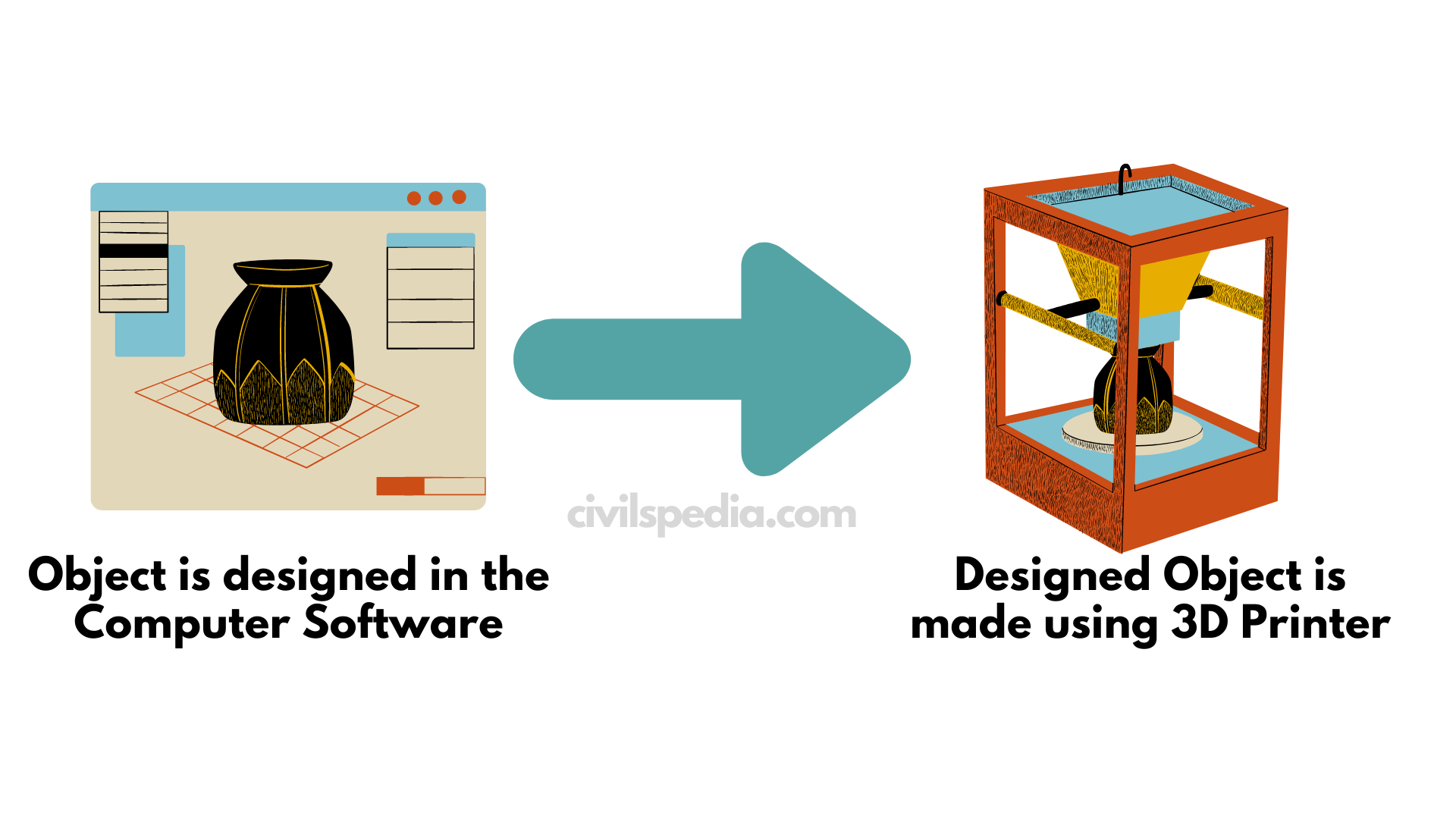
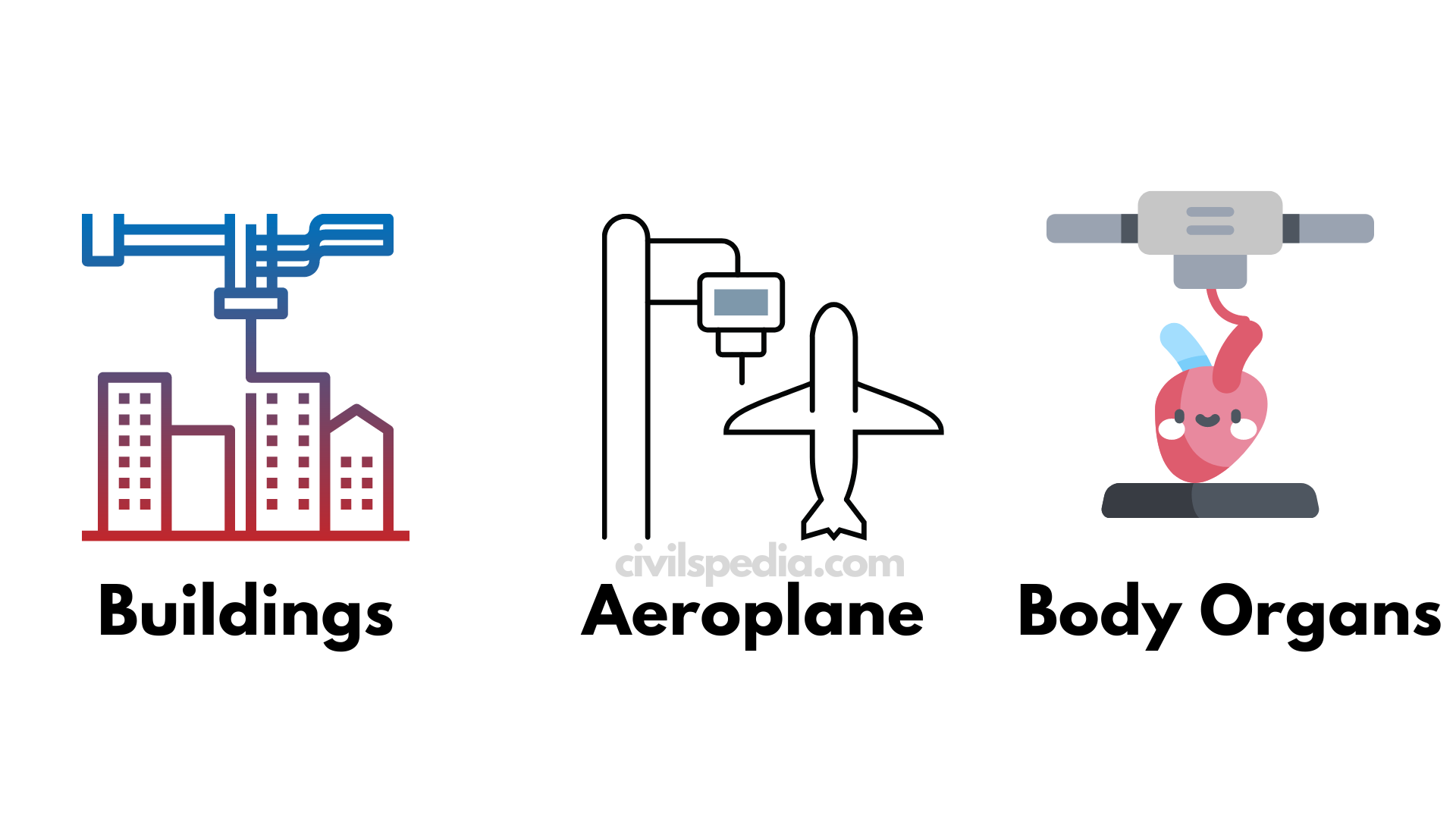
