This article deals with ‘Super Computers .’ This is part of our series on ‘Science and Technology which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles on Science and Technology, you can click here
Table of Contents
Super Computers
- Super-Computers are computers with gigaflop capabilities.
- Currently, American “Summit” is the fastest Computer. But China has the most number of Supercomputers in the Top 500.
- Uses: Super Computers are used where large processing power is required. Their uses include
- Weather forecasting (eg: timely warning of cyclones)
- Codebreaking
- Genetic analysis
- Scientific research (like at CERN)
- Data Mining & Big Data Analysis
National Supercomputing Mission
- It was launched in 2015.
- It is the joint mission of the Ministry of Electronics and IT (MEITY) and the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and implemented by C-DAC & IISc (Bangalore).
- The mission envisages empowering academic and R&D institutions by installing a supercomputing grid comprising more than 70 high-performance computing (HPC) facilities.
- PARAM Shivay is the first supercomputer built under this project and installed at IIT-BHU. Later, Param Shakti was installed in IIT-Kharagpur and Param Brahma was installed in IISER-Pune.
- Under the mission, India has also signed an agreement with French company Atos to design and instal a supercomputer named BullsSequana.
Supercomputers of India
- Pratyush
- Mihir
- Sahastra T
- TIFR Colour Boson
- Param
- Saga 220
Pratyush and Mihir
- Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) has set up a high-performance computing (HPC) system consisting of two supercomputers Mihir and Pratyush (which can be connected with each other to solve high-level computations).
- Pratyush installed at the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune having a capacity of 4 petaflops.
- Mihir installed at National Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasting, Noida having a capacity of 2.8 petaflops
- (=> giving a total capacity of 6.8 petaflops.)
- It is India’s first multi-petaflop supercomputer and is the fourth fastest supercomputer in the world which is dedicated to weather and climate research after Japan, U.S.A. and United Kingdom.
- It has also taken India up from the earlier 365th position to top 30 in the infrastructural ranking of Top 500 HPC facilities in the world.
Saga 220
- SAGA = Supercomputer for Aerospace with GPU Architecture
- SAGA 220 is a supercomputer built by ISRO in 2011 with 220 Teraflops peak performance. It can be scaled up to Petaflop (i.e. 1000 Teraflop) capability.
- Use: Space scientists use it to solve complex aerospace problems.
- The project is worth (just) 14 crore and it consumes a power of only 150 kilowatts (=> It is presented as a Model of cheap and environmentally green Super-computer).
Quantum Computer
- Quantum Computer is the computer design that uses the principle of quantum physics to increase computational power beyond what is attainable by a traditional computer.
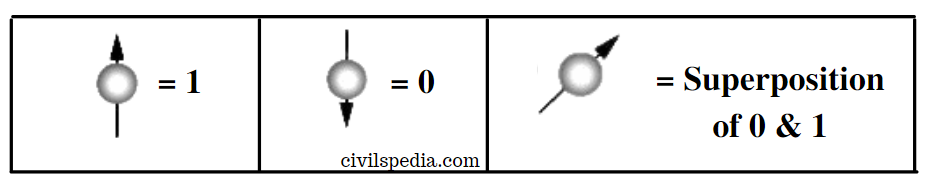
- Normal computer functions by using 1s and 0s retained in electronic components such as transistors. But Quantum Computer would store information as either 1,0 or a quantum superposition of two states enhancing computational capabilities.
- The basic unit of quantum computing the qubit (quantum + bit). While the bit in conventional computers is either a digital “1″ or “0”, the qubit can contain “1″, “0” or ‘or a quantum superposition of two states”.
Applications of Quantum Computers
- High-level R&D with the help of simulations.
- Quantum communications are very secure and fast.
- Quantum Cryptography
- Big Data Analysis
- Deep Learning
- Quantum computing can bring down the space needed to store data.
Steps taken by India to promote Quantum Computing
- Budget 2020 announced that the Government of India will start the National Mission on Quantum Technologies for a period of 5 years.
- Department of Science and Technology started Mission Mode Project called QuST (Quantum Science and Technology) aimed at making Quantum Computer.
- Quantum Communication based Satellite named QuEST (Quantum Experiments Using Satellite Technology) is being built by ISRO.
- Niti Aayog has pitched for using Quantum Computing for Big Data Analysis.
Challenges of Quantum Computers
- Quantum Computers have the potential to decode and crack the world’s encrypted data by breaching security measures easily, thus posing threat to data as well as internal security.
- Hardware difficulties in developing a system such as qubits which are made from silicon atoms and work at a very low temperature, near-zero degree kelvin.
- Funding issues as huge funds are required to set up labs.
- Issues in building Public-Private and Academia-Industry Partnership.
Grid Computing
- Grid Computing is the cheapest model to make supercomputer using unused power of computers that are on the same network.
- It is the emerging computing model which provides the ability to perform higher throughput by taking advantage of many networked computers.
- It is the parallel division of labour between processes. It uses the resources of many separate computers connected by a network usually the internet to solve large scale computational problems.
- A large problem is solved by breaking it into smaller parts.
Common features of Grid Computing
- It is the model for solving the massive computational problem by making use of unused resources of a large number of computers.
- It has the design goal of solving problems too big for any single supercomputer.
Applications of Grid Computing
| Climate Modelling | It can solve the massive computational problem by means of combining unutilised power in thousands of personal computers worldwide. |
| Educational institutions | It provides a cheaper option for educational institutions using a cluster of standard computers that can achieve teraflop performance. Usually, such educational institutions can’t afford the cost of the supercomputer. |
| Government agencies | Grid Computing can be used to combine geographically spread high-performance computing resources to tackle national tasks like electoral rolls or tax databases. |
Other Developments in Grid Computing
| Garuda | It is an Indian Grid Computing initiative connecting 17 cities across India & 45 participating institutions. |
| World Community Grid (WCG) | – Supported by IBM which has donated hardware, software & technical services. – One can join WCG by downloading software application from the internet. – When the computer is idling, this software programme will use its power to work on the grid’s project & when it is in normal use, the software will stop working for the grid. |
Memcomputer
- Memcomputer is a new type of computer that works by mimicking the human brain.
- In conventional computers, processing & memory occur at separate places. Hence, it consumes time & energy putting limitations on computations. But in Memcomputers, processing & storage occur at the same place (just like our brain) leading to fast processing.
- The processing capability of the order of Quantum Computers which operate at extremely low temperature can be achieved in memcomputers operating at normal temperature.
