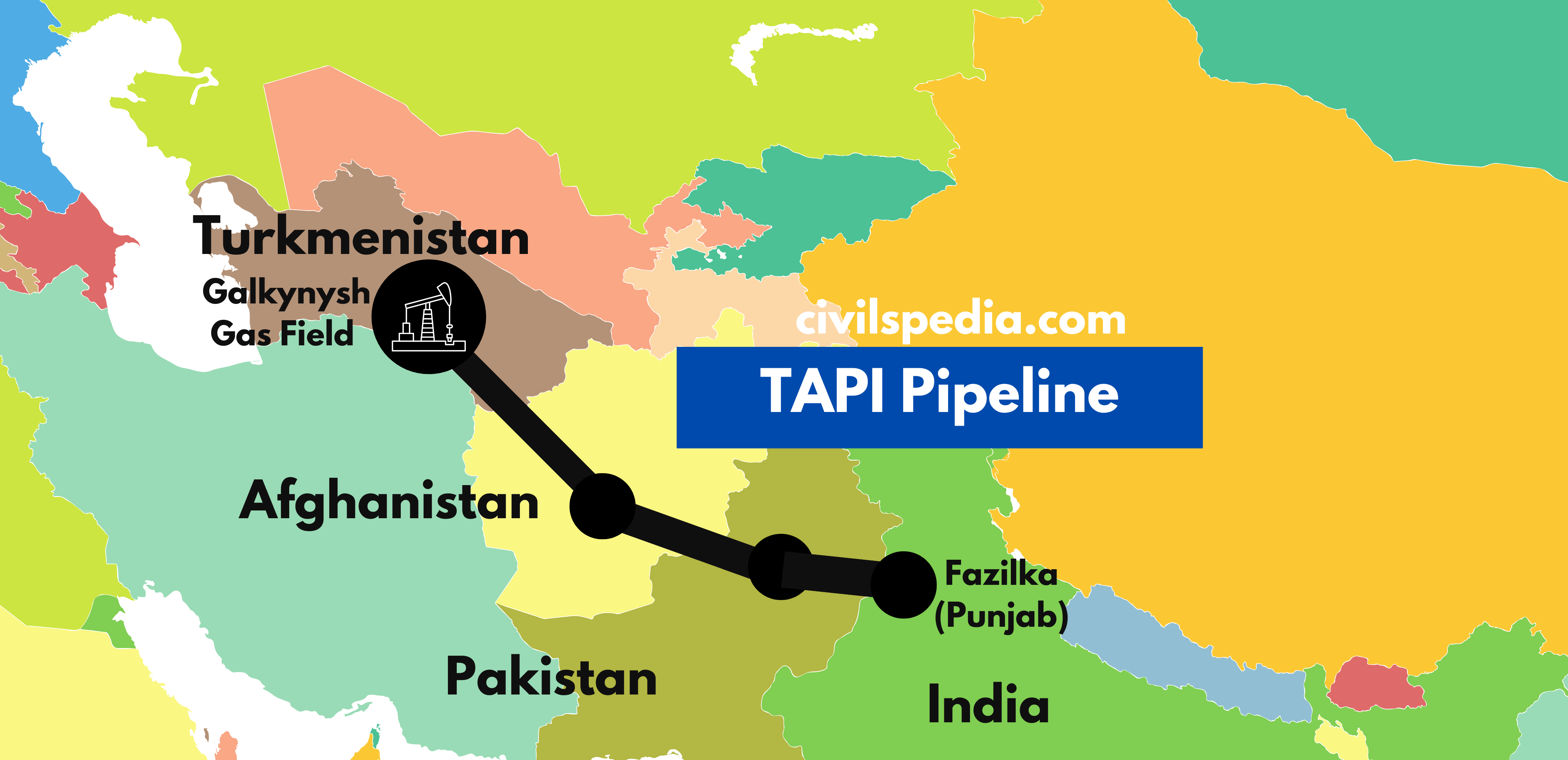
- TAPI pipeline aims to bring gas from Turkmenistan to India while passing through Afghanistan and Pakistan.
It has the following advantages
- It will help bring energy to India and its neighbours at a competitive price.
- It will help India diversify its fuel basket.
- It can help to normalize the relations between India, Pakistan and Afghanistan.
- It will help stabilize Afghanistan as it can earn revenue through transit fees.
But there are challenges as well
- Finance: Nearly 85 % of the project cost is expected to be incurred by Turkmenistan, which is currently facing economic hardship
- Security: The region through which the TAPI pipeline passes is turbulent.
- Geopolitics: Diplomatic relations between India and Pakistan are not conducive for a venture such as the TAPI pipeline.
Connect Central Asia (2012)
- India’s initiative for political, economic & cultural proximity with Central Asia
- It was propounded in 2012.
- The main Aspects of the initiative include
- Cooperation in science and technology
- Educational Exchange
- Helping Infrastructural Development in Central Asia
- Regular Summit Meetings and other exchanges
- It focuses on socio-economic-political cooperation.
Ashgabat Agreement
- The agreement was signed between the governments of Iran, Oman, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, which Kazakhstan and Pakistan later joined in 2016. India joined the grouping in 2018.
- The agreement aims to establish international transport and transit corridor linking Central Asia with the Persian Gulf. It will be achieved via easy customs clearances, fast transport etc.
| First | Joining Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan and Iran via Rail line |
| Second | Making shipping corridors at Bandar Abbas and Chabahar |
Constraints in relation
1. Landlocked and Inaccessible
- Central Asian region is landlocked and has poor connectivity with India.
- To address this, the following connectivity initiatives have been started
- International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC)
- Building Chabahar Port in Iran
- India has joined Shanghai Cooperation Organization
- The process of signing the free trade agreement (FTA) with the Eurasian Economic Union has been fast-tracked
- India has signed Ashgabat Agreement
- Connect Central Asia Policy
- TAPI Pipeline
2. Takeover of Afghanistan by Taliban
- It has made access to Central Asian countries even more difficult.
3. Chinese presence and interest
- China is making considerable inroads in Central Asia through the One Belt One Road initiative.
4. Radicalisation and Terrorism
- Central Asia is vulnerable to radical Islamist influences like Al Qaeda, Islamic State, Taliban, IUM, Hizb-ut-Tahrir and others.
5. Other Issues
- “Youth bulge” with huge unemployment and limited economic opportunities
- Serious and worsening corruption
- Potentially restive minority populations (such as the ethnic Uzbeks in Kyrgyzstan )
- Drug trafficking
Chinese Challenge
- China has invested a massive $35 Billion in Central Asian states.
- Central Asian states are an important part of the Silk Road Economic Belt (SREB).
- Most of the Chinese investments are in the field of energy. Notable projects include
- Pipeline from Turkmenistan To China
- Pipeline from Kazakhstan to China
Investment Comparison: India vs. China
| China | India | |
| Investment | $35 billion | $1.6 billion |
| Trade | $50 billion | $2 billion |
Way Forward
- India should consider setting up an India-Central Asia Forum (on the lines of the India-Africa Forum)
- India should develop the Chabahar port on a priority basis.
- India should focus on Telemedicine, Tele-education etc., i.e. areas where India is strong & where geography doesn’t matter much.
- India should utilize the potential of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization.
