Telecom Governance
This article deals with ‘ Telecom Governance.’ This is part of our series on ‘Science and Technology’ which is an important pillar of the GS-3 syllabus. For more articles, you can click here.
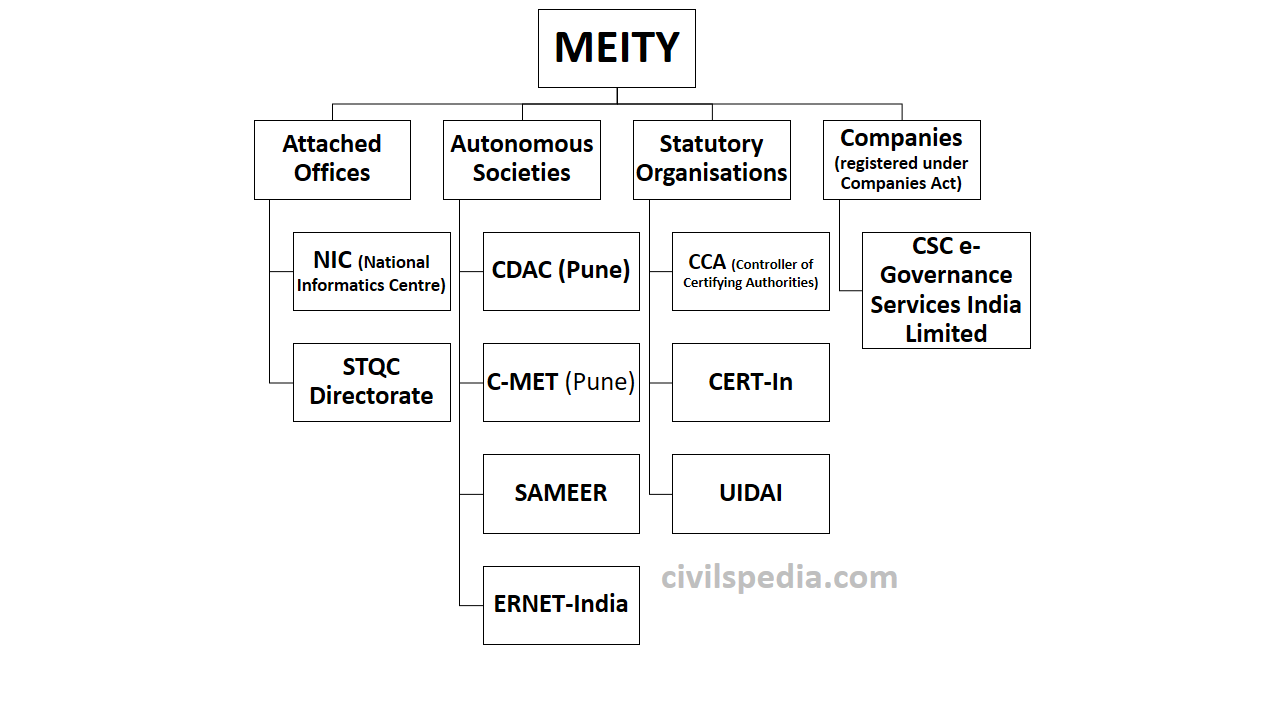
Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MEITY)
- Earlier, it was a department under the Ministry of Communication & Information Technology. But now it has been made a full-fledged Ministry.
- Vision: e-Development of India as the engine for transition into a developed nation & empowered society.
- Its main objectives include
- e-Government: To provide e-infrastructure for delivery of e-services.
- e-industry: To promote electronics manufacturing and the IT industry.
- e-Innovation: To provide support for the creation of Innovation Infrastructure in the emerging areas of technology.
- e-Education: To provide support for the development of e-skills and knowledge network.
- e-Security: To secure India’s cyberspace.
C-DAC (Centre for Development of Advanced Computing )
Origin
- It was established in 1988 as an autonomous scientific society of MEITY.
- C-DAC was started because of the abortive attempt of IISc in purchasing supercomputer purely for academic purposes from the US. The demand for purchase was rejected under the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR).
- Two thrust areas of its first decade were
- Supercomputing
- Indian Language Computing
- But in the subsequent period, C-DAC has diversified its activities to various areas like financial & capital market simulation & modelling, networks & internet software, health care, e-governance, artificial intelligence etc.
Various Missions of C-DAC
1. Supercomputer
- C-DAC made the first supercomputer of India i.e. Param 8000.
