Table of Contents
World Bank
This article deals with the ‘World Bank .’ This is part of our series on ‘Economics’ which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
World Bank Group & World Bank
- World Bank Group is a family of 5 international organizations that give loans to developing countries.
- It is a ‘Specialized Agency of UN’.
- Bank came into existence in 1945 following the Bretton woods conference.
- It is headquartered in Washington DC.
- Each institution of the World Bank is owned by its member governments & its membership gives certain voting rights to all countries. But additional votes depend on the financial contribution to World Bank.
- The President of the World Bank is usually an American & the present President is David R. Malpass (US economist).
Institutions
IBRD & IDA constitute World Bank while All 5 constitute World Bank Group.
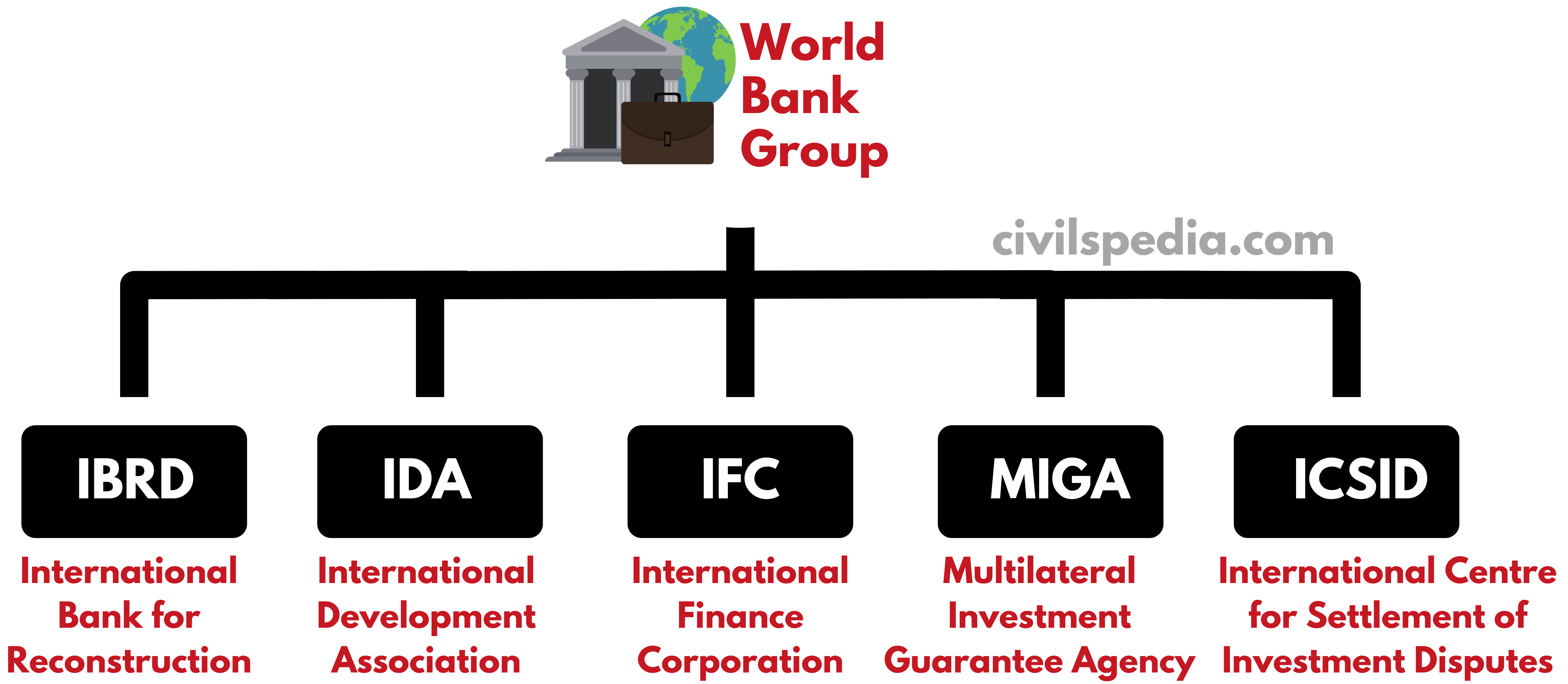
1 . International Bank for Reconstruction & Development (IBRD)
- IBRD is the oldest of all World Bank institutions that started working in 1945.
- It commenced lending to India in 1949.
Main functions
- Initially, the primary function of IBRD was the reconstruction of war-ravaged regions (after World War II).
- Later, it evolved to the development of middle income & creditworthy developing economies of the world.
- Arranging the loans or providing guarantees on loans by various other channels to execute essential projects.
- IBRD facilitates different kinds of technical services to the member countries through Staff College and experts.
- Human development was the main focus of development lending with a very low-interest rate (1.55% per annum) – the area of focus being agriculture, healthcare, family welfare etc.
Note: The name “International Bank for Reconstruction and Development” was first suggested by India to the drafting committee.
2. International Development Association (IDA)
- It was set up in 1960.
- IDA is known as the soft window of the World Bank.
- It gives long term credit with the basic aim of developing infrastructure & extended to economies having per capita income lesser than $895. Credit is for 35-40 years, interest-free except for a small charge to cover the administrative fee. Every developing nation make enough diplomatic attempts to get money from here because of additional benefits.
- India has been one of the biggest beneficiaries. But, since 2014, India stopped receiving soft loans from IDA as it breached the $895 per capita income mark.
3. International Finance Corporation (IFC)
- IFC was set up in 1956.
- It is called the ‘Private arm of the World Bank‘ because it lends the money to private companies of member nations. Interests charged on the loans backed by IFC are low.
- It plays a catalytic role, stimulating & mobilising private investment in the developing world by demonstrating that investment there can be profitable too.
4. Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA)
- It was set up in 1988.
- It offers insurance to foreign investments in the member countries due to non-commercial ( i.e. political) activities such as currency transfer, expropriation, war & civil disturbance, thus encouraging foreign investment in developing countries.
5. International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID)
- ICSID was set up in 1966.
- It is an investment settlement body whose decisions are binding on parties. It settles disputes arising between investing foreign companies & host countries.
- India is not a member of ICSID.
- Membership of ICSID encourages foreign investment in the country but also infringes upon sovereignty.
Bilateral Investment Promotion & Protection Agreement (BIPA)
- BIPA is an Indian version of ICSID since India is not a member.
- It promotes & protects the investment of investors on a reciprocal basis.
- Till now, India has signed BIPA with 72 nations.
- Objective: To promote & protect the interest of either country in the territory of other.
India and World Bank
- India has been a member of 4 institutions of the World Bank Group except for ICSID.
- World Bank has given sizeable financial assistance to India for economic development. Until China became a member of the World Bank in 1980, India was the largest beneficiary of the World Bank assistance.
- World Bank assistance to India started in 1948 when funding for Agricultural Machinery Project was approved. The World Bank has also assisted in developing infrastructures such as electric power, transport, communication, irrigation projects and steel industry.
- The first investment of IFC in India took place in 1959 with US$ 1.5 million. Presently, IFC has been helping India to raise foreign capital via ₹ denominated Masala and Maharaja Bond.
Notable Reports of World Bank
- Ease of Doing Business Report
- Remittances and Migration Report
- World Development Report
- Global Economic Prospects Report