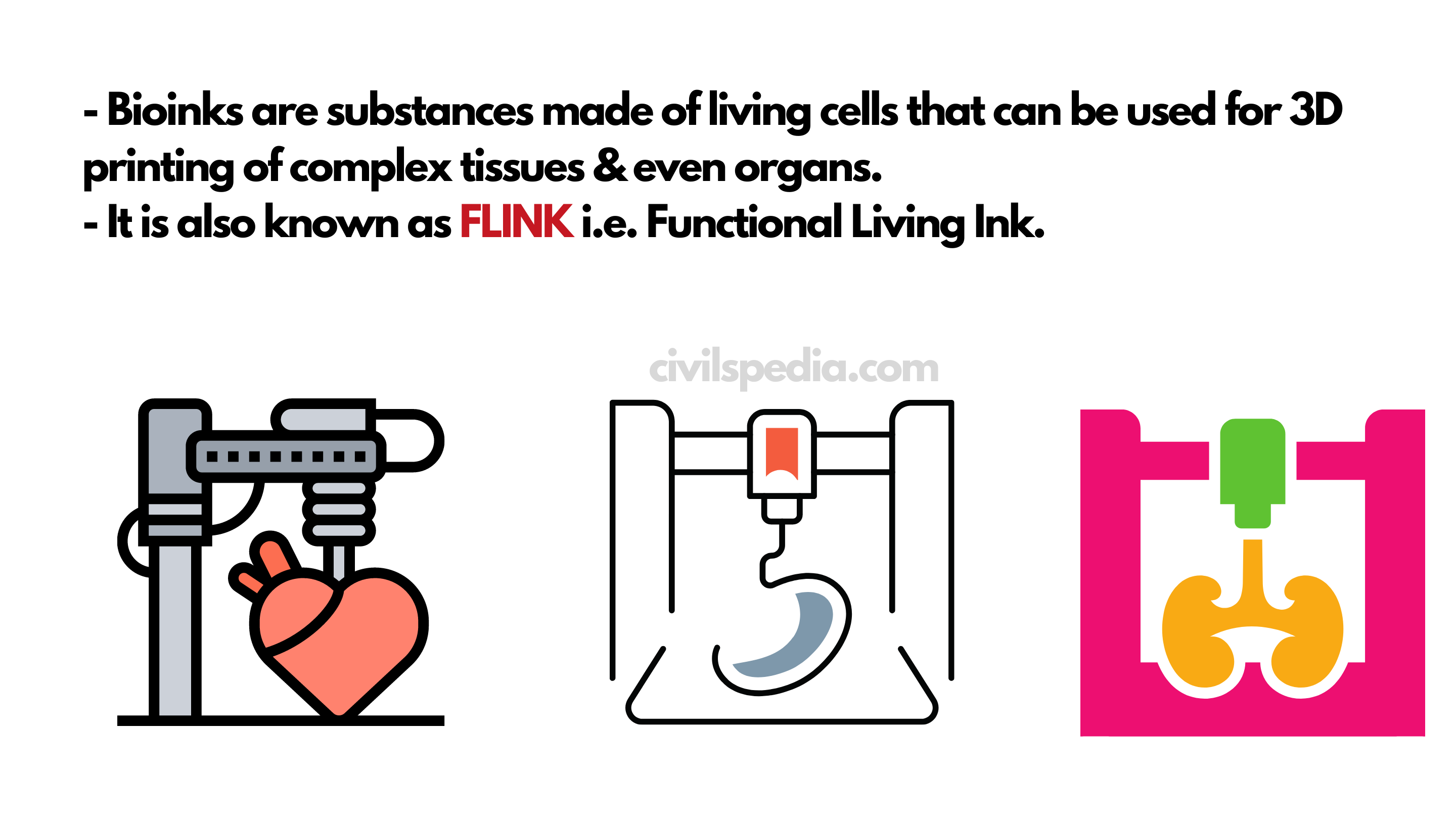
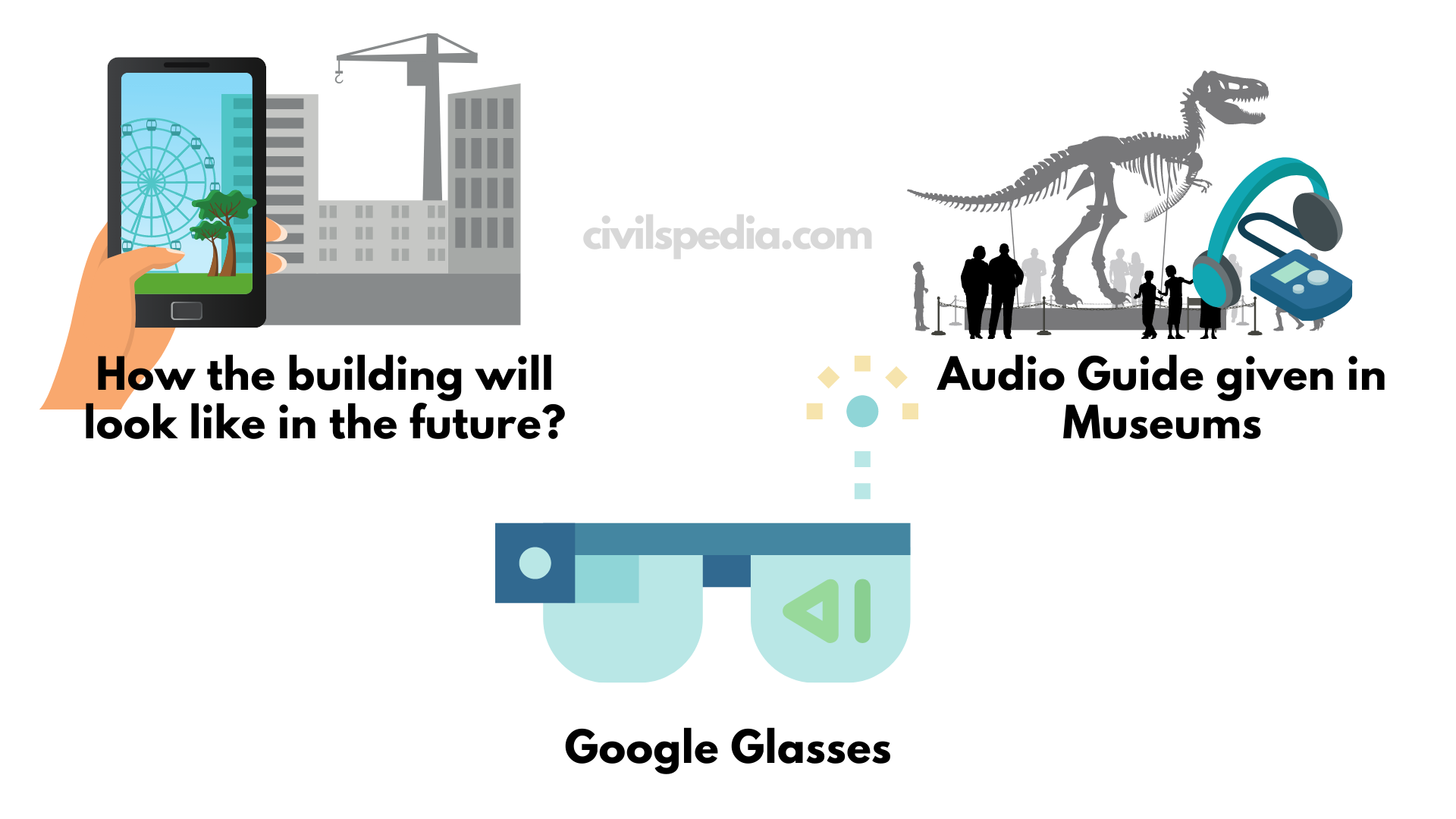
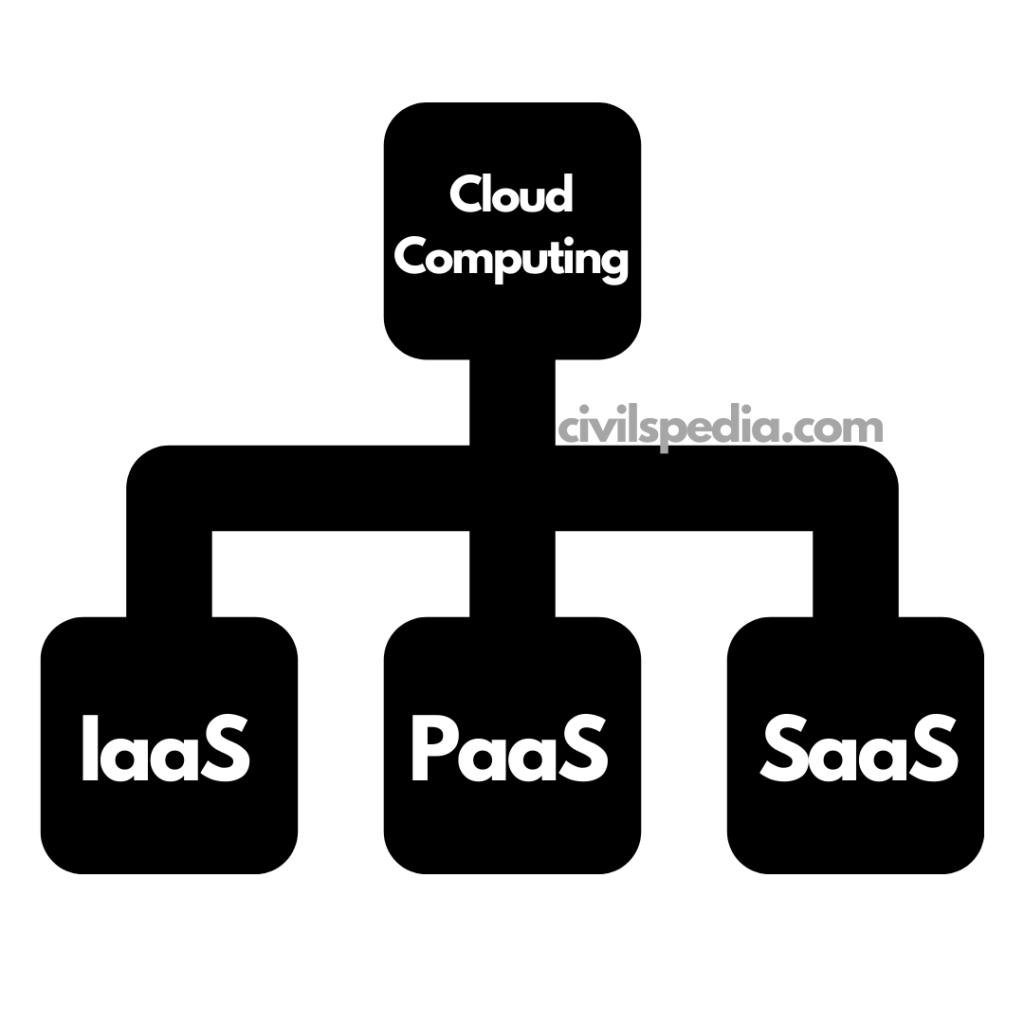