- After that, it made various supercomputers like Param Ananth, Param Padma (using Cluster Architecture) and Param Garuda (using Grid Computing).
- In 2019, C-DAC has started National Supercomputing Mission & PARAM Shivay was the first supercomputer designed & built under the mission at IIT-BHU.
2. Cloud Computing
- C-DAC has played important role in making Meghraj (Government of India’s cloud).
3. Current Focus
C-DAC was initially started with a mandate to make supercomputer & Indian language computing but later diversified its scope in years to areas like
- Artificial Intelligence & Speech Processing
- Power Electronics
- Embedded Systems & VLSI design
- Cyber Security
- Broadband, wireless & internet technology
- Health Informatics
- E-Governance & ICT for removing Digital Divide
- E-Learning
Achievements of C-DAC
- C-DAC made the first Supercomputers in India with gigaflop capabilities (Param 8000, Param 10000, Param Ananth etc.).
- C-DAC has made National Knowledge Network (NKN) in which Academic Centres, R&D labs, Educational Institutes etc. are connected with the grid so that they can use supercomputing facilities.
- C-DAC has played important role in developing Simulation Modelling for weather, defence and other sectors.
- C-DAC developed Indian Language Computing. Examples include e-Shiksha and Megh Shikshak.
- Health Informatics: For managing the diseases in the country through the use of ICT, C-DAC has developed systems like E-Shushruta Program for Cancer Patients.
- Internal Security: C-DAC is working in the following areas for strengthening the Internal Security of India:-
- Cyber Forensics to analyse cellphone data, hard drives etc.
- Encryptology i.e. Method to encrypt information so that only authorized parties can access it.
- Bioinformatics: CDAC has made a supercomputing system called Param Bio-Blaze which helps to capture the movement of molecules and interaction between two molecules.
TRAI
- TRAI = Telecom Regulatory Authority of India
- It is the statutory body constituted under the provisions of the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) Act, 1997.
- Functions of TRAI
- Regulation of telecom services and tariffs.
- Look into various complaints and acts as a quasi-judicial body.
- Licensing a new company and looking into the sale of spectrum.
- Regulate DTH services.
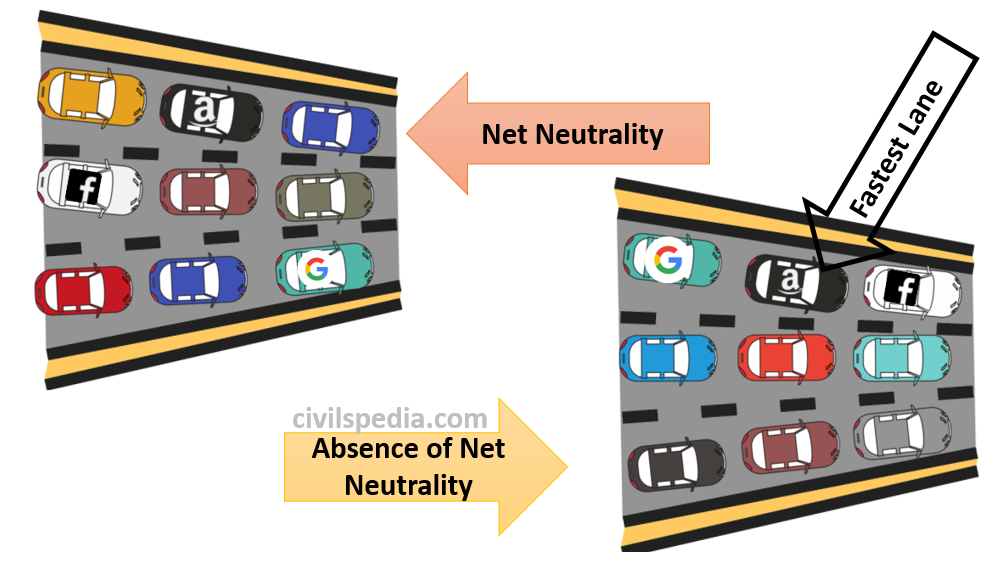
- Ensuring Net Neutrality in India.
TDSAT
- TDSAT = Telecom Dispute Settlement Appellate Tribunal
- It was established in 2000.
- Membership = Chairman and 2 Members
- If a person/company is not satisfied with the decision of TRAI, he/she can approach TDSAT.
NASSCOM
- NASSCOM = National Association of Software and Services Companies (NASSCOM)
- NASSCOM is a trade organisation of the Indian IT and Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) industry.
