Last Updated: May 2023 (Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe)
Table of Contents
Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe
This article deals with ‘Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe ’. This is part of our series on ‘Society’ which is an important pillar of the GS-1 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Safeguarding Measures for SC and ST
1. Constitutional Measures
1.1 Affirmative Action
| Article 15(4) | The state can make special provisions for the advancement of socially and educationally backward (SEB) classes of citizens, including SCs and STs. |
| Article 16(4) | Reservation in public services |
| Article 355 | Claims of SCs and STs shall be taken into consideration in making appointments to the public services. |
1.2 Protective Measures
| Article 17 | Abolition of Untouchability |
| Article 23 | Forced labour is prohibited. |
| Article 25 | The state is empowered to throw open Hindu religious institutions to all classes and sections of Hindus |
1.3 Political Measures
| Article 330 | Reservation of seats in Lok Sabha in the proportion of their population |
| Article 332 | Reservation in Legislative Assembly |
| Article 243-D(1) | Reservation in Panchayat |
| Article 243-T(1) | Reservation in Municipality |
1.4 Administrative rights
| Schedule 5 | Provisions for Scheduled Areas |
| Schedule 6 | Provisions for Tribal Areas |
| Article 338 | National Commission for SC |
| Article 338-A | National Commission for ST |
1.5 Specifically for STs
| Article 19(5) | The state can impose restrictions on freedom of movement or residence for the benefit of Scheduled Tribes. |
| Article 164 | Appoint special minister for tribal welfare in MP, Bihar, and Orrisa. |
| Schedule 5 & 6 | Discussed in Polity |
2. Legal Measures
2.1 For Scheduled Castes
- Protection of Civil Rights Act (PCRA), 1955: The act deals with untouchability
- Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of the Atrocities) Act, 1989
- Prevents commission of atrocities against SC/ST by a person other than SCs & STs.
- Establishment of special courts for speedy trial of such offences.
- Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013
2.2 For Scheduled Tribes
- Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of the Atrocities) Act, 1989
- PESA, 1996
- Forest Rights Act, 2006
How particular tribe is added to the list of Scheduled Tribes?
It is done under the provisions of Article 342 in the following way
- President, by public notification, specifies the tribal communities to be declared as Scheduled Tribe.
- Parliament amends the list for including or omitting names of communities in the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950.
SCs and STs (Prevention of the Atrocities) Act, 1989
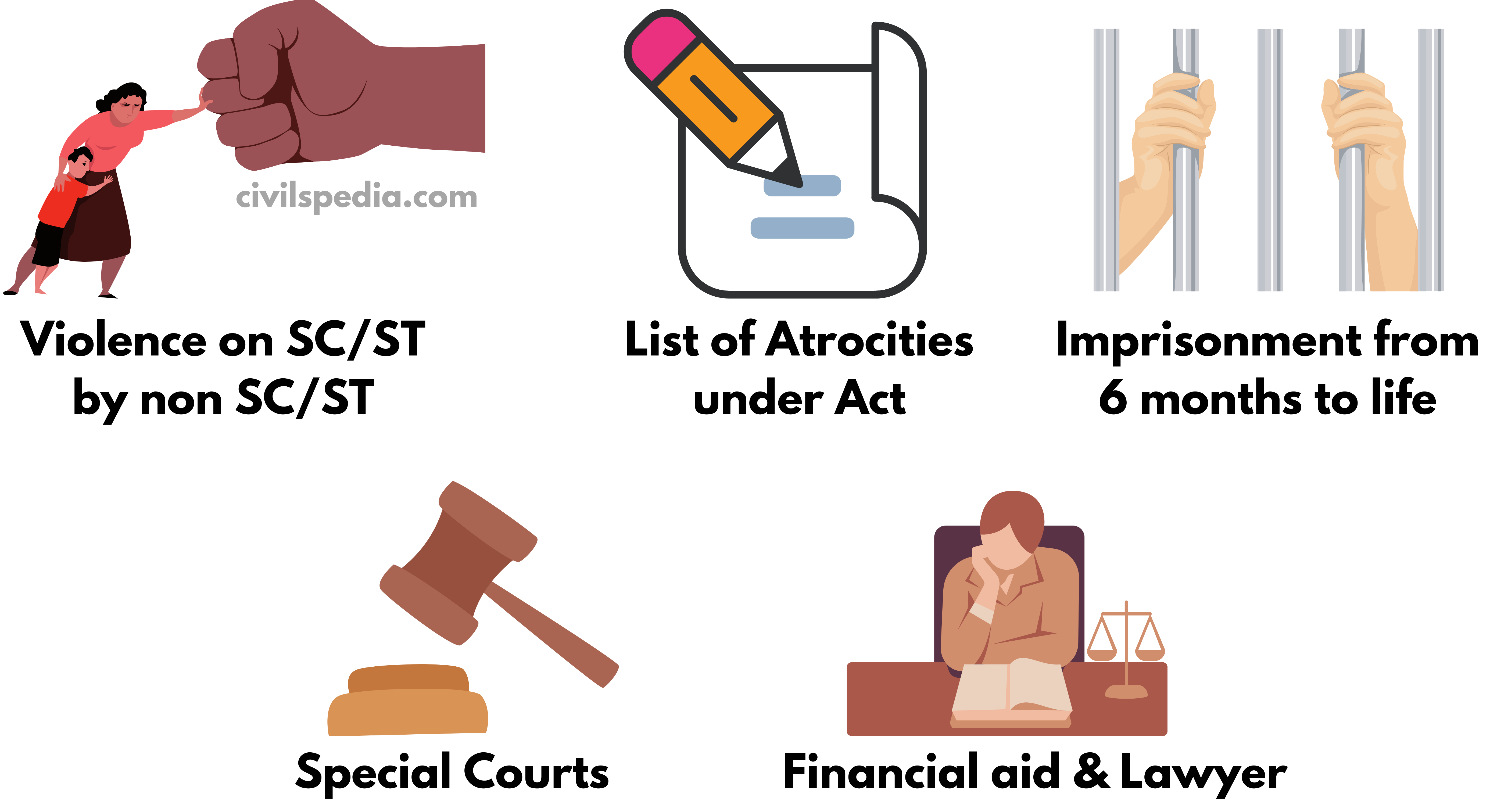
Meaning of the Atrocities