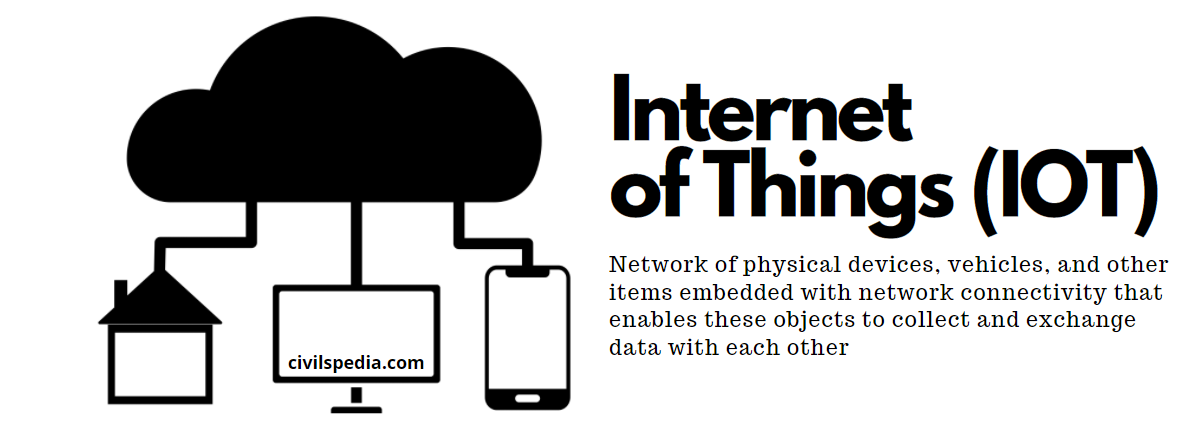
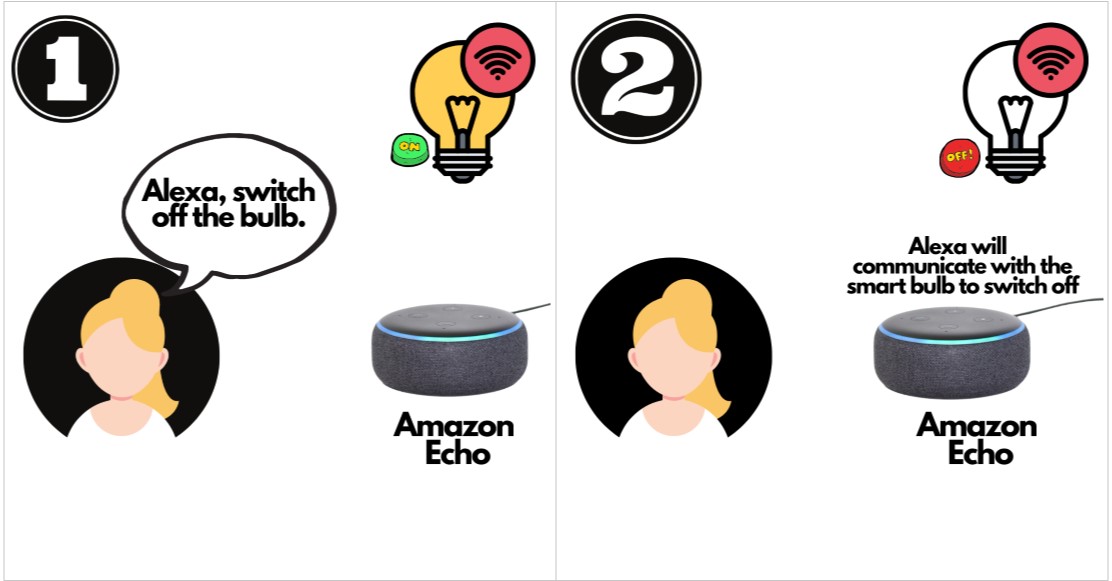