- It was set up in 1988, as a non-profit organisation and registered under the Indian Societies Act, 1860.
Telecommunication Companies
Indian Telecommunication sector can be divided into public and private companies.
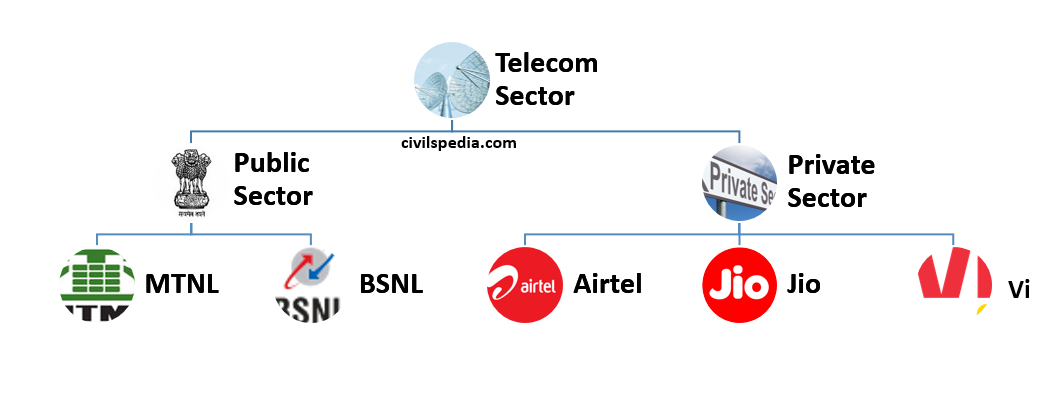
PSUs
MTNL
- MTNL = Metropolitan Telephone Nigam Limited.
- MTNL was set up in 1986.
- Objectives of MTNL
- Expand quality telecom network.
- Raise revenue for developing telecommunication facilities in India’s key metros i.e. Delhi and Mumbai.
BSNL
- BSNL = Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited
- It was set up in 2000 in the whole of India except Delhi and Mumbai.
- Rural areas as well as broadband connectivity was its thrust areas.
Private Players
The main players in the private sector are
- Jio
- Airtel
- Vi (Idea and Vodafone)
Controversy: Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR)
- As part of the LPG reforms of the 1990s, private telecom companies were allowed to operate in India. To start operation, companies have to obtain the license and pay annual fees in the proportion to their Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR).

- There was an issue regarding the method to calculate the AGR and the matter went to Supreme Court. Companies wanted that only their income from the subscriber base should be counted as their AGR while the government wanted to include income from the subscriber base as well as income from other sources as well (like rent from properties etc.). Supreme Court ordered in favour of the government and ordered telecom companies to pay the AGR dues to the Government of India. Eg: Bharti Airtel has been ordered to pay AGR dues of ₹36,000 crores and Vodafone-Idea will have to pay ₹58,000 crores.
# Various Schemes
1. Digital India Mission
- Digital India Mission is implemented by MEITY (Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology)
- It has 9 components.

1. Broadband Highway
- To take fast internet to all rural and urban areas using National Optical Fibre Network (NOFN) and many other projects.
2. Public Internet Access points
- Public internet access points are needed to access the internet.
- For this following things would be created
- CSC (Common Service Center)
- 1.5 Lakh Post offices
- Public Wi-Fi to be provided via Smart city projects, Amrut, Prasad, Hriday etc.
- Railway stations will have wi-fi.
3. Universal Mobile
- Since by any way, one cant use wi-fi at all places. For those not covered via wi-fi, internet services on their mobiles can be provided.
- This will be funded by Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF).
4. E-Governance
E-Governance will be promoted via systems like
- Automatic Workflow in office.
- Public grievances redressal via ONLINE TICKET SYSTEM.
- Digital Locker to save all certificates ranging from school certificate to Voter ID card.
5. E -Kranti Module
The government will develop more infrastructure, apps, websites and portals to improve efficiency and reduce corruption. These include
| E-Education | – Massive Online Open Courses (MOOCs) – Free Wi-Fi in the schools. |
| E-Healthcare | – Online Medical Records – Telemedicine |
| E-Justice | – E-Courts – Prosecution Database |
| Financial Inclusion | – e-Banking – UPI and BHIM |
| Security | – CERT-In – CERT-Fin |
6. Info to all
There will be two-way communication between citizens & the government. The government will do this via
- Social networking sites like Twitter
- Mygov.in
7. Zero import
- Import of IT appliances will be reduced to zero.