- The term atrocity is not defined in law (but the list of atrocities is given).
Applicable to
- The act is applicable in connection with Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes who are subjected to violence and brutalities by any person who is not a member of a Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
Atrocities mentioned in the Act
Atrocities under the act include (but are not limited to):
- Social discrimination
- Beating, lashing and other forms of torture
- Arson-the burning of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes communities and their homes
- Violence against women
- Bonded labour
- Denial of rights, especially land rights
- Deny to give job or do business with a person belonging to SC/ST
- Forcibly remove cloth
- Forcing to eat something
- Denying access to a public place
- Police abuses against Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes and custodial abuse
Imprisonment
- The person will be put behind bars at the same instant when FIR is lodged against the person.
- There is no provision of Anticipatory Bail. Only High Court can grant bail.
- The act has the provision of imprisonment ranging from 6 months to life.
Regarding Government Servant
- If any government servant indulges in such activity, there is a provision of imprisonment of 6 months to 1 year.
- The case can be registered against a government servant only when he is found guilty in the investigation.
Other Provisions
- Special Courts have been established to deal with these cases.
- SC/ST are provided with financial aid and a lawyer to fight the case.
Working Appraisal of Act
- There are only 194 Special courts which amount to only 1 out of 3 districts having special courts.
- The conviction rate is very low,
- The awareness about the act is very low among the community it is designed to protect.
- The police, which in most of the states is filled up with dominant caste, guard the door to justice by not filing FIRs.
Forest Rights Act,2006
- Forest Rights Act or Scheduled Tribes and Other Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act came into force in 2006.
- It has been enacted to recognize and vest the forest rights and occupation of forest land in forest-dwelling Scheduled Tribes and other traditional forest dwellers, who have been residing in such forests for generations, but whose rights could not be recorded.
Main provisions of the act
- The authority to vest forest rights in forest-dwelling Scheduled Tribes and traditional forest dwellers have been vested with the Gram Sabha.
- It guarantees the following rights
- Title Rights: The right in the land is granted to STs and the people who have been residing there for 75 years but don’t have documents (maximum 4 hectares)
- Right of use of resources. E.g., Minor Forest Produce (honey, herbs etc.), common property resources etc.
