Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal security
This article deals with ‘Security challenges and their management in border areas.’ This is part of our series on ‘Internal Security’, which is an important pillar of the GS-2 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
Definition: State Actors vs Non-State Actors
State Actors (SA)
- State Actors are based on the premise of sovereignty, recognition of statehood and control of territory & population.
- E.g., India, the US, and Micronesia (irrespective of size).
Non-State Actors (NSA)
- In the Post-Cold War Era and with the advent of Globalisation, the concept of the Nation-State has experienced erosion, and Non-State Actors have become the force to reckon with.
- Non-State Actors are not always sympathetic to national interests, but their loyalty lies with group, corporation or community interests.
- The traditional hierarchy, which used to exist earlier with the military dominating economic & social interests, doesn’t exist anymore because of the rise of Non-State Actors.
- Examples of NSAs include
| International Government Organisation | NATO, UNO etc. |
| NGO | Amnesty International, Greenpeace etc. |
| Multi-national Corporations | Operating in multiple sovereign states eg Shell(oil) |
| International Media | BBC, Al-Jazira, CNN etc. |
| Violent Non-State Actors | Al-Qaeda , Drug Cartels |
| Religious Groups | Roman Catholic Church |
| Transnational Diasporic Communities | Indian Diaspora affects policies back home |
Challenges to India’s Internal Security from NSAs

1 . Terrorism
- Non-State Actors, mainly terrorist groups, are involved in the execution of terror attacks. Notably, in the case of India, these terrorist groups are either secessionists or Islamic fundamentalists.
- These Terrorist Organizations have been banned under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act of 1967.
- Examples of Terrorist Non-State Actors include
| Lashkar e Taiba | Jaish e Mohammad |
| Harkat ul Mujahideen | Hizb ul Mujahideen |
| United Libration Front Of Assam | National Demo Front of Bodoland |
| LTTE | CPI (Maoist) |
| Babbar Khalsa International | Khalistan Commando Force |
2. Naxalism
- Naxalism was started as a movement for land reforms. Later, it took a violent & dangerous turn aiming at overpowering the democratic structure of India via violent armed struggle.
- Naxalists get financial, ideological and technological support from external Non-State Actors (especially foreign leftist organizations from the Philippines, Turkey and China.).
3. Insurgency
- Many insurgent groups are active in North-East with demands ranging from separate states to regional autonomy to complete independence.
- It is difficult to handle these insurgents because of the rugged terrain, porous border & external support of adjoining states.
- There is massive unemployment in the North-East region. Hence, unemployed youth provide an easy target for recruiters.
- Interlinkages between outfits ensure a smooth transfer of military hardware & technology. Even the weakest outfit has access to sophisticated technology ranging from satellite communication to automatic guns.
- State and Non-State Actors help the insurgents in various ways. The examples mentioned below will help in understanding this.
3.1 Naga Insurgents
- Naga insurgents receive patronage from the Chinese regime.
- They enjoy safe havens in Bhutan, Bangladesh & Myanmar.
- Naga outfits like NSCN (IM) have close links with NDFB, Naxalists etc. They even have links with Burmese groups like United Wa Army and Kaichin Independence Army (KIA).
3.2 ULFA
- ULFA waged an international struggle by attending meetings of the Unrepresented Nations Peoples Organisation.
4. Cyber Attacks
- Cyber attacks are carried out by cyber criminals, cyber terrorists and other foreign states.
- While cybercriminals indulge in such activities for monetary gains, cyber terrorists want to further their political objectives.
- India’s exponential growth in the IT sector and various e-governance measures make it extra vulnerable to such attacks. E.g., the 2010 Commonwealth Games hosted by India witnessed Cyber attacks from Pakistan & China to damage information systems.
- It has been noticed that most cyber attacks on India originate from the US, China, Russia, East Europe & Iran.
5. Counterfeit Currency / Economic
- It is tough to distinguish between fake & real currency nowadays because the fake currency is printed with state-of-the-art technology using security paper supplied by state actors.
- It is a sub-conventional warfare strategy pursued by Pakistan against India.
- Fake currency is mainly brought to India through the porous borders of Nepal & Bangladesh.