8. IT Jobs
- MEITY will train a 1 crore IT-ready workforce in RURBAN areas.
- The government will promote BPOs in the North East because of the proficiency of North-Easterners in English.
- The government will give large benefits to mobile manufacturers to set up their manufacturing units in India. Eg: World’s largest Mobile factory has been set up in Noida by Samsung (in 2018).
9. Early harvest programs
There were some programmes on which work was already going on. They will be completed rapidly. These include
- Secure email service for all employees.
- Standardised government email/file design /template to decrease time.
- E-greeting through mygov.in
- Biometric attendance in public offices.
Side Topic: Common Service Centres
- It is part of the Digital India Mission.
- CSCs are hi-tech kiosks having broadband connectivity. Through CSCs, even a poor person who doesn’t own a computer can have access to digital services provided at CSC.
- Common Service Centres have been opened in all gram panchayats.
- Each CSC will employ a minimum of 4 persons directly or indirectly, thus creating jobs in India.
- In 2020, CSC started a program named ‘Gramin e-store’ under which rural entrepreneurs can sell their product online using the infrastructure of CSCs.
Side Topic: Pradhan Mantri Grameen Digital Saksharta Abhiyaan (PMGDISHA)
- PMGDISHA was started in 2017 under Digital India Mission.
- PMGDISHA aims to increase digital literacy in rural areas as only 6% of rural households have a computer. Hence, a large number of households in rural India are digitally illiterate.
- Aim: Make 6 crore rural households digitally literate.
Criticism of Digital India Mission
- NIC /MEITY is not equipped with the manpower to deliver public internet & e-governance on such a large scale.
- Giving internet connection to people is not end in itself. People should also have a mobile, tab or PC to access it.
- India has one of the lowest spectrum per million customers in the world. This should be improved.
Human Resource Issues
- NIC is not equipped for a fraction of this task. It needs a serious revamping.
- MEITY needs more program managers – at least 4 times more officers at the senior levels.
Coordination Issues
- The program covers many other departments. Hence, there is a need for commitment and effort.
How to overcome the challenges?
- Bharat Net Program should be executed in mission mode.
- Availability of spectrum should be looked into.
- Private telecom operators should take a proactive role in the expansion of services in rural areas.
- E-literacy among senior citizens in rural areas should be taken up. In this, Internet Saathi by Tata Trust & Google can serve as an example.
- The cost of smartphones should be brought down.
- A viable PPP Model to execute the projects at a faster pace should be devised.
- Overall mindset of people should be changed.
2. Bharat Net Project
- It was earlier known as National Optical Fibre Network (NOFN).
- It was started in 2011 by the Ministry of Communication.
- Aim:
- Providing broadband connectivity to over 2 lakh gram panchayats (GPs) with a minimum of 100 Mbps bandwidth given to each Gram Panchayat.
- Enable the Centre to provide e-services and e-applications nationally.
- Present Status: First Phase has been completed (i.e. 1 Lakh Gram Panchayats have been connected with Optical Fibre Network) & the Memorandum of Understanding for the Second Phase is under consideration.
- Implementing Agency: Bharat Broadband Network Ltd. ( special purpose vehicle created under the Companies Act of 1956 ) under telecom ministry with BSNL, Railtel & Power Grid Corporation as main executing Agency.
- Idukki district of Kerala was the first district to connect all its Gram Panchayats with NOFN.
- The project is funded by Universal Service Obligation Fund and ₹20,000 crores will be spent on it.
Other models at work in different states
- States such as Andhra Pradesh took up the work of laying the optical fibre cable network with the Centre paying earmarked fund to Andhra Pradesh to speed the project.
- Tamil Nadu and Gujarat have also come up with a similar proposal for the implementation of the NOFN/Bharat Net project.