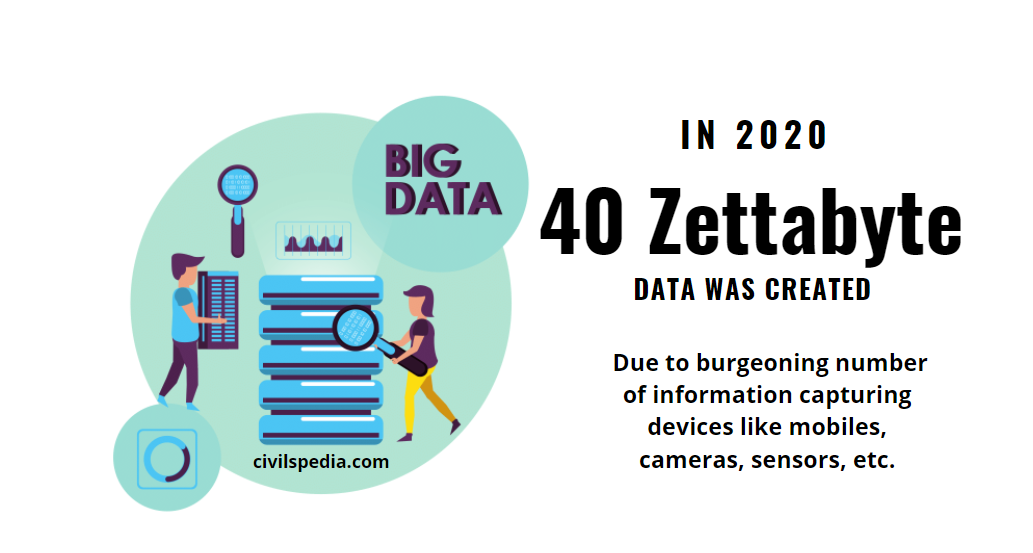
Artificial Intelligence
This article deals with ‘Artificial Intelligence .’ This is part of our series on ‘Science and Technology’ which is important pillar of GS-3 syllabus . For more articles , you can click here
What is Artificial Intelligence?