- Terrorist organizations like Hizb ul Mujahideen use the fake currency to fund their programs.
- To tackle this, the government has taken various measures like
- Demonetisation of Indian currency notes.
- New notes have more security features. Hence, they are difficult to counterfeit.
- A special cell under NIA has been formed to counter terror funding and fake currency.
6. Communalism
- Various reports highlight that domestic extremist organizations get financial & ideological support from external religious organizations (Non-State Actors) and Foreign States (Pakistan, China etc.).
- E.g.:
- Pakistan (state actor) funds Kashmiri Terrorists.
- Islamic terrorists are getting ideological support from ISIS.
- Saudi Arabia is promoting and funding radical Wahhabism in the world.
- Zakir Naik’s Islamic Research Foundation and Peace TV are radicalizing Muslim Youth in India and Bangladesh.
7. Drug Trafficking
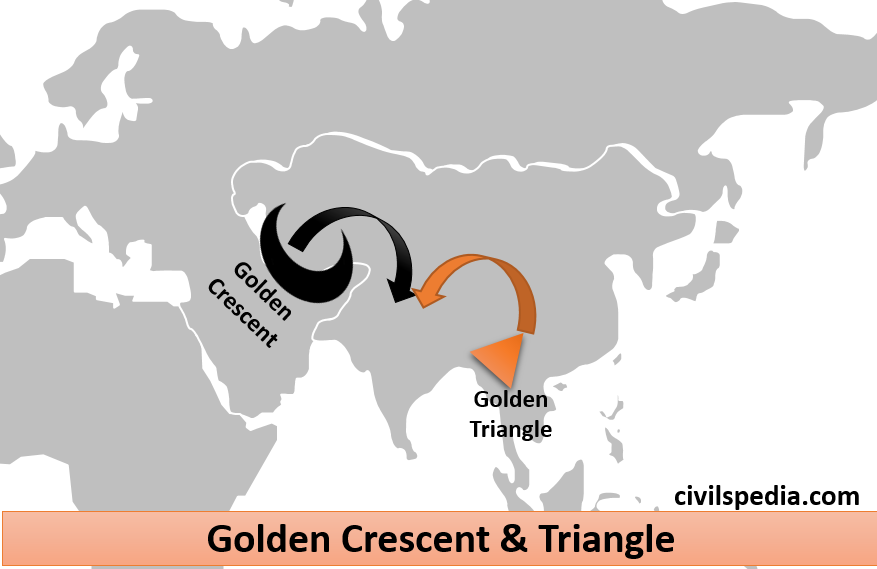
- Due to its location, India has become a transit hub & destination for drugs originating from GOLDEN TRIANGLE (Myanmar, Thailand and Laos) & GOLDEN CRESCENT (Afghanistan, Pakistan and Iran).
- There is nexus between drug traffickers, organized criminal networks & terrorists, which is powerful enough to destabilize even the whole nation. Money generated by this trade is also used to fund insurgents & terrorists.
8. Human Trafficking
- Human trafficking, in major part, involves the abduction, buying and selling of women and children for prostitution, forced marriages and bonded labour.
- India has been both the source and destination of human trafficking.
- Women and children are trafficked from Nepal and Bangladesh to be sold inside the country for prostitution.
- Women are trafficked from India to the Middle East and other European countries, where they are employed as low-skilled labourers, domestic workers and sexual exploitation.
9. Piracy
- Piracy is a serious threat to India because the Indian economy heavily depends on the export and import of goods. Securing the Sea Lane of Commerce is vital for India.
- In the Indian Ocean, Somalian pirates are active around the Horn of Africa, which poses a great threat to India’s energy security as oil tankers also pass through this region. To tackle this, the Indian government has taken various measures, including escort vessels in the Gulf of Aden.
10. Security threats posed by Indian Diaspora
- Indian (Muslim) diaspora in Gulf nations is indoctrinated during their stay and used for carrying out terrorist activities and propaganda on their return to India.
- A large number of Sri Lankan Tamils were forced to take refuge in Tamil Nadu during the Civil War in Sri Lanka between Sri Lankan Army and LTTE. They, along with the people of Tamil Nadu, exert pressure on Tamil Nadu and the Indian government to take a stand against Sri Lankan government, causing strain in Indo-Lanka relations.
- Indian (Sikh) diaspora in countries like the UK, Canada, USA, Australia etc., support the Khalistan issue.
11. Threats posed by Multi-National Corporations (MNCs)
- In today’s globalized world, MNCs are influencing the global economy, and some MNCs (like Facebook, Coke etc.) have become more powerful than nation-states.
- Actions of powerful mining MNCs like Vedanta and POSCO and subsequent encroachment of the lands of Adivasis resulted in the emergence of Naxal / Maoist movements in these areas.
- Powerful seed companies like Monsanto and Bayer can pose a great threat to the nation’s food security by patenting the technology used to manufacture GM and HYV seeds.
- MNCs shatter the faith of the common public in the government. Government loses legitimacy, and people tend to believe that it is working for these MNCs and big corporates.
12. Threats posed by NGOs
- NGOs have a soft glove and apologist attitude towards Naxalites, Insurgents & Terrorists.
- NGOs like Amnesty International force governments to repeal acts like AFSPA, which can prove dangerous in some situations.
- Intelligence Bureau (2014) also brought to the forefront the obstructionist role played by Foreign Funded NGOs and the loss of GDP to the tune of 2% happening due to their protests.
To counter this, Parliament passed Foreign Contributions Regulation Act (FCRA) in 2010 to regulate the flow of foreign funds to NGOs.
Part 2: Role of External State Actors in creating threats to Internal Security of India
2.1 Internal Security threats posed by China
- India and China have a long-standing border dispute which leads to frequent Chinese intrusions into Indian territories. Recently, China has been following an assertive policy, as evident from the Galwan clashes (2020).
- China is supporting the insurgents in the North-East States, corroborated by the fact that counter-insurgency operations in the North East have resulted in the recovery of dozens of made-in-China rifles, pistols, grenades and other ammunition. NIA has found evidence that the National Socialist Council of Nagaland (NSCN-IM) and the National Democratic Front of Bodoland (NDFB) are buying weapons from Norinco (a state-owned weapon manufacturer in China).
- China also provides shelter to North Eastern ethnic separatist militants (Eg, NSCN, ULFA etc.).
- Since the beginning, the Maoist/ Naxalism movement has received philosophical, moral, financial, and intellectual support from China.
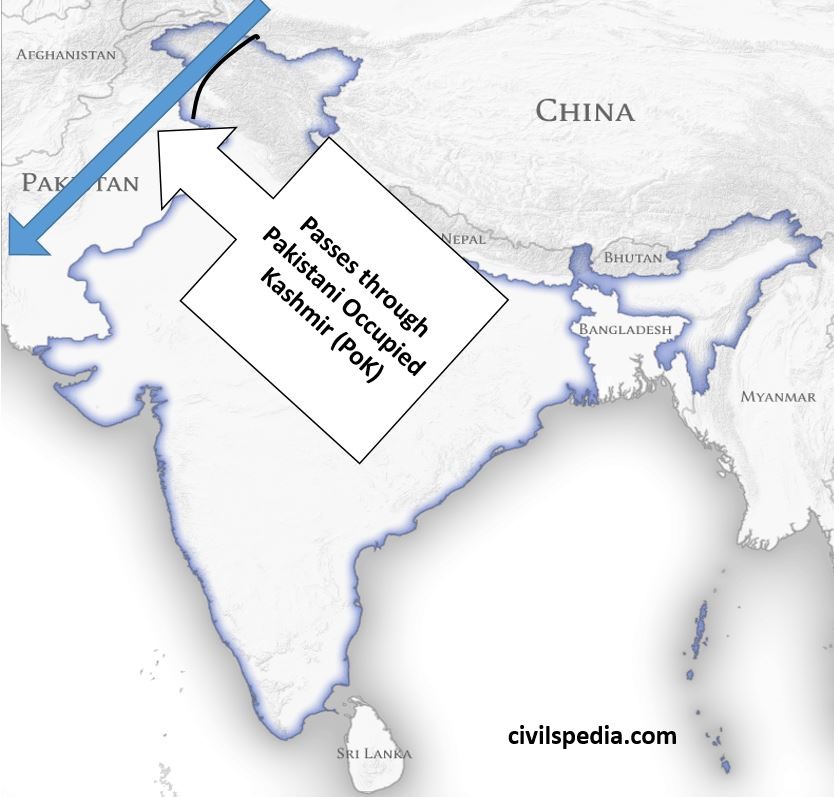
- China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), which connects Xinxiang with Gwadar port, passes through Pakistani Occupied Kashmir and undermines Indian sovereignty over the region.
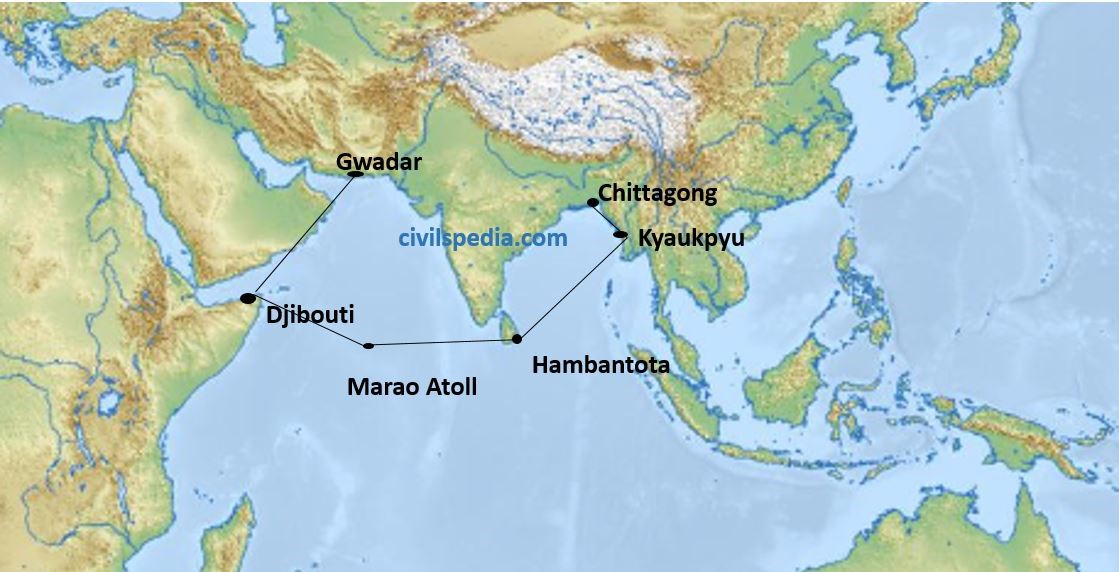
- China is building a large number of naval bases in the Indian Ocean to encircle India through its String of Pearl strategy.
- Cheap Chinese mobiles sold in the Indian market manufactured by companies like Xiaomi pose a threat of surveillance and data leakage by the Chinese state. The Indian military has barred its employees from using Chinese mobiles.
2.2 Internal Security threats posed by Pakistan

- Terrorism in the UT of Jammu and Kashmir is the direct manifestation of Pakistan’s policy of bleeding India through a thousand cuts.
- ISI of Pakistan also supports Naxal groups to foment disturbance and law and order problems in India.
- In the North-East, Pakistan’s ISI has trained and financially supported insurgent groups such as ULFA.
- Pakistan is encouraging non-state actors like the Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT) with active funding and logistical and military support to foment unrest in India.
- Pakistan is trying to flood India with fake currency so as it impact the Indian economy and weaken the trust of the public in the Indian currency.
- Pakistan is flooding the border states with drugs to destroy India’s youth and produce unrest in the country.
- Pakistan indulges in complex cyber attacks on Indian companies, government websites and databases.
2.3 Internal Security threats posed by Bangladesh

- Bangladesh acts as a safehouse for terrorists. During Khalida Zia’s regime, DGFI (Bangladesh’s intelligence agency) also used to support insurgent groups in the North-East.
- Illegal migration from Bangladesh to North-Eastern states has been the source of communal and ethnic tension in India, resulting in large-scale demographic changes in the North-East region.
- Due to the porous nature of the border, there is a rampant drug, human and cattle trafficking. While there is no evidence of direct state involvement in this case, it is its inactivity to resolve the issue that is concerning.