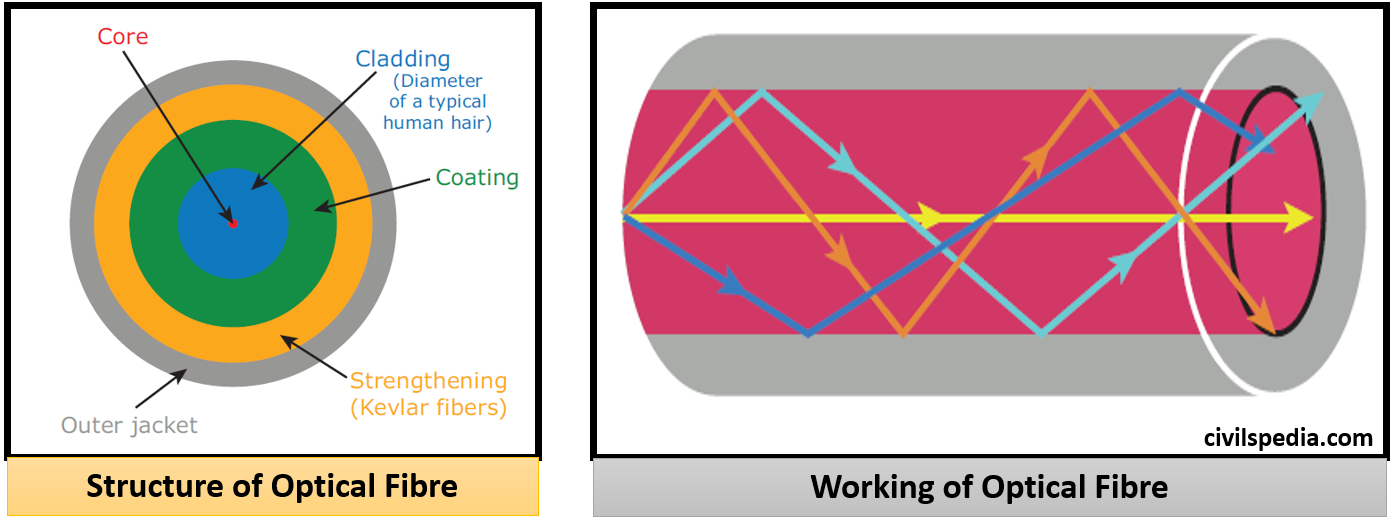
Side Topic: Optical Fibre
- Optical fibres are long and thin strands of very pure glass about the diameter of a human hair that works on the principle of Total Internal Reflection.
- Using Optical Fibres, signals can be sent from one place to another without any loss.
- Indian Government is connecting all villages through Optical Fibres under Bharat Net Project to provide broadband services.
- Optical Fibres are also used by doctors in endoscopy.
- He invented optical fibre and coined the term ‘fibre optics’. He is known as the ‘father of fibre optics’ for his contribution.
- He was a great inventor and has more than 100 patents in his name.
- The scientific community feels that he deserved a Noble Prize but Royal Swedish Academy failed to appreciate his work.
- Timelines
| 1948 | Graduated from Agra University. |
| 1955 | Completed PhD from Imperial College (London). |
| 1961 | Company named ‘Optics Technology’ was started by him in Silicon Valley. |
| 1999 | Fortune named him as ‘Unsung Heroes’ of Science. |
| 2020 | Died in the USA. |
3. PM-WANI Scheme
- PM WANI = Prime Minister Wi-Fi Access Network Interface
- The scheme has been started by the Ministry of Communication in 2020.
- Aim: To provide public Wi-Fi Service to all by opening public data offices (PDOs).
How will it work?
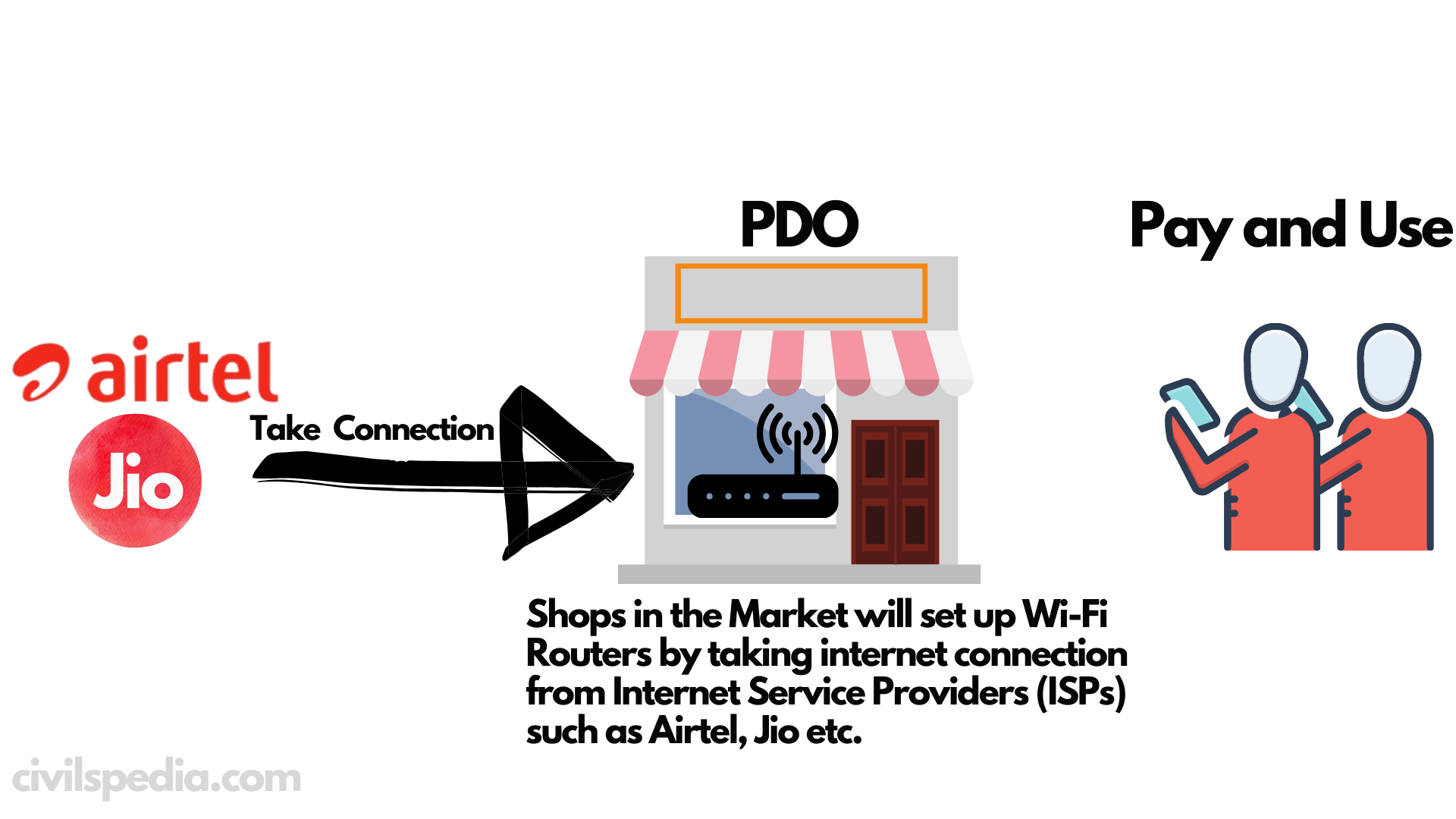
- PDO will deliver broadband services to the customers by starting Wi-Fi Access points using the internet taken from Internet Service Providers such as Jio, Airtel, Vi etc.
- The customer who wants to access the internet can do so after making payment for the usage of data and eKYC authorisation.
Benefits
- It will create employment in India.
- It will enhance the disposable income of small and medium entrepreneurs in India.
- It will help in making broadband accessible to millions of users.
- It will help in making India a digital economy.
Criticism
- It will be difficult to ensure the safety of data.
- Wi-Fi has lost its relevance in India due to very cheap mobile data rates.
4. Digital India Aatma-Nirbhar Bharat Innovate Challenge
- In 2020, MEITY and Niti Aayog (under Atal Innovation Mission) has launched Digital India Aatma-Nirbhar Bharat Innovate Challenge to identify the best Indian Apps that are already being used by citizens and have the potential to scale and become world-class in their respective categories.
- Top-three under each of the categories will get Rs 20 lakh, Rs 15 lakh, and Rs 10 lakh for first, second, and third positions
- It has 8 broad categories:
| Office Productivity & Work from Home | Zoho Workplace & Cliq and SureMDM |
| Entertainment | CaptionPlus, Meme Chat and FTC Talent |
| News | Logically and IsEqualTo |
| Games | Hitwicket Superstars, ScarFall: The Royale Combat and World Cricket Championship 2 |
| E-learning | Disprz, Kutuki Kids Learning App, and Hello English: Learn English |
| Business | Zoho Invoice, Books & Expense , Mall91 and GimBooks |
| Social Networking | Chingari, YourQuote and Koo |
| Others | MapmyIndia Move, AskSarkar, and myitreturn |
- Apart from that, government agencies like NIC too are preparing indigenous apps like
| Sandesh App | Messenger app (similar to Whatsapp) made by NIC. |
| Government Instant Messaging System (GIMS) | Messenger app for central and state govt organizations for Intra and inter-organization communication. |
5. Bharat QR
- Bharat QR code has been developed jointly by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), Visa, MasterCard and American Express under instructions from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Note: QR is a two-dimensional machine-readable matrix. QR Code can store up to 7089 digits as compared to conventional bar codes which can store a maximum of 20 digits.
