Table of Contents
Rocks and Minerals
This article deals with ‘Rocks and Minerals.’ This is part of our series on ‘Geography’ which is important pillar of GS-1 syllabus . For more articles , you can click here
Minerals
- Naturally occurring organic and inorganic substance, having an orderly atomic structure and a definite chemical composition and physical properties.
- Composed of two or more elements. But, sometimes single element minerals like sulphur, silver, gold, graphite etc. are found
- Magma is the source of almost all minerals.
Types of Minerals
a. Metallic Minerals
These minerals contain metals and can be sub-divided into
| Precious Metals | gold, silver, platinum |
| Ferrous Metals | iron and other metals often mixed with iron to form various kinds of steel. |
| Non-Ferrous Metals | include metals like copper, lead, zinc, tin, aluminium etc. |
b. Non-Metallic Minerals
- These minerals do not contain metal content.
- Sulphur, phosphates and nitrates are examples of non-metallic minerals.
- Cement is a mixture of non-metallic minerals.
Rocks
- A rock is an aggregate of one or more minerals.
- Rocks do not have definite composition of mineral constituents.
- Petrology is the science of rocks.
- The age of the rock is determined based on Carbon-14 dating.
Type of rocks
a. Igneous Rocks
- Igneous rocks (Ignis in Latin means ‘Fire’) are formed when magma cools and solidifies.
- They are known as primary rocks
- Igneous rocks are classified based on texture.
- If cooled slowly at great depths : Large grains
- Sudden cooling (at the surface) : small grains.
- Intermediate cooling : intermediate size of grains .
- Granite, gabbro, pegmatite, basalt, volcanic breccia and tuff are some of the examples of igneous rocks.
b. Sedimentary Rocks
- Formed by lithification of sediments
- They are also known as detrital rocks
- Examples : sandstone, shale, loess , chalk, coal , limestone etc
c. Metamorphic Rocks
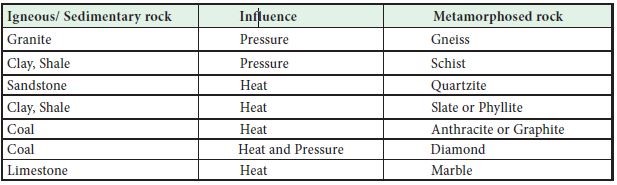
- Metamorphic rocks are formed when already consolidated rocks undergo reorganization in structure due to excessive pressure (through the process called Metamorphism)
- Eg : Gneiss, syenite, slate, schist, marble, quartzite, anthracite, diamond etc.
Igneous and metamorphic rocks together account for 95 percent of the earth while rest 5% are sedimentary rocks.
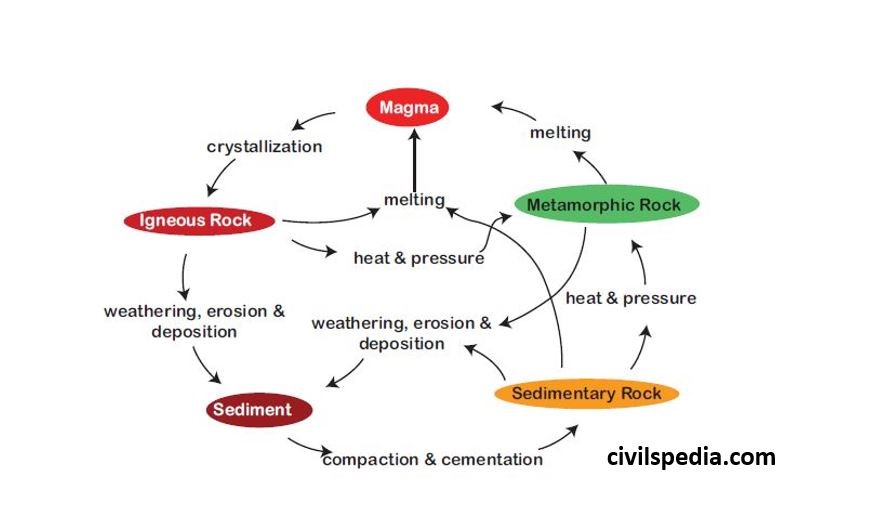
Rock Cycle
Rocks do not remain in their original form for long but may undergo transformation. Rock cycle is a continuous process through which old rocks are transformed into new ones.