- Relief and Developmental Rights: In case of any displacement of tribals, proper relief packages should be given.
- Forest Management Rights of the Forest Dwellers to protect forests and wildlife.
Issues wrt Forest Right Act
- The task of documenting the claims of communities is very tedious.
- Reluctance on the part of the bureaucracy
- The narrow interpretation of the law
- Opposition from wildlife conservationists
- The Forest Rights Act is often in conflict with other laws, e.g., rights in protected areas like wildlife sanctuaries, national parks, etc.
Dalit Capitalism
- Dalit activist Chandra Bhan Prasad coined the term.
- It is a process in which capitalism is seen as a solution for the upliftment and emancipation of dalits.
Government steps like
- Stand Up Scheme
- MUDRA Bank
- PSL lending to SCs
are inline with Dalit Capitalism
But there is a fundamental flaw with the concept
- It wants to correct one exploitative system, i.e. Caste System, using another exploitative system, i.e. capitalism.
- Dalit Capitalism will not uplift the poorest of poor dalits.
Stand Up India

Every bank branch will provide
- a loan from Rs 10 lakh to Rs 1 crore
- to one Dalit or Adivasi member and one woman each
- For greenfield enterprises in the non-farm sector without collateral.
Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTG)
- 1973: Dhebar Commission created Primitive Tribal Groups (PTGs) as a separate category, who are less developed among the tribal groups.
- 2006: The government of India renamed it to Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
- At present, they are 75 in numbers like Asurs of Bihar, Seharias of Rajasthan, Jarawas, Sentinelese and Onges of Andaman and Nicobar.
PVTGs have some basic characteristics

Problems faced by them
- The growth of PVTGs’ population is either stagnating or declining.
- The health status of PVTGs is in awful condition because of poverty, illiteracy, lack of safe drinking water, bad sanitary conditions etc.
- The condition of education is also deplorable, with an average literacy rate of 10% to 44% in PVTGs.
Scheme: Scheme for Development of PVTGs
- It identifies 75 PVTGs as the most vulnerable among the Scheduled Tribes.
- It gives state governments flexibility in planning initiatives.
- Long term Conservation cum Development plan for five years for each PVTG to be established by States.
- The scheme is funded entirely by the Central government.
Eklavya Schools
- The government opened Eklavya Schools in budget 2018.
- Eklavya schools were established in all Tribal blocks with more than 50% ST population.
- Eklavya schools provide boarding and lodging facilities to tribal students.
- These schools will have special facilities for preserving local art and culture besides providing sports and skill development training.
Aadi Mahotsav
- Aadi Mahotsav is an annual initiative of TRIFED to showcase the tribal culture on the national stage and promote tribal crafts, cuisines and culture.
TRIFED or Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India
- TRIFED was formed in 1987.
- It works under Tribal Ministry
- It performs the following two functions
- Minor Forest Produce Development
- Retail Marketing Development of tribal products
Pradhan Mantri Van Dhan Yojana
- The Van Dhan Vikas Yojana aims to promote the development of tribal communities by fostering the creation of groups that focus on enhancing the value of forest resources through processing.
- The initiative provides essential support to these groups, including infrastructure, tools, and equipment, as well as training in value addition and entrepreneurship.
Umbrella Scheme for SCs
After rationalization of Centrally Sponsored Schemes, all the Schemes for Scheduled Castes are taken under one Grand scheme, Umbrella Scheme for Scheduled Castes, which is Core of the Core Scheme and is 100% Centrally Sponsored.
Some of the Schemes under this are
1. Educational Empowerment
- Pre-Matric Scholarships to SC Students
- Post Matric Scholarship for SC students
- Full financial support for pursuing studies beyond 12th class, in notified institutes of excellence like IITs, NITs, IIMs, reputed Medical/Law and other institutions.
- National Fellowship: Financial assistance to SC students for pursuing research studies
- National Overseas Scholarship: for pursuing higher studies of Master level and PhD programmes abroad.
- Babu Jagjivan Ram Chhatrawas Yojna
2. Economic Empowerment
- Standup India
- Venture Capital Fund for Scheduled Castes