Advantages
- It eliminates the need for using card swiping machines for digital payments. There is no need to have Swiping Machines in Shops. Just have QR printed & payments can be easily done via that.
- Interoperability: Using the BharatQR code, the merchants will be required to display only one QR code instead of multiple ones.
- For the buyer, there is no need to carry a Card. Payment can be done via Mobile.
6. #OpenGovDataHack / Hackathon
- #OpenGovDataHack is an on-site 24Hrs Challenge organised by Government.
- Till now, it has been conducted in 2017, 2018 and 2019.
- Participating teams are required to submit the app prototype and infographics by using Open Government Data. Out of these, selected apps are taken up for further development and the winner is being awarded.
7. Internet Saathi
- It is a joint venture of Google India and Tata.
- Aim: Increasing digital literacy among women in rural India.
- The program trains the Saathi’s in villages that in turn educate other women from their village in the use of the internet.
- It has reached up to 2.6 lakh villages in 18 states. In 2019, it was expanded to Punjab and Odisha as well.
#Various Policies
Telecom Policies
National Telecom Policy, 2012
To develop the telecom sector in India, the Government of India made Telecom Policy in 2012 having following features:-
- Provide secure, affordable and high-quality telecom services to citizens.
- Implementation of One Nation, One License Policy.
- Implement provision of Mobile Number Portability.
- Develop broadband infrastructure in the country.
- Achieve 70% telecom density in rural areas by 2017 & 100% by 2020.
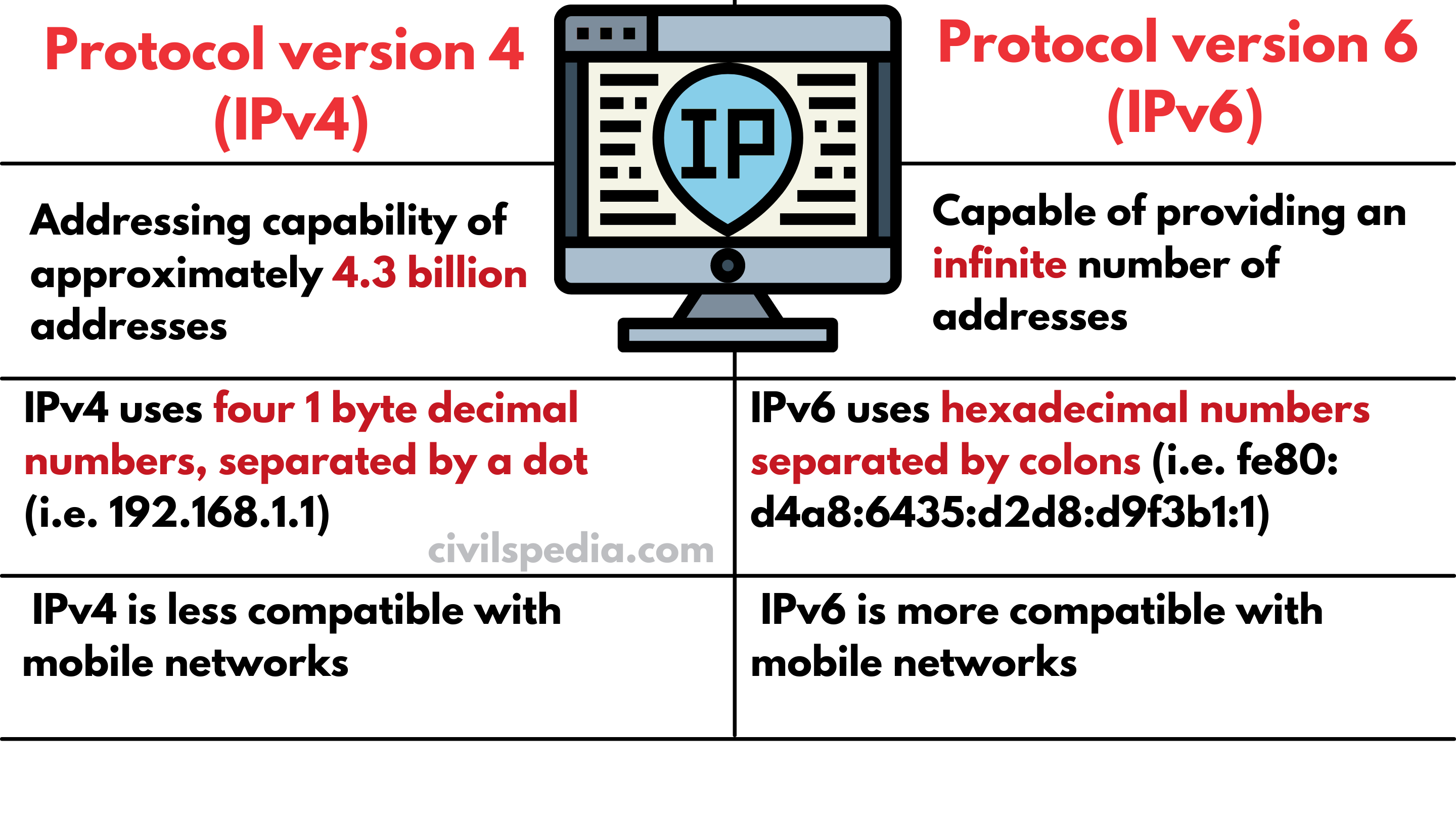
- Develop IPV – 6 till 2020.