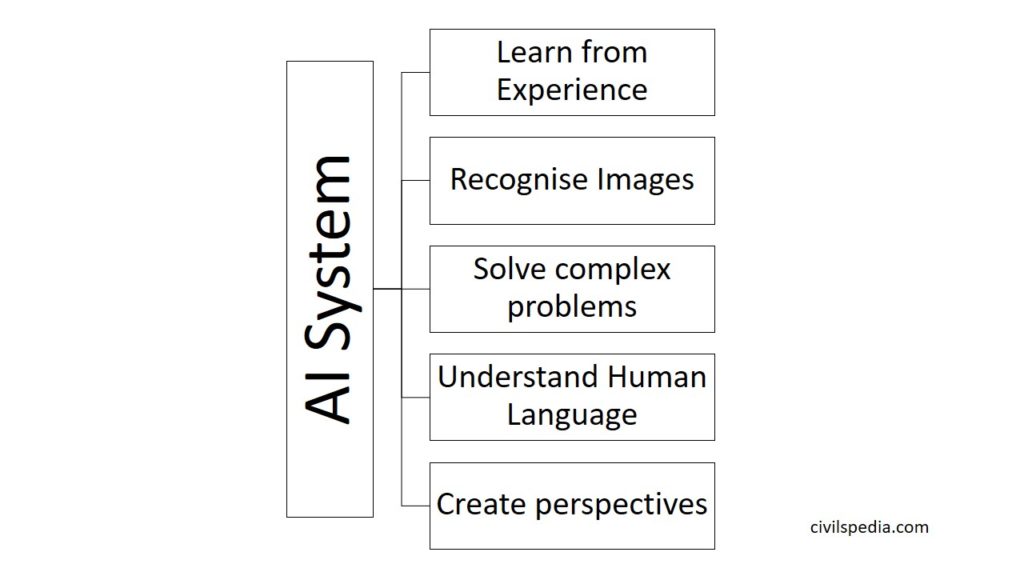
- Artificial intelligence is the branch of computer science concerned with making computers behave like humans
- It is concerned with
- Learning from experience
- Recognising images
- SolveComplex Problems
- Understand Human Language
- Create perspectives
Side Topic : Machine Learning and Deep Learning
- Machine Learning, a term coined by Artur Samuel in 1959, based on the idea that systems can learn from data, identify patterns and make decisions with minimal human intervention.
- Deep Learning is a technique for implementing Machine Learning. It is inspired by the structure and function of the brain called artificial neural networks.
Examples
- Driverless Cars
- Games playing: AI intelligent games learn from their mistakes and are not monotonous.
- Expert systems : programming computers to make decisions in real-life situations
- Natural language : programming computers to understand natural human languages.
- Robotics : programming computers to see and hear and react to other sensory stimuli (this is what we want to achieve ultimately)
Some problems
- The problem of creating machines smarter than humans but lacking the ethical-moral impulses like compassion
- Possibility of machines trying to dominate humans eg Terminator & I-Robot type of situation
- Job Loss : Much of India’s advanced IT services industry might get replaced by AI
- High levels of inequality : Society will have high levels of inequality because there will be jobs for high skilled persons only. Low skill jobs will be taken up by AI Machines
- Ensuring data security, protection, privacy, and ethical use
- Rigorous auditing to ensure non-contamination by human biases & prejudices
But new avenues too
- Will create new jobs in high end technology
- Many uses in Governance and public delivery
- Security : Any terrorist on wanted list can be recognised by AI Computer by stream of videos coming from CCTVs
- Analysis of Schemes and suggestions for better results
- Personal Assistants : Companies like Google, Amazon(Alexa) etc are coming with personal assistants . They work on AI. Hence, now everybody can have personal assistant for free
- Better Logistics : Uber, Google Maps suggesting best way etc use AI for logistic management.
- Use for specially abled people
Indian Govt and AI
- 2018: Defence ministry set up a task for on AI for national security under N Chandrashekharan of Tata Sons.
- 2018-Budget gave ₹100 crore to Department of Science & Technology for a Mission on cyber physical systems.
- 2018 : NITI Ayog working on National Artificial Intelligence Mission (N-AIM).
- 2019-Interim-Budget announced a National Programme & Centre & webportal on ‘Artificial Intelligence‘.
- Samarth Udyog Bharat 4.0 by Ministry of Heavy Industries to make manufacturing industry ready for Industry 4.0 by 2025.
- NITI Aayog paper highlights the potential for India to become an AI ‘garage’, or solutions provider of the world.
What India can learn from other countries?
- US, the global leader in AI has AI sector driven by the private sector.
- China has ambition of becoming world leader in AI by 2030. The top 9 universities of China have received government funding to establish AI schools.