Table of Contents
Ways to Control Climate Change
This article deals with ‘Ways to Control Climate Change – UPSC.’ This is part of our series on ‘Environment’, an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles on Science and technology, you can click here.
Introduction
- It is a deliberate, large-scale intervention carried out in Earth’s natural systems to reverse the impacts of climate change.
- It involves techniques to physically manipulate the global climate to cool the planet.
- These techniques fall primarily under three categories:
- Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS)
- Climate Engineering
- Carbfix Project
- Controlling the Emissions of Ruminants
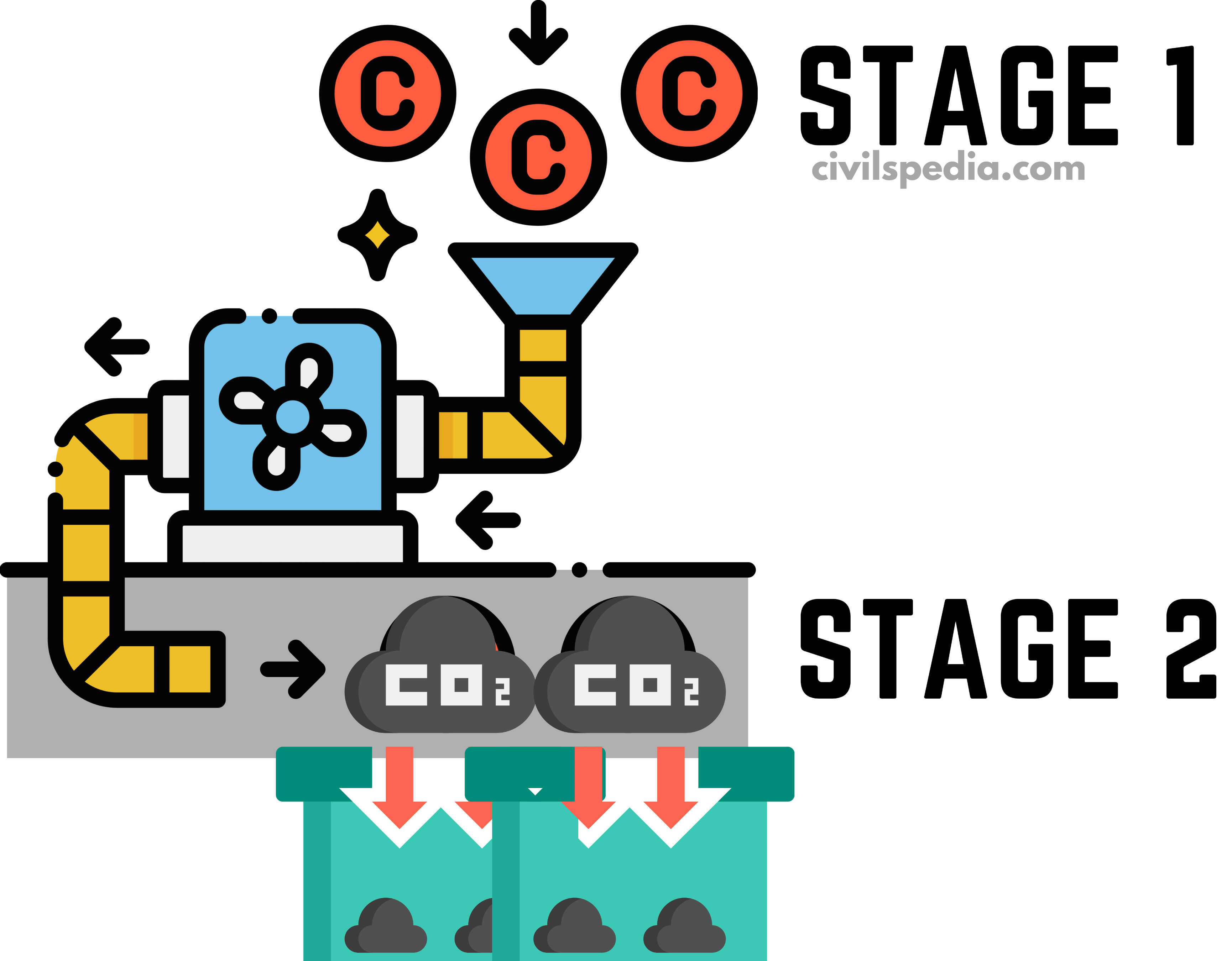
1. Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS)
It is the process of removing carbon from the atmosphere & depositing it in a reservoir.
First Capture CO2
- Firstly, we need to capture the CO2 directly from the atmosphere or at the end of combustion & industrial processes.
- It is done using technologies such as
- Chemical Solvent: Preferred when dealing with gas streams that are lean in CO2 and have relatively lower pressures, such as flue gas streams from power plants etc.
- Adsorption: Suitable for gas streams with moderate to high pressure and moderate CO2 concentration, such as steam methane reforming (SMR) flue gas.
- Cryogenic Separation: Preferred in cases where the cost of power is low.
Transport and then store CO2 in Reservoir (Carbon Sequestration)
The captured CO2 is then stored in reservoirs, which can include
- Depleted Oil and Gas Reserves
- Unmineable Coal Seams
- Deep Saline Aquifers
- Enhancing the productivity of ocean biosystems through fertilization, e.g. algae
- Inject CO2 into the deep ocean
- Enhancing and manipulating the forests, wetlands etc.
- Artificial Upwelling: This water will absorb more CO2
- Ocean fertilization
Issues with the concept
- There is general agreement about the need to halt fossil fuel emissions, particularly in industrialized countries. However, instead of moving ahead with drastic reductions in energy use and initiating a transition towards low-carbon economies, forests’ ability to (temporarily) sink carbon is being used to justify continued fossil fuel use.
- Afforestation – especially afforestation in northern tundra regions – may accelerate global Warming. Dark green forests absorb more sunlight than tundra or farmland, adding to the warming trend (snow reflects).
- All carbon is not the same. Fossil carbon is generally static, whereas that which is in the active carbon pool (the atmosphere and the biosphere) can be easily released through activities beyond government control, such as forest fires).
- Lands dedicated to carbon sink projects require contractual agreements that lock the land up for years, often decades.
- High Cost: Upfront capital investment for carbon capture technology, transport pipelines, and geological storage is high, and significant energy and water usage is required to capture and compress CO2.
- Insufficient geological information: Due to a lack of geological survey technology, companies lack geological information before the project is carried out. Therefore, they cannot accurately predict project risks.
2. Climate Engineering
- Climate engineering describes a diverse and largely hypothetical array of technologies and techniques for intentionally manipulating the global climate to moderate or forestall the (most severe) effects of climate change.
- These include
- Space Mirrors: Reflect Solar Energy and not allowing it to enter the atmosphere
- Reflective Aerosols in Stratosphere (proponents claim that it can reduce Global Warming by 1 C)
- Cloud Seeding: Clouds are good reflectors of sunlight
- Using pale-coloured roofing material or growing high albedo crops
- Cirrus cloud manipulation: cirrus clouds are removed or thinned so that their long-wave trapping capacity is reduced, thus cooling the surface.
3. Other Projects for Carbon Fixation going on
3.1 Carbfix Project
- It is a project in Iceland that aims to lock away CO2 by reacting it with basaltic rocks.
- Carbonated water is injected into the rocks to react with Calcium, Magnesium or Silicate material present in Basaltic rocks. It is called enhanced weathering. Thus, the CO2 is captured permanently without releasing any harmful by-products.
3.2 Controlling the Emissions of Ruminants

Philanthropists such as Bill Gates are funding startups to develop feed called Rumin8 that will reduce the amount of methane they emit in the atmosphere.