All these have been implemented.
National Telecom Policy, 2018
Given the changing needs and world stepping into the age of modern technological innovations in the Telecom Sector such as 5G, IoT etc., the Government released Telecom Policy in 2018 with the following provisions:-
- Providing broadband facility to all (512 kbps).
- Attract investment of $100 billion in the Indian Telecom Sector.
- Creating at least 40 lakh jobs in the digital sector.
- Increase the contribution of the digital sector to 8% of GDP.
- Strengthening Digital Connectivity through the following:-
- Using Bharatnet,
- Connecting rural panchayats with 10 Gbps internet broadband.
- Nagar Net to provide 10 lakh public Wi-Fi’s.
- Jan Wi-Fi to provide 20 lakh WI-FIs in villages.
- Securing Big Data in India.
- Safeguarding ‘Digital Sovereignty’ of India.
- Ensuring complete data protection, individual privacy, autonomy and choice.
- Giving support to Net Neutrality.
- Creating a roadmap for transition to Industry 4.0 by 2020.
- Recognizing Spectrum as a key natural resource.
National Electronic Policy, 2019
- To make India a global hub for Electronics Manufacturing and R&D, the National Electronic Policy was made in 2019.
- Targets for 2025 under the National Electronic Policy of 2019 are
- Achieve turnover of $400 billion.
- Produce 100 crore units of mobile handsets & export 60 crores units out of that.
- Create 1 crore jobs.
- The government will do the following:-
- Tax benefit, subsidies and other incentives for R&D.
- Focus on training and skill development.
- Sovereign Patent Fund: Government will buy patents from innovators and corporate companies and allow MSME industries to use those Intellectual Property Rights for electronics manufacturing, without paying large royalties to the original patent holder.
- The government will set up 15 new laboratories under PPP Model for testing hardware and software before their launch in the market.
- The government will allow 100% FDI via automatic route in data processing, software development, consultancy services and business market research services.
National Software Policy, 2018
To make India a ‘Software Product Nation‘ and create 65 lakh jobs by 2025, the Government of India formulated National Software Policy in 2018 with the following terms:-
- It aims to establish an Indian Software products Industry worth $70-80 billion which will, directly and indirectly, employ 3.5 million by 2025.
- Creating an Indian Software Ecosystem by creating an Indian Software Product Registry.
- Creating incubation centres.
- Creating Software Product Development Fund (SPDF).
- Promoting Software Startups through Hackathons (at least 10,000 Startups especially in Tier-2 and 3 cities).
- Overcoming Language Barriers.
Mobile Number Portability (MNP)
- This facility allows the subscribers to retain their existing telephone numbers even after switching their service provider or from one technology to another of the same service provider.
Interconnection Usage Charge (IUC)
- IUC is the charge that one telecom operator (originating network) pays to other (receiving network) for carrying through or even terminating a call.
- It is decided by TRAI. In September 2017, TRAI has reduced it from the existing 14 paise per minute to 6 paise per minute. It has been scrapped on 1st Jan 2021.
- IUC was seen as a great entry barrier and restrict the competition in the telecom sector as the new operator will have to pay a large amount as IUC as most of its limited user-base will make calls to the users of existing telecom operators.
- The move to scrap IUC altogether is going to benefit Jio which had a higher proportion of outgoing calls to other wireless operators since its launch a few years ago, thus having to pay significant net interconnection charges